Association fallacy
An association fallacy is an informal inductive fallacy of the hasty-generalization or red-herring type and which asserts, by irrelevant association and often by appeal to emotion, that qualities of one thing are inherently qualities of another. Two types of association fallacies are sometimes referred to as guilt by association and honor by association.
Form
In notation of first-order logic, this type of fallacy can be expressed as (∃x ∈ S : φ(x)) ⇒ (∀x ∈ S : φ(x)), meaning "if there exists any x in the set S so that a property φ is true for x, then for all x in S the property φ must be true."
- Premise A is a B
- Premise A is also a C
- Conclusion Therefore, all Bs are Cs
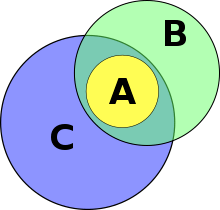
The fallacy in the argument can be illustrated through the use of an Euler diagram: "A" satisfies the requirement that it is part of both sets "B" and "C", but if one represents this as an Euler diagram, it can clearly be seen that it is possible that a part of set "B" is not part of set "C", refuting the conclusion that "all Bs are Cs".
Guilt by association
Examples
Some syllogistic examples of guilt by association:
- John is a con artist. John has black hair. Therefore, all people with black hair are con artists.
- Lyle is a crooked salesman. Lyle proposes monorail. Therefore, monorail is folly.
- Jane is good at mathematics. Jane is dyslexic. Therefore, all dyslexic people are good at mathematics.
- Simon, Karl, Jared, and Brett are all friends of Josh, and they are all petty criminals. Jill is a friend of Josh; therefore, Jill is a petty criminal.
Guilt by association as an ad hominem fallacy
Guilt by association can sometimes also be a type of ad hominem fallacy, if the argument attacks a person because of the similarity between the views of someone making an argument and other proponents of the argument.[1]
This form of the argument is as follows:
- Source S makes claim C.
- Group G, which is currently viewed negatively by the recipient, also makes claim C.
- Therefore, source S is viewed by the recipient of the claim as associated to the group G and inherits how negatively viewed it is.
An example of this fallacy would be "My opponent for office just received an endorsement from the Puppy Haters Association. Is that the sort of person you would want to vote for?"
Honor by association
The logical inverse of "guilt by association" is honor by association, where one claims that someone or something must be reputable because of the people or organizations that are related to it or otherwise support it. For example:
Examples:
- Citizens of Country X won more Nobel Prizes, gold medals, and literary awards than citizens of Country Y. Therefore, a citizen of Country X is superior to a citizen of Country Y.
- In many advertisements, businesses heavily use the principle of honor by association. For example, an attractive spokesperson will say that a specific product is good. The attractiveness of the spokesperson gives the product good associations.
Galileo Gambit
A form of the association fallacy often used by those denying a well-established scientific or historical proposition is the so-called "Galileo Gambit". The argument goes that since Galileo was ridiculed in his time but later acknowledged to be right, that since their non-mainstream views are provoking ridicule and rejection from other scientists, they will later be recognized as correct too.[2]
The Galileo Gambit gained public attention during the 2012 United States presidential campaign, when Texas governor Rick Perry expressed skepticism about global warming. The Galileo Gambit is flawed in that being ridiculed does not necessarily correlate with being right and that many people who have been ridiculed in history were, in fact, wrong.[3] Similarly, Carl Sagan has stated that while they laughed at Columbus and the Wright Brothers, "they also laughed at Bozo the Clown".[4]
See also
Notes
- ↑ "Fallacy: Guilt By Association." The Nizkor Project. The Nizkor Project, n.d. Web. 12 June 2014. <http://www.nizkor.org/features/fallacies/guilt-by-association.html>.
- ↑ Amsden, Brian. "Recognizing Microstructural Fallacies" (PDF). p. 22. Retrieved 24 March 2014.
- ↑ Collins, Loren (2012). Bullspotting: Finding Facts in the Age of Misinformation. Prometheus Books.
- ↑ Shapiro, Fred R. (2006). The Yale Book of Quotations. Yale University Press. p. 660. ISBN 9780300107982.
References
- Damer, T. Edward (2009), Attacking Faulty Reasoning: A Practical Guide to Fallacy-free Arguments (6th ed.), Wadsworth, ISBN 978-0-495-09506-4
- Fallacies: Classical and Contemporary Readings, edited by Hans V. Hansen and Robert C. Pinto (1995).
- Bibliography on Fallacies: http://www.ditext.com/eemeren/bib.html
External links
- The Fallacy Files Guilt by Association
- Propagandacritic.com "Transfer technique"
- Propagandacritic.com "Testimonial"