French Naval Aviation
| Force maritime de l'aéronautique navale French Naval Aviation | |
|---|---|
 Cockade of Naval Aviation. The naval anchor on this insignia was generalized between 1940 and 1945. | |
| Founded | 1912 |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Type | Naval aviation |
| Size | 6800 personnel; 179 aircraft[1] |
| Nickname(s) |
Sky Navy La Marine du Ciel |
| Motto(s) | Honneur, patrie, valeur, discipline |
| Anniversaries | March 20, 1912 |
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Contre-amiral Guillaume Goutay |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
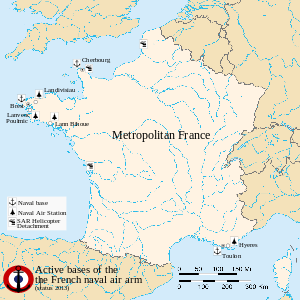
French Naval Aviation (often abbreviated in French to: « l'Aéronavale », or « Aviation navale » or more simply « l'Aéro ») is the naval air arm of the French Navy. The long-form official designation is Force maritime de l'aéronautique navale. Born as a fusion of carrier squadrons and the naval patrol air force, the Aéronavale was created in 1912. The force is under the command of a flag officer officially named Admiral of Naval Aviation (ALAVIA) with his headquarters at Toulon naval base. It has a strength of around 6,800 military and civilian personnel. It operates from four airbases in Metropolitan France and several detachments in foreign countries or French overseas territories. Carrier-borne pilots of the French navy do their initial training at Salon-de-Provence Air Base after which they undergo their carrier qualification with the US Navy.
Aircraft inventory
| Type | Origin | Class | Role | Introduced | In service | Total | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aérospatiale Alouette III | France | Rotorcraft | Utility | 18 | Retired.[2][3][1] | ||
| Breguet Atlantique II | France | Propeller | MPA | 22 | [1] | ||
| Dassault Falcon 10 M | France | Jet | Utility | 6 | [1] | ||
| Dassault Falcon 50 M | France | Jet | Patrol | 8 | [1] | ||
| Dassault Falcon 200 Guardian | France | Jet | Patrol | 5 | [1] | ||
| Dassault Rafale M | France | Jet | Multi-role | 41[4] | [1][5] | ||
| Embraer EMB 121 Xingu | Brazil | Propeller | Utility | 11 | [1] | ||
| Eurocopter SA365 Dauphin | France | Rotorcraft | SAR | 8 | [1] | ||
| Eurocopter AS565 Panther | France | Rotorcraft | Utility | 16 | [1] | ||
| Grumman E-2C Hawkeye | USA | Propeller | AEW&C | 3 | [1] | ||
| Mudry CAP 10 | France | Propeller | Trainer | 7 | [1] | ||
| NHIndustries NH90 Caiman Marine | France | Rotorcraft | Attack/SAR | 21 | [1] | ||
| Westland Lynx | UK | Rotorcraft | Attack | 16 | [1] |
Structure
Components
The flight personnel of the French Navy falls into three categories: fighter aviation, fixed-wing aviation and helicopter aviation.
Operationally the French Naval Aviation has four components:
- Embarqued Air Group (Le Groupe aérien embarqué) of the aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle: Rafale M, E-2 Hawkeye
- Naval Patrol and Maritime Surveillance Aviation (l'Aviation de patrouille et de surveillance maritime): Atlantique 2, Falcon 50, Falcon 200
- Shipborne and Shore-based Helicopters (Les hélicoptères embarqués et basés à terre): Dauphin, Panther, Lynx, Alouette III, Caïman Marine
- Support Aviation (l'Aviation de soutien): Falcon 10, EMB-121 Xingu, SR20, Cap-10, Dauphin, EC120 Colibri
Units
Operational squadrons are known as Flottilles and normally consist of 12 aircraft :
- 1F to 10F are carrier based anti-submarine squadrons
- 11F to 20F are fighter and attack squadrons
- 21F to 30F are maritime patrol squadrons
- 31F to 39F are helicopter squadrons
Shore-based training and transport squadrons are known as Escadrilles de Servitude :
- 1S to 19S are communications squadrons
- 20S to 29S are helicopters squadrons
- 50S to 59S are training squadrons
| Squadron | Insignia | Type | Aircraft | Base | Role | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embarqued Air Group (Le Groupe aérien embarqué)[6] | ||||||
| 4F | Fixed wing | E-2C Hawkeye | Lann Bihoue | Carrier Airborne Early Warning | [7] | |
| 11F | Fixed wing | Rafale M | Landivisiau | Strike Fighter | [8] | |
| 12F | Fixed wing | Rafale M | Landivisiau | Strike Fighter | [9] | |
| 17F | Fixed wing | Rafale M | Landivisiau | Strike Fighter | [10] Ended conversion to Rafale M on June 2016. | |
| Det. PEDRO | Rotary | Eurocopter AS365 Dauphin | Hyères | Plane guard | Not part of the GAE. The Charles de Gaulle sets sail to cruises with 2 Dauphin helicopters from 35F. | |
| Naval Patrol and Maritime Surveillance Aviation (l'Aviation de patrouille et de surveillance maritime)[11] | ||||||
| 21F | Fixed wing | Atlantique II | Lann Bihoue | Anti-Submarine Warfare / Naval patrol | [12] Detachments at Dakar and Djibouti. | |
| 23F | Fixed wing | Atlantique II | Lann Bihoue | Anti-Submarine Warfare / Naval patrol | [13] | |
| 24F | Fixed wing | Falcon 50 M | Lann Bihoue | Maritime surveillance / Search and Rescue | [14] | |
| 25F | Fixed wing | Falcon 200 Guardian | GAM Faa’a | Maritime surveillance / Search and Rescue | [15] Detachment at Nouméa. | |
| Shipborne and Shore-based Helicopters (Les hélicoptères embarqués et basés à terre) | ||||||
| 31F | Rotary | NH90 Caiman | Hyeres | Search and Rescue | [16] | |
| 33F | Rotary | NH90 Caiman | Lanveoc | Anti-Submarine Warfare / Search and Rescue | [17] | |
| 34F | Rotary | Westland Lynx | Lanveoc | Anti-Submarine Warfare | To convert to NH90 Caiman.[18] | |
| 35F | Rotary | Eurocopter AS365 Dauphin, Alouette III | Hyeres | Search and Rescue | Detachments at La Rochelle, Le Touquet-Paris-Plage[19] and Faa’a. | |
| 36F | Rotary | Eurocopter AS565 Panther | Hyeres | Small ship flights | [20] | |
| Support Aviation (l'Aviation de soutien) | ||||||
| 10S | Rotary/ Fixed wing/UAV | Alouette III, Westland Lynx, Schiebel S-100 Serval | Hyeres | Experimental | Aviation and airborne weapons research and development, evaluation at several locations. | |
| 22S | Rotary | Dauphin, EC120 Colibri | Lanveoc | Rotary operational training / Liaison | ||
| 28F | Fixed wing | Embraer Xingu | Lann Bihoue | Naval patrol and maritime surveillance operational training / Utility / Liaison | [21] | |
| 50S | Fixed wing | SR20 and CAP-10 | Lanveoc | Elementary flying training | ||
| 57S | Fixed wing | Falcon 10 M | Landivisiau | Combat aviation operational training | [22] | |
Gallery
 Insignia of pilots of Naval aviation.
Insignia of pilots of Naval aviation. Arm insignia of personnel of Naval aviation.
Arm insignia of personnel of Naval aviation.- Two Super Étendard, two Rafale fighters and a E-2C Hawkeye at the 2010s French Naval Aviation Centenary Airshow
 Rafale fighter on the flight deck of Charles de Gaulle at dawn.
Rafale fighter on the flight deck of Charles de Gaulle at dawn. Rafale fighters on the flight deck of the aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle
Rafale fighters on the flight deck of the aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle.jpg) Atlantique 2 maritime patrol aircraft
Atlantique 2 maritime patrol aircraft Lynx WG13 helicopter armed with a Mk46 torpedo on the deck of a frigate
Lynx WG13 helicopter armed with a Mk46 torpedo on the deck of a frigate Offshore rescue by French Navy Dauphin helicopter
Offshore rescue by French Navy Dauphin helicopter Panther helicopter lifts off the deck of Guépratte
Panther helicopter lifts off the deck of Guépratte
Retired Aircraft[23][24]
- Blanchard Brd.1 HB3
- Borel-Odier T BO-2
- Bréguet 521 Bizerte
- CAMS 30E
- CAMS.37A/37²/37.11/Lia
- CAMS 46 Et2
- CAMS 55.1/55.2/55.6/55.10
- Consolidated PBY-5 Catalina
- Coutant RMC Type 17
- Donnet-Denhaut 140/150 hp
- Donnet-Denhaut 160 hp
- Donnet-Denhaut 200 HP HS Triplace/RR/BB
- Donnet-Denhaut 275hp
- Donnet-Denhaut bimoteur
- Dornier Do 24T
- Farman Lévy HB2 450 hp
- Farman F60 Torp Goliath/F65
- Farman F.165/F.166/F.168 Torp
- FBA Type C
- FBA Type H
- FBA Type S
- FBA type 14 HE2
- FBA.17HL1/HL2/HMT2/HE2
- FBA.19HMB2
- Georges Lévy 280 HB2
- Gourdou Leseurre GL.810/811/812/813 HY
- Gourdou Leseurre GL.832 HY
- Grumman JRF-5 Goose
- Hanriot HD.2 C1
- Hanriot HD.3 C2
- Hanriot HD.14 E2
- Hanriot HD.17 E2
- Latham HB3 Type 43
- Latécoère 290
- Latécoère 298

- Levasseur PL.14 Tb2B2
- Levasseur PL.15 T2B2
- Lévy Besson 200 hp
- Lioré et Olivier LeO.20 Bn3
- Lioré et Olivier H.13/H.136
- Lioré et Olivier H.43
- Lioré et Olivier H.193
- Lioré et Olivier H.257 Bis/H258
- Loire 130 Cl
- Loire 210
- Martin P5M-2 Marlin
- Nieuport IV.H
- Nieuport VI.H
- Nieuport 12
- Potez 452
- SCAN 20
- Short Sunderland Mk.III/V
- SNCAC/Farman NC.470
- SNCAN N1402 Noroit

- Sopwith 130hp Clerget
- SPAD XIV Canon
- Supermarine Sea Otter
- Supermarine Walrus
- Tellier Canon 200 hp
- Tellier 200 hp
- Tellier 350Hp
- Tellier BM 400 hp
- Voisin 13,5m
- Voisin Canard
- Amiot AAC.1 (Junkers Ju 52)
- Avro Anson
- Avro Lancaster Mk.VII
- Beechcraft SNB-5/JRB-4
- Blériot-SPAD S.42
- Bloch MB.151 C1
- Breguet BRE.14B2/A2
- Breguet BRE.19 B2

- Bréguet 1050 Alizé
- Bréguet 1150 Atlantic
- Caudron Cau 59 ET2
- Caudron C635 Simoun
- Caudron C.445 Goéland
- Canadian Car & Foundry Harvard II
- Chance Vought F4U-7/AU-1 Corsair
- Consolidated PB4Y-2 Privateer
- Curtiss SBC4/SB2C5 Helldiver
- Dassault MD 312 Flamant
- De Havilland 100 Vampire Mk.V
- Dewoitine 7 C1
- Dewoitine D.373/D.376
- Dewoitine D.510
- Dewoitine D.520
- Douglas SBD-5 Dauntless
- Douglas C-47D Dakota
- Farman F.223.4
- Fouga CM.175 Zéphyr
- Dassault Étendard IVM/P
- Gourdou Leseurre ET1 Type 22
- Gourdou Leseurre LGL.32
- Grumman F6F-5 Hellcat
- Grumman TBM-3S/E/W/UT Avenger

- Hanriot HD.14 E2
- Hanriot H.41
- Junkers Ju 188
- Levasseur PL.4 R3b
- Levasseur PL.5 C2b
- Levasseur PL.7 T2B2b
- Levasseur PL.10 R3b/PL.101 R3b
- Lioré et Olivier LeO.7.3
- Lioré et Olivier LeO.20 Bn3
- Lockheed P2V-1 Ventura
- Lockheed P2V-6/7 Neptune
- LTV/Vought F-8E(FN) Crusader
- Martin 167-A3
- Maurice Farman Type 1910
- Morane Saulnier MoS.130 Et2
- Morane Saulnier MoS.149 Ep2
- Morane Saulnier MS.225 C1
- Morane Saulnier MS.230 Et2
- Morane Saulnier MS.406 C1
- Morane Saulnier MS.500/MS.502 Criquet
- Morane Saulnier MS.733 Alcyon
.jpg)
- Morane Saulnier MS760 Paris
- Nieuport N.21/N.23
- Nieuport NiD.62 C1/NiD.622 C1
- Nord 262 Frégate
- North American NAA.57 P2
- North American SNJ-3/4/5
- Piper PA-31 Navajo
- Potez 25 A2/TOE
- Potez 567
- Potez 631 C3
- Salmson Sal.2 A2
- SNCAC NC.701/NC.702 Martinet
- SNCAN N.1001/N.1002 Pingouin
- SCAN N.1101 Noralpha
- SNCAN SV.4C Stampe
- SNCAO/Loire-Nieuport LN.401/LN.411
- SNCASE R.82 Romano
- SNCASE Leo.451
- SNCASE SE.161 Languedoc/Bloch MB.160
- SNCASE Aquilon
- SNCASO/Bloch MB.175
- SNCASO SO.94/95 Corse
- SNCASO SO.30P Bretagne
- SOCATA MS.880 Rallye
- Sopwith Sop.1 A2
- Sopwith Triplan
- SPAD S.VII C1
_Crusader_in_flight_over_the_Med_1976.jpeg)
- SPAD S.XIII
- Stinson 105
- Supermarine Seafire Mk.III/IX/XV
- Tampier T.4
- Taylorcraft L-2
- Villiers Vil.2AM C2
- Vickers Wellington
- Voisin LAP VIII
- Voisin LAS Type Armée III
- Vought V.156-F
- Wibault Wib.74 C1
Helicopters and Autogyros
See also
References & notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Defence Key Figures: 2016 Edition". Defense.gouv.fr. (download PDF file or see HTML version Archived September 6, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.)
- ↑ "En attendant le H160, l'armée va louer des Dauphin pour remplacer ses antiques Alouette".
- ↑ http://www.defense.gouv.fr/content/download/511454/8625925/Les%20chiffres%20cle%CC%81s%20de%20la%20D%C3%A9fense%20%C3%A9dition%202017%20EN.pdf
- ↑ https://www.dassault-aviation.com/wp-content/blogs.dir/2/files/2018/07/Dassault-Aviation-Press-Conference-July-19-2018.pdf
- ↑ https://www.dassault-aviation.com/wp-content/blogs.dir/2/files/2017/07/Dassault-Aviation-Press-Conf-July-26-2017.pdf
- ↑ https://www.defense.gouv.fr/marine/dossiers/ban/le-groupe-aerien-embarque
- ↑ "Flotilla 4F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 11F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 12F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 17F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ https://www.defense.gouv.fr/english/marine/dossiers/ban/l-aviation-de-patrouille-et-de-surveillance-maritime
- ↑ "Flottilla 21F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 23F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 24F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 25F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 31F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 33F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 34F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 35F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 36F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ "Flottilla 28F". French Navy. Retrieved 25 October 2016.
- ↑ https://www.defense.gouv.fr/marine/operations/forces/aeronautique-navale/escadrilles/escadrille-57s
- ↑ "Military Factory - Site detailing past and present military systems and technology including aircraft, vehicles, guns and navy vessels of the world". Retrieved 2017-08-22.
- ↑ "Office of the Historian". www.history.state.gov. Retrieved 2017-08-22.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aviation navale. |
- French Fleet Air Arm, about French naval aviation.