Circumambulation
Circumambulation[1] (from Latin circum around[2] and ambulātus to walk[3]) is the act of moving around a sacred object or idol.[4]
Circumambulation of temples or deity images is an integral part of Hindu and Buddhist devotional practice (known in Sanskrit as pradakśina or pradakshinaṇā).[5] It is also present in other religions, including Christianity, Judaism, and Islam.
Hinduism
In many Hindu temples, the temple structure reflects the symbolism of the Hindu association of the spiritual transition from daily life to spiritual perfection as a journey through stages. Ambulatory passageways for circumambulation are present through which worshipers move in a clockwise direction, starting at the sanctuary doorway and moving inward toward the inner sanctum where the deity is enshrined. This is a translation of the spiritual concept of transition through levels in life into bodily movements by the worshipers as they move inwardly through ambulatory halls to the most sacred centre of spiritual energy of the deity.[6] Circumambulation is done in a clockwise direction and in an odd rather than even number of times. Circumbulatory walking around the shrine, by keeping time, is a common form of Hindu prayer. The circumbulary pathway made of stone around the shrine is called the Pradakshina path.[7]
Christianity
In the Catholic Church, a priest sometimes circumambulates an altar while incensing it with a thurible. Also, at some Catholic shrines, it is a tradition to circumambulate around the cult object of the place, usually relics of a saint or an image of Jesus or the Virgin Mary. Often this is performed three times, as a reference to the Trinity.
In Romania, there is an Easter custom to circumambulate the church three times by singing priests leading the people, just before finishing Easter Mass. It symbolizes the funerary procession of the burial of Jesus Christ.[8]
Circumambulation is common in many Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox services. In the Coptic tradition, during the liturgy, the priest circumambulates while an acolyte (altar boy) holds a cross high on the opposite side of the altar.
Islam

Tawaf (طواف) is one of the Islamic rituals of pilgrimage. During the Hajj and Umrah, Muslims are to circumambulate the Kaaba (most sacred site in Islam) seven times, in a counter-clockwise direction.[4][9] The circling is believed to demonstrate the unity of the believers in the worship of the One God, as they move in harmony together around the Kaaba, while supplicating to Allah.
Also the Kaaba is the most circumambulated structure in this world. The Kaaba is constantly circumambulated by pilgrims at all times except for the time of prayers, when small birds and angels are said to circumambulate the Kaaba.
Judaism
Judaism uses circumambulation in the Hakafot ritual during the Festival of Sukkot culminating in seven Hakafot on Hoshanah Rabbah, the end of the Festival. The circumambulations are also performed during Hakaphot on Simchat Torah, where Jews dance often by circumambulating the Torah Scrolls. Traditionally, Jewish brides circumambulate their grooms during the wedding ceremony under the chuppah and much Jewish dancing at weddings and Bar Mitzvahs is done by moving in a circle.
Buddhism
In Zen Buddhism, ‘jundo’ can mean any ritual circuit or circumambulation. At Tassajara each morning, the Doshi visits four different altars on his/her way to the zendo, to make bows and offerings of incense. This jundo begins with the first rolldown of the han, and ends as the Doshi enters the zendo with the third rolldown. After offering incense and bowing at the altar, the Doshi walks around the zendo behind the meditators, in what is called the ‘kentan’, or ‘inspection of the sitting platform’. As the Doshi passes, each resident raises his/her hands in gassho without bowing; this joins Doshi and sitters in mutual acknowledgement.
Sikhism
In Lavan Pheras which is performed during wedding ceremonies, the four rounds of pheras symbolize the warding off of evil by circumambulating a purifying and transforming object, in this case the holy book, Sri Guru Granth Sahib.
Bahá'í
Bahá'ís perform circumambulation of both the Shrines of the Báb and Bahá'u'lláh during their pilgrimage to Haifa and Bahjí, in Israel. While circumambulating, observance of these Manifestations of God is done in complete silence and also performed on holy days such as the birth and ascension of Bahá'u'lláh as well as the birth and martyrdom of the Báb.[10]
Bön
The Bönpo in the Tibet traditionally circumambulate (generally) in a counter-clockwise direction, that is a direction that runs counter to the apparent movement of the Sun.
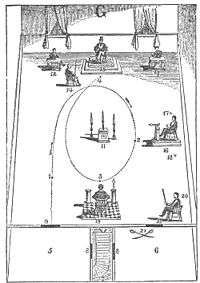
Freemasonry
Candidates for the three principle degrees of Freemasonry circumambulate the altar in the lodge room. This part of the ritual is distinct from many other world rituals in that it is done in a clock-wise fashion. The number of times which candidates ambulate around the altar depends on which degree is being presented.[11]
See also
- Sunwise (clockwise)
- Widdershins (counter-clockwise)
- Circle dance
- Parikrama
- Svastika
- Sauvastika
- Stupa
References
- ↑ Goblet d'Alviella, Eugène (1908). Circumambulation in: Encyclopædia of Religion and Ethics, Volume 3, 667 - 669. Edinburgh: Clark.
- ↑ "Circum-". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 2014-03-07.
- ↑ "Ambulate". Dictionary.com. Retrieved 2014-03-07.
- 1 2 Bowker, John (1999). The Oxford Dictionary of World Religions. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 224. ISBN 0-19-866242-4.
- ↑ Buddhamind.info: Circumambulation
- ↑ Michell, George (1988). The Hindu Temple. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. p. 66. ISBN 1477470573.
- ↑ "Architecture of the Indian Subcontinent - glossary". indoarch.org. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ↑ http://www.crestinortodox.ro/paste/saptamana-patimilor/slujba-prohodului-88660.html
- ↑ World Faiths, teach yourself - Islam by Ruqaiyyah Maqsood. ISBN 0-340-60901-X page 76
- ↑ "http://hastenforth.com/2010/07/07/circumambulation-of-bahji-from-dawn-until-dusk/". External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Duncan, Malcolm. Duncan's Ritual of Freemasonry. p. 8. ISBN 0-226-53230-5.
