Basilica of San Vitale
| Church of San Vitale | |
|---|---|
 The Church of San Vitale | |
| Basic information | |
| Location | Ravenna, Italy |
| Geographic coordinates | 44°25′12″N 12°11′46″E / 44.42°N 12.196°ECoordinates: 44°25′12″N 12°11′46″E / 44.42°N 12.196°E |
| Affiliation | Roman Catholic |
| Province | Archdiocese of Ravenna-Cervia |
| Region | Emilia-Romagna |
| Year consecrated | 547 |
| Website | http://www.ravennamosaici.it/ |
| Architectural description | |
| Architectural style | Byzantine |
| Groundbreaking | 527 |
| Completed | 547 |
| Construction cost | 26,000 solidi |
| UNESCO World Heritage site | |
| Official name | Church of St. Vitale |
| Part of | Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna |
| Criteria | Cultural: (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) |
| Reference | 788-002 |
| Inscription | 1996 (20th Session) |
| Area | 0.14 ha (0.35 acres) |

The Basilica of San Vitale is a church in Ravenna, Italy, and one of the most important surviving examples of early Christian Byzantine art and architecture in Europe. The Roman Catholic Church has designated the building a "basilica", the honorific title bestowed on church buildings of exceptional historic and ecclesial importance, although it is not of architectural basilica form. It is one of eight Ravenna structures inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
History

The church was begun by Bishop Ecclesius in 526, when Ravenna was under the rule of the Ostrogoths and completed by the 27th Bishop of Ravenna, Maximian, in 547 preceding the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna.
The construction of the church was sponsored by Julius Argentarius, a banker and architect, of whom very little is known, except that he also sponsored the construction of the Basilica of Sant'Apollinare in Classe at around the same time.[1] (A donor portrait of Julius Argentarius may appear among the courtiers on the Justinian mosaic.) The final cost amounted to 26,000 solidi (gold pieces).[2] It has been suggested that Julian originated in the eastern part of the Byzantine Empire, where there was a long-standing tradition of public benefactions.
The central vault used a western technique of hollow tubes inserted into each other, rather than bricks. This method was the first recorded structural use of terra-cotta forms, which later evolved into modern structural clay tile. The ambulatory and gallery were vaulted only later in the Middle Ages.[3]
The Baroque frescoes on the dome was made between 1778 and 1782 by S. Barozzi, U. Gandolfi and E. Guarana.[4]
Architecture
.jpg)
_v2.jpg)


The church has an octagonal plan. The building combines Roman elements: the dome, shape of doorways, and stepped towers; with Byzantine elements: polygonal apse, capitals, narrow bricks, and an early example of flying buttresses. The church is most famous for its wealth of Byzantine mosaics, the largest and best preserved outside of Constantinople. The church is of extreme importance in Byzantine art, as it is the only major church from the period of the Emperor Justinian I to survive virtually intact to the present day. Furthermore, it is thought to reflect the design of the Byzantine Imperial Palace Audience Chamber, of which nothing at all survives. The belltower has four bells, the tenor one dates to the 16th century. According to legends, the church was erected on the site of the martyrdom of Saint Vitalis.[5] However, there is some confusion as to whether this is the Saint Vitalis of Milan, or the Saint Vitale whose body was discovered together with that of Saint Agricola, by Saint Ambrose in Bologna in 393.
Mosaic art
The central section is surrounded by two superposed ambulatories. The upper one, the matrimoneum, was possibly reserved for married women. A series of mosaics in the lunettes above the triforia depict sacrifices from the Old Testament:[6] the story of Abraham and Melchizedek, and the Sacrifice of Isaac; the story of Moses and the Burning Bush, Jeremiah and Isaiah, representatives of the twelve tribes of Israel, and the story of Abel and Cain. A pair of angels, holding a medallion with a cross, crowns each lunette. On the side walls the corners, next to the mullioned windows, have mosaics of the Four Evangelists, under their symbols (angel, lion, ox and eagle), and dressed in white. Especially the portrayal of the lion is remarkable in its ferocity.
The cross-ribbed vault in the presbytery is richly ornamented with mosaic festoons of leaves, fruit and flowers, converging on a crown encircling the Lamb of God. The crown is supported by four angels, and every surface is covered with a profusion of flowers, stars, birds and animals, including many peacocks. Above the arch, on both sides, two angels hold a disc and beside them a representation of the cities of Jerusalem and Bethlehem. They symbolize the human race (Jerusalem representing the Jews, and Bethlehem the Gentiles).
All these mosaics are executed in the Hellenistic-Roman tradition: lively and imaginative, with rich colors and a certain perspective, and with a vivid depiction of the landscape, plants and birds. They were finished when Ravenna was still under Gothic rule. The apse is flanked by two chapels, the prothesis and the diaconicon, typical for Byzantine architecture.
Inside, the intrados of the great triumphal arch is decorated with fifteen mosaic medallions, depicting Jesus Christ, the twelve Apostles and Saint Gervasius and Saint Protasius, the sons of Saint Vitale. The theophany was begun in 525 under bishop Ecclesius. It has a great gold fascia with twining flowers, birds, and horns of plenty. Jesus Christ appears, seated on a blue globe in the summit of the vault, robed in purple, with his right hand offering the martyr's crown to Saint Vitale. On the left, Bishop Ecclesius offers a model of the church.
Justinian and Theodora panels
At the foot of the apse side walls are two famous mosaic panels, completed in 547. On the right is a mosaic depicting the East Roman Emperor Justinian I, clad in Tyrian purple with a golden halo, standing next to court officials, Bishop Maximian, palatinae guards and deacons. The halo around his head gives him the same aspect as Christ in the dome of the apse, but is part of the tradition of rendering the imperial family with haloes describe by Ernst Kantorowicz in the King's Two Bodies. Justinian himself stands in the middle, with soldiers on his right and clergy on his left, emphasizing that Justinian is the leader of both church and state of his empire. The later insertion of the Bishop Maximian's name above his head suggests that the mosaic may have been modified in 547, replacing the representation of the prior bishop with that of the Maximian.
The gold background of the mosaic shows that Justinian and his entourage are inside the church. The figures are placed in a V shape; Justinian is placed in the front and in the middle to show his importance with Bishop Maximian on his left and lesser individuals being placed behind them. This placement can be seen through the overlapping feet of the individuals present in the mosaic.[7]
Another panel shows Empress Theodora solemn and formal, with golden halo, crown and jewels, and a group of court women as well as eunuchs. The Empress holds the Eucharistic vessel for wine, and her panel differs from that of Justinian in having a more complex background, with a fountain, cupola, and lavish hangings.
See also
.jpg) | |
|
|
- A La Ronde, an 18th-century house in Devon, England, that is supposedly based on the Basilica.
- List of Roman domes
- History of Roman and Byzantine domes
Gallery
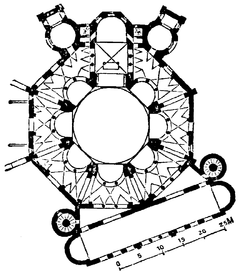 Ground plan of the building
Ground plan of the building.jpg) Apse mosaic
Apse mosaic The mosaic of Emperor Justinian and his retinue
The mosaic of Emperor Justinian and his retinue.jpg) Empress Theodora and attendants
Empress Theodora and attendants.jpg) The mosaic Sacrifice of Isaac
The mosaic Sacrifice of Isaac- The interior of San Vitale
 The presbytery
The presbytery
References
- ↑ Rivoira, Giovanni, Giovanni Teresio (1910). Lombardic Architecture: Its Origin, Development and Derivatives, Vol. 1. London: William Heinemann. pp. 64–65.
- ↑ Kleiner and Mamiya. Gardner's Art Through the Ages, p. 332.
- ↑ Krautheimer, Richard (1986). Early Christian and Byzantine Architecture (4 ed.). New Haven, CT: Yale University Press. p. 234. ISBN 978-0-300-05294-7.
- ↑ Basilica of S. Vitale: Justification for the inclusion to the World Heritage List. Archived October 29, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on May 30, 2015.
- ↑ Kleiner, Fred, Fred S.; Christin J. Mamiya (2008). Gardner's Art Through the Ages: Volume I, Chapters 1-18 (12th ed.). Mason, OH: Wadsworth. p. 332. ISBN 0-495-46740-5.
- ↑ Kleiner and Mamiya. Gardner's Art Through the Ages, p. 333.
- ↑ Kleiner and Mamiya. Gardner's Art Through the Ages, pp. 333, 336.
- ↑ "Byzantine Art: San Vitale, Ravenna". Smarthistory at Khan Academy. Retrieved January 8, 2013.
Further reading
- Andreas Agnellus. The Book of Pontiffs of the Church of Ravenna. Translated by D. Mauskopf Deliyannis. Washington: The Catholic University of American Press, 2004.
- Andreescu-Treadgold, Irina and Warren Treadgold. "Procopius and the Imperial Panels of San Vitale." Art Bulletin, 79, 1997, pp. 708–723.
- Mango, Cyril. Art of the Byzantine Empire, 352-1453: Sources and Documents. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1986.
- Procopius. On Buildings. Loeb Classical Library Series. Translated by H.B. Dewing and Glanville Downey. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1961.
- Von Simson, Otto G. Sacred Fortress: Byzantine Art and Statecraft in Ravenna. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1986.
- Weitzmann, Kurt, ed., Age of spirituality : late antique and early Christian art, third to seventh century, no. 65-66, 593, 1979, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York, ISBN 9780870991790; full text available online from The Metropolitan Museum of Art Libraries
External links
![]()