Atlantic seaboard watershed
| Atlantic Seaboard | |
| watershed | |
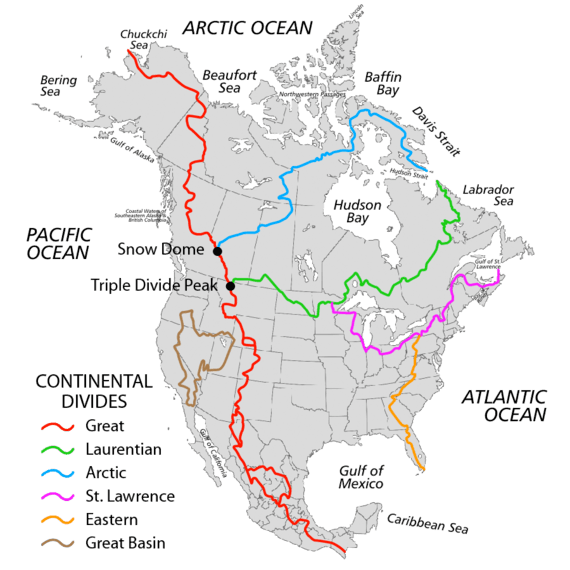 The Atlantic Seaboard Watershed is a narrow continental area which extends southward along the Atlantic Ocean from Cape North (Nova Scotia peninsula) to the southern limit of the Eastern Continental Divide (yellow), which ends at the drainage into the 1937 Okeechobee Waterway. | |
| Countries | Canada, United States |
|---|---|
| Area | 233,961 sq mi (605,956 km2) lower bound (from sum of listed areas) |
The Atlantic seaboard watershed is a watershed of North America along both:
- the Atlantic Canada (Maritimes) coast south of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence Watershed, and
- the East Coast of the United States north of the watershed of the Okeechobee Waterway.
The relatively narrow continental area is demarcated on the south by drainage to the Okeechobee Waterway (which drains both westward to the Gulf and eastward to ocean), the Eastern Continental Divide (ECD) to the west, and the Saint Lawrence divide to the north. US physiographic regions of this watershed are the Atlantic Plain and the Appalachian Mountains & Highlands. Major sub-watersheds of the Atlantic Seaboard are the following (north-to-south):
- Sub-watersheds adjacent to the Saint Lawrence divide
- Chedabucto Bay: 2,148 square miles (5,560 km2)[1]
- Gulf of Maine: 69,115 square miles (179,010 km2)
- Long Island Sound: 16,246 square miles (42,080 km2)
- Lower New York Bay: >14,000 square miles (36,000 km2)
- Other notable sub-watersheds
- Delaware Bay: 14,119 square miles (36,570 km2) — larger than several, but not adjacent to either divide
- Chesapeake Bay: 64,299 square miles (166,530 km2) — adjacent to both divides (at the Triple Divide point)
- Sub-watersheds adjacent to the Eastern Continental Divide
- Albemarle Sound: >14,380 square miles (37,200 km2)[2]
- Winyah Bay: >7,221 square miles (18,700 km2)[3]
- Santee River: >4,531 square miles (11,740 km2)[4]
- Savannah River: 9,850 square miles (25,500 km2)
- St. Johns River: 8,840 square miles (22,900 km2)
- Biscayne Bay: >2,800 square miles (7,300 km2)
- Kissimmee River: 3,000 square miles (7,800 km2)
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-07-06. Retrieved 2010-04-10.
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.