Caesium hydroxide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Cesium hydrate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.298 |
| EC Number | 244-344-1 |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | FK9800000 |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2682 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CsOH | |
| Molar mass | 149.912 g/mol |
| Appearance | Whitish-yellow deliquescent crystals |
| Density | 3.675 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 272 °C (522 °F; 545 K)[1] |
| 300 g/100 mL at 30 °C | |
| Solubility | Soluble in ethanol[2] |
| Basicity (pKb) | -1.76 (CsOH(aq) = Cs+ + OH–) [3] |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
69.9 J·mol−1·K−1[4] |
Std molar entropy (S |
104.2 J·K−1·mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−416.2 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 1592 |
| GHS pictograms | 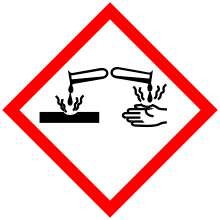   |
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H302, H314, H318, H361, H373 | |
| P201, P202, P260, P264, P270, P280, P281, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P310, P314, P321, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | Not flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
570 mg/kg (oral, rat)[5] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[6] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 2 mg/m3[6] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[6] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Caesium oxide Caesium fluoride |
Other cations |
Lithium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide Potassium hydroxide Rubidium hydroxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Caesium hydroxide or cesium hydroxide (CsOH) is a chemical compound consisting of caesium ions and hydroxide ions. It is a strong base (pKb=-1.76), much like the other alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. In fact, caesium hydroxide is corrosive enough to quickly corrode through glass.
Due to its high reactivity, caesium hydroxide is extremely hygroscopic. Laboratory caesium hydroxide is typically a hydrate.
It is an anisotropic etchant of silicon, exposing octahedral planes. This technique can form pyramids and regularly shaped etch pits for uses such as Microelectromechanical systems. It is known to have a higher selectivity to etch highly p-doped silicon than the more commonly used potassium hydroxide.
This compound is not commonly used in experiments due to the high extraction cost of caesium and its reactive behaviour. It acts in similar fashion to the compounds rubidium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide, although more reactive.
References
- ↑ "ICSC 1592 - Cesium Hydroxide".
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 4–51, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ "Sortierte Liste: pKb-Werte, nach Ordnungszahl sortiert. – Das Periodensystem online".
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 5–14, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Chambers, Michael. "ChemIDplus - 21351-79-1 - HUCVOHYBFXVBRW-UHFFFAOYSA-M - Cesium hydroxide - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information".
- 1 2 3 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0111". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
