Digitonin
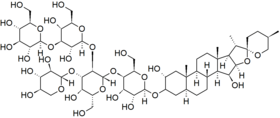 Chemical structure of digitonin | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Digitin | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.129 |
| EC Number | 234-255-6 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C56H92O29 | |
| Molar mass | 1,229.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Melting point | 244.0–248.5 °C (471.2–479.3 °F; 517.1–521.6 K)[1] |
Chiral rotation ([α]D) |
-40° (589.3 nm; 20 °C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
23 mg/kg (rat, intravenous)[2]
4 mg/kg (mouse, intravenous)[3] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Digitonin is a steroidal saponin (saraponin) obtained from the foxglove plant Digitalis purpurea. Its aglycone is digitogenin, a spirostan steroid. It has been investigated as a detergent, as it effectively water-solubilizes lipids. As such, it has several potential membrane-related applications in biochemistry, including solubilizing membrane proteins, precipitating cholesterol, and permeabilizing cell membranes.[4][5]
Digitonin is sometimes confused with the cardiac drugs digoxin and digitoxin and all three can be extracted from the same source.
Chemical properties
- Critical micelle concentration = < 0.5 mM
- Average micellar weight = 70000
- Aggregation number = 60
References
- 1 2 Tschesche, R.; Wulff, G. (January 1963). "Über saponine der spirostanolreihe—IX". Tetrahedron (in German). 19 (4): 621–634. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)98548-5.
- ↑ Segal, Ruth; Milo-Goldzweig, Ilana; Kaplan, Gideon; Weisenberg, Emil (April 1977). "The protective action of glycyrrhizin against saponin toxicity". Biochemical Pharmacology. 26 (7): 643–645. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(77)90039-9.
- ↑ Pitha, Josef; Szente, Lajos (February 1984). "Digitonin derivatives of low toxicity: Potential solubilizers for lipophilic compounds". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 73 (2): 240–243. doi:10.1002/jps.2600730224.
- ↑ Geelen, Math J.H. (December 2005). "The use of digitonin-permeabilized mammalian cells for measuring enzyme activities in the course of studies on lipid metabolism". Analytical Biochemistry. 347 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.032. PMID 16291302.
- ↑ Fiskum, Gary (April 1985). "Intracellular levels and distribution of Ca2+ in digitonin-permeabilized cells". Cell Calcium. 6 (1–2): 25–37. doi:10.1016/0143-4160(85)90032-6.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.