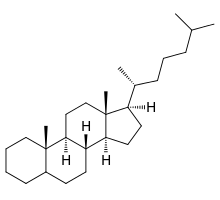
Cholestane
 | |
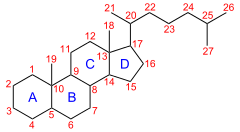 IUPAC numbering[1] | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(8R,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-Dimethyl-17-[(2R)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.876 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H48 | |
| Molar mass | 372.68 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.911 g/ml |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cholestane is a saturated 27-carbon tetracyclic triterpene. Cholestane, along with ergostane and stigmastane are used as biomarkers for early eukaryotic life[2]. High abundance of cholestane relative to the others has been interpreted as the presence of rhodophytes[3].
Derivatives of cholestane
Derivatives are classified in two families:
- Sterols (with an alcohol group)
- Cholestenes (with a double bond)
Some steroids, such as cholesterol, are both a sterol and a cholestene.
See also
References
- ↑ The Nomenclature of Steroids, IUPAC
- ↑ Brocks, Jochen J.; Jarrett, Amber J. M.; Sirantoine, Eva; Hallmann, Christian; Hoshino, Yosuke; Liyanage, Tharika. "The rise of algae in Cryogenian oceans and the emergence of animals". Nature. 548 (7669): 578–581. doi:10.1038/nature23457.
- ↑ Summons, Roger E; Brassell, Simon C; Eglinton, Geoffrey; Evans, Evan; Horodyski, Robert J; Robinson, Neil; Ward, David M. "Distinctive hydrocarbon biomarkers from fossiliferous sediment of the Late Proterozoic Walcott Member, Chuar Group, Grand Canyon, Arizona". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 52 (11): 2625–2637. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(88)90031-2.
External links
- Cholestanes at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.