Dryopithecini
| Dryopithecini | |
|---|---|
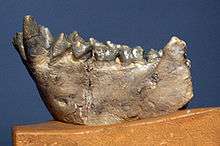 | |
| mandible fragment of Dryopithecus fontani from Saint-Gaudens, France (Middle Miocene, 11.5 My) ; cast from Museum national d'histoire naturelle, Paris | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hominidae |
| Subfamily: | Homininae |
| Tribe: | †Dryopithecini |
| Genera | |
|
Oreopithecus | |
The dryopithecines consists of a tribe of Eurasian apes that are believed to be close to the ancestry of gorillas, chimpanzees and humans.[1][2]
Taxonomy
- Tribe Dryopithecini†
- Oreopithecus (placement disputed)
- Oreopithecus bambolii
- Nakalipithecus
- Nakalipithecus nakayamai
- Anoiapithecus
- Anoiapithecus brevirostris
- Dryopithecus
- Dryopithecus wuduensis
- Dryopithecus fontani
- Neopithecus
- Neopithecus brancoi
- Hispanopithecus
- Hispanopithecus laietanus
- Hispanopithecus crusafonti
- Rudapithecus
- Rudapithecus hungaricus
- Oreopithecus (placement disputed)
References
- ↑ Haaramo, Mikko (2005-01-14). "Hominoidea". Mikko's Phylogeny Archive.
- ↑ Moya-Sola, S.; Alba, D. M.; Almecija, S.; Casanovas-Vilar, I.; Kohler, M.; De Esteban-Trivigno, S.; Robles, J. M.; Galindo, J.; Fortuny, J. (2009). "A unique Middle Miocene European hominoid and the origins of the great ape and human clade". PNAS. 106 (24): 9601–9606. doi:10.1073/pnas.0811730106. PMC 2701031. PMID 19487676. .
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.