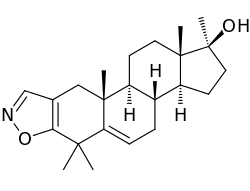
Azastene
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | WIN-17625; 4,4,17α-Trimethylandrosta-2,5-dieno(2,3-d)isoxazol-17β-ol |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 355.522 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Azastene (INN, USAN) (developmental code name WIN-17625) is a steroidogenesis inhibitor described as a contraceptive, luteolytic, and abortifacient which was never marketed.[1][2] It acts as a competitive inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (IC50 = 1 μM), and thereby inhibiting the formation of progesterone, corticosteroids, androgens, and estrogens.[3][4] Due to inhibition of corticosteroid synthesis, azastene is immunosuppressive.[2]
Synthesis
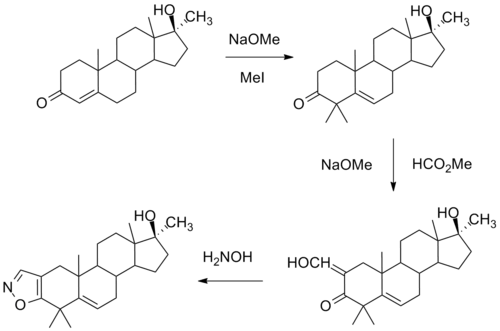
One synthesis of this compound involves initial alkylation of methyl testosterone by means of strong base and methyl iodide to afford the 4,4-dimethyl derivative. Formylation with alkoxide and methyl formate leads to the 2-hydroxymethyl derivative. Reaction of this last with hydroxylamine leads to formation of an isoxazole ring. There is then obtained azastene.
See also
References
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 113–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- 1 2 George W.A Milne (8 May 2018). Drugs: Synonyms and Properties: Synonyms and Properties. Taylor & Francis. pp. 1457–. ISBN 978-1-351-78989-9.
- ↑ B. Runnebaum; T. Rabe; L. Kiesel (6 December 2012). Future Aspects in Contraception: Proceeding of an International Symposium held in Heidelberg, 5–8 September 1984 Part 1 Male Contraception. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 74–. ISBN 978-94-009-4910-2.
- ↑ Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. Elsevier. 5 April 1991. pp. 259–. ISBN 978-0-08-086276-7.
- ↑ Gordon O. Potts, Sterling Drug Inc. U.S. Patent 3,966,926 (1976).