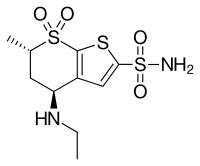
Dorzolamide
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Trusopt |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a602022 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Topical (eye drops) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | ~33% |
| Elimination half-life | 4 months |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H16N2O4S3 |
| Molar mass | 324.443 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Dorzolamide (trade name Trusopt) is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. It is an anti-glaucoma agent, and acts by decreasing the production of aqueous humour.[1] It is administered as a topical ophthalmic in the form of a 2% solution.[2]
History
This drug, developed by Merck, was the first drug in human therapy (market introduction 1995) that resulted from structure-based drug design. It was developed to circumvent the systemic side effects of acetazolamide which has to be taken orally.[2]
Uses
Dorzolamide hydrochloride is used to lower increased intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
Pharmacodynamics
Side effects
Ocular stinging, burning, itching and bitter taste.[2] It causes shallowing of the anterior chamber and leads to transient myopia.
References
Further reading
- Kubinyi H (1999). "Chance favors the prepared mind--from serendipity to rational drug design". J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 19 (1–4): 15–39. doi:10.3109/10799899909036635. PMID 10071748.
- Plummer C, MacKay E, Gelatt K (2006). "Comparison of the effects of topical administration of a fixed combination of dorzolamide-timolol to monotherapy with timolol or dorzolamide on IOP, pupil size, and heart rate in glaucomatous dogs". Vet Ophthalmol. 9 (4): 245–9. doi:10.1111/j.1463-5224.2006.00469.x. PMID 16771760.
- Grover S, Apushkin M, Fishman G (2006). "Topical dorzolamide for the treatment of cystoid macular edema in patients with retinitis pigmentosa". Am J Ophthalmol. 141 (5): 850–8. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2005.12.030. PMID 16546110.
- Almeida G, Faria e Souza S (2006). "Effect of topical dorzolamide on rabbit central corneal thickness". Braz J Med Biol Res. 39 (2): 277–81. doi:10.1590/S0100-879X2006000200015. PMID 16470316.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.