Blayais Nuclear Power Plant
| Blayais Nuclear Power Plant | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Official name | Centrale nucléaire du Blayais |
| Country | France |
| Location | Blaye, Gironde, Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
| Coordinates | 45°15′21″N 0°41′35″W / 45.25583°N 0.69306°WCoordinates: 45°15′21″N 0°41′35″W / 45.25583°N 0.69306°W |
| Status | Operational |
| Construction began |
Units 1–2: January 1, 1977 Units 3–4: April 1, 1978 |
| Commission date |
Unit 1: December 1, 1981 Unit 2: February 1, 1983 Unit 3: November 14, 1983 Unit 4: October 1, 1983 |
| Owner(s) | EDF |
| Operator(s) | EDF |
| Nuclear power station | |
| Reactor type | PWR |
| Reactor supplier | Framatome |
| Cooling source | Gironde estuary |
| Power generation | |
| Units operational | 4 × 910 MW |
| Make and model | CP1 |
| Thermal capacity | 4 × 2785 MWth |
| Nameplate capacity | 3640 MW |
| Capacity factor |
82.73% (2017) 75.15% (lifetime) |
| Annual net output | 26,380 GWh (2017) |
|
Website Centrale nucléaire du Blayais | |
The Blayais Nuclear Power Plant is a nuclear plant on the banks of the Gironde estuary near Blaye, South Western France operated by Électricité de France.
Description
The power plant has 4 pressurized water reactors – producing 951 MW gross and 910 MW net each[1]. They were commissioned from 1981 to 1983. The plant has 1200 EDF employees and 350 permanent workers.
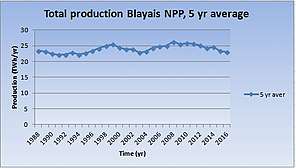
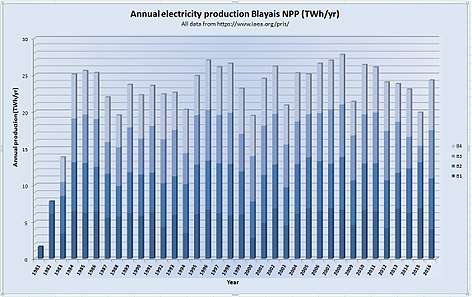
The four reactors produce about 25 TWh per year[1] which is about 5% of the total electricity consumption in France (2015: 476 TWh)[2]. Since its commissioning, the Blayais nuclear power plant has produced more than 800 TWh[1], nearly twice the equivalent of the French electricity production in one year.
In its 2016 annual report[3], the Nuclear Safety Authority (ASN) finds that "the nuclear safety and environmental protection performance of the Blayais NPP on the whole matches ASN's general assessment of EDF and that it's radiation protection performance stands out positively", but asked for "more effective management of the nuclear waste produced during reactor outages".
Selected incidents
2002 earthquake
In 2002 and 2003, EDF reported two level 1 incidents on the INES scale about the seismic resilience of the plant.
The incident reported on the 14 October 2002 earthquake advised the keeping of water reservoirs to ensure the cooling of the core in case of accident. The work required to bring the plant into compliance was completed in December 2005.
The incident on 28 October 2003 reported seismic behavior of piping connected to a tank of water affected by the incident of 14 October 2002.
1999 flooding
On the evening of 27 December 1999, a combination of the incoming tide and high winds overwhelmed the sea walls at the plant and causing parts of the plant to be flooded.[4] The event resulted in the loss of the plant's off-site power supply and knocked out several safety-related backup systems, resulting in a 'level 2' event on the International Nuclear Event Scale.[5]
At the time, units 1, 2 and 4 were at full power, while unit 3 was shut down for refuelling.[4] The operation of units 1 and 2 were affected by flood damage to a number of water pumps and distribution panels, all four units lost their 225 kV power supplies, while units 2 and 4 also lost their 400 kV power supplies.[4] Diesel backup generators were employed to maintain power to plants 2 and 4 until the 400 kV supply was restored.[4] Over the following days an estimated 90,000 m3 (3,200,000 cu ft) of water was pumped out of the flooded buildings.[4]
On 5 January, the regional newspaper Sud-Ouest ran the following headline without being contradicted:Very close to a major accident, explaining that a catastrophe had been narrowly avoided.[6]
The flooding resulted in fundamental changes to the evaluation of flood risk at nuclear power plants, and in the precautions taken.[7]
In Germany the flooding prompted the Federal Ministry for Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety to order an evaluation of the German nuclear power plants.[4]
Opposition

The continued operation of the Blayais plant is opposed by the local anti-nuclear group 'TchernoBlaye' (a portmanteau of the French spelling of Chernobyl and Blaye, the nearest town), formed by Stéphane Lhomme on 15 December 1999.[8]
References
- 1 2 3 "IAEA PRIS Power Reactor Information System - France". Retrieved 2017-09-30.
- ↑ "2015 Annual Electricity Report" (PDF). RTE, the French transmission system operator. Retrieved 2017-09-30.
- ↑ "2016 ASN Annual Report". ASN - Autorité de Sûreté Nucléaire. Retrieved 2017-09-30.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Generic Results and Conclusions of Re-evaluating the Flooding in French and German Nuclear Power Plants Archived 2011-10-06 at the Wayback Machine. J. M. Mattéi, E. Vial, V. Rebour, H. Liemersdorf, M. Türschmann, Eurosafe Forum 2001, published 2001, accessed 2011-03-21
- ↑ COMMUNIQUE N°7 - INCIDENT SUR LE SITE DU BLAYAIS Archived 2013-05-27 at the Wayback Machine. ASN, published 1999-12-30, accessed 2011-03-22
- ↑ Sud-Ouest, 5 janvier 2000 - Centrale de Blaye : Très près de l'accident majeur
- ↑ Lessons Learned from 1999 Blayais Flood: Overview of the EDF Flood Risk Management Plan, Eric de Fraguier, EDF, published 2010-03-11, accessed 2011-03-22
- ↑ L'histoire de TchernoBlaye TchernoBlaye, accessed 2011-03-29
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Blayais Nuclear Power Plant. |