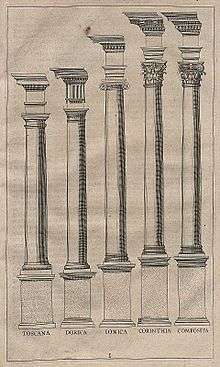
Composite order

.jpg)
%2C_Budapest.jpg)
The composite order is a mixed order, combining the volutes of the Ionic order capital with the acanthus leaves of the Corinthian order.[1] In many versions the composite order volutes are larger, however, and there is generally some ornament placed centrally between the volutes. The column of the composite order is typically ten diameters high, though as with all the orders these details may be adjusted by the architect for particular buildings. The Composite order is essentially treated as Corinthian except for the capital, with no consistent differences to that above or below the capital. The composite order is not found in ancient Greek architecture and until the Renaissance was not ranked as a separate order. Instead it was considered as an imperial Roman form of the Corinthian order. Though the Arch of Titus, in the forum in Rome and built in 82 AD, is sometimes cited as the first prominent surviving example of a composite order, the order was probably invented "a little before Augustus's reign, and certainly well-developed before his death, the very time when the Roman version of Corinthian was being established."[1]
With the Tuscan order, a simplified version of the Doric order, also found in ancient Roman architecture but not included by Vitruvius in his three orders, the Composite was added by Renaissance writers to make five classical orders. Sebastiano Serlio (1475–1554) published his book I sette libri d'architettura in 1537 in which he was the second to mention the composite order as its own order and not just as an evolution of the Corinthian order as previously suggested by Leon Battista Alberti. Leon Battista Alberti in his De re aedificatoria (English: On the Art of Building) mentions the composite order, calling it "Italic".[2]
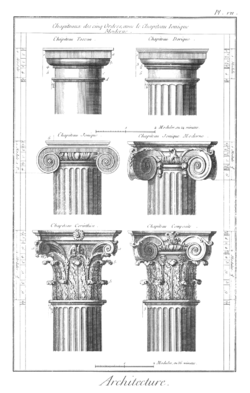
Form of the capital
The Composite is partly based on the Ionic order, where the volutes (seen frontally) are joined by an essentially horizontal element across the top of the capital, so that they resemble a scroll partly rolled at each end. Despite this origin, very many Composite capitals in fact treat the two volutes as different elements, each springing from one side of their leafy base. In this, and in having a separate ornament between them, they resemble the Archaic Greek Aeolic order, though this seems not to have been the route of their development in early Imperial Rome.
Equally, where the Greek Ionic volute is usually shown from the side as a single unit of unchanged width between the front and back of the column, the Composite volutes are normally treated as four different thinner units, one at each corner of the capital, projecting at some 45° to the facade. This has the advantage of removing the necessity to have a different appearance between the front and side views, and the Ionic eventually developed bending forms that also allowed this.
The treatment of details has often been very variable, with the inclusion of figures, heraldic symbols and the like in the capital. The relationship of the volutes to the leaves has been treated in many different ways, and the capital may be distinctly divided into different horizontal zones, or may treat the whole capital as a single zone. The composite order, due to its delicate appearance, was deemed by the Renaissance to be suitable for the building of churches dedicated to The Virgin Mary or other female saints. In general it has been since been used to suggest richness and grandeur.
Examples
Bramante (1444–1514) used the composite order in the second order of the cloister of Santa Maria della Pace, Rome. For the first order, the Ionic order was used. Francesco Borromini (1599–1667) developed the composite order in San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane, Rome (1638). The interior of the church has 16 composite columns. The load-bearing columns placed underneath the arches have inverted volutes. This choice was highly criticised at the time, thinking it was a lack of knowledge of the Vittruvian orders that led him to his decision.
The inverted volutes can also be seen in Borromini's Oratorio dei Filippini in the lower order. There the controversy was even higher, considering that Borromini also removed the acanthus leaves, leaving a bare capital.[3]
- Roman
- Arch of Titus, Rome
- Arch of Septimius Severus, Rome
- Santa Costanza, Rome, interior, mid-4th century
- Modern
- Ospedale degli Innocenti, Florence, 1421, Filippo Brunelleschi
- Palazzo Valmarana, Vicenza, 1565, Andrea Palladio
- Palazzo del Capitaniato, Vicenza, 1571-1572, Andrea Palladio
- Lescot Wing, Louvre Palace, Paris
- Church of the Gesù, Rome
- Easton Neston, England, c. 1700
- Palazzo Madama, Turin, c. 1720, Filippo Juvarra
- Archbasilica of St. John Lateran
- Somerset House, London, 1776, William Chambers
- Narva Triumphal Arch, Saint Petersburg, 1814
- Ethnographic Museum (former Palace of Justice), Budapest
- Alabama Governor's Mansion, 1907
Gallery, variations
- Late Roman/Byzantine, at the Euphrasian Basilica
 Palazzo Recalcati, Milan
Palazzo Recalcati, Milan Palazzo Capitaniato, Vicenza, Andrea Palladio
Palazzo Capitaniato, Vicenza, Andrea Palladio- Santa Croce in Fossabanda, Pisa
- Brescia, San Giovanni by Stefano Bolognini
 Kirche am Hof, Vienna
Kirche am Hof, Vienna
Notes
References
- Buonincasa, Carmine (1978). Architettura come dis-identità. Bari: Dedalo librerie.
- Zampa, Paola (1993). L'ordine composito: alcune considerazioni. Reggio calabria: Dipartimento Patrimonio Architettonico e Urbanistico.
External links
