Dinogunellin
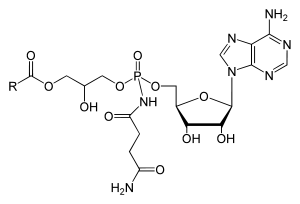
Dinogunellin is a toxic phospholipid of some fish (Ichthyotoxin).
Occurrence
Dinogunellin was detected in the mature eggs of some fish, e.g. in cabezon (Scorpaenichthys marmoratus)[1] or northern blenny (Stichaeus grigorjewi) roe. It is also the found in the blood of eel.
Pharmacology
Dinogunellin causes hemolysis and local mucosal irritation. When consumed, Ichthyotoxins cause vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, a rapid and irregular pulse, cyanosis, fever, and dizziness.
As countermeasures after consumption of ichthyotoxic poisons an immediate gastric emptying and giving of activated charcoal comes into question.
There is no specific antidote, therefore above mentioned symptoms of poisoning are treated symptomatically.
After a few days, poisoning victims usually recover again.
References
- ↑ Hashimoto, Yoshiro; et al. (1976). "Occurrence of a toxic phospholipid in cabezon roe". Toxicon. 14 (2): 141–143. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(76)90105-7.
- Dinogunellins A-D
- Dinogunellin in northern blenny roe
- Structure of Dinogunellin
- Dinogunellin B (Pubchem)