Annona reticulata
Annona reticulata is a small deciduous or semi-evergreen tree in the plant family Annonaceae.[2] It is best known for its fruit, called custard apple, a common name it shares with fruits of several other species in the same genus: A. cherimola[3] and A. squamosa[4] or sometimes it is called wild-sweetsop, bull's heart, bullock's-heart, or ox-heart. The flavor of the fruit is sweet and pleasant, but less popular than that of A. cherimola.
Description
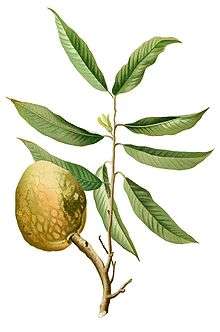
It is a small deciduous or semi-evergreen tree reaching 8 metres (26 ft) to 10 metres (33 ft) tall with an open, irregular crown.[5]

- Stems and leaves
- The slender leaves are hairless, straight and pointed at the apex (in some varieties wrinkled), 10 centimetres (3.9 in) to 20 centimetres (7.9 in) long and 2 centimetres (0.79 in) to 7 centimetres (2.8 in) wide.[5]
- Flowers
- The yellow-green flowers are generally in clusters of three or four 2 centimetres (0.79 in) to 3 centimetres (1.2 in) diameter, with three long outer petals and three very small inner ones.[5]
- Fruits and reproduction
- The fruits varies in shape, heart-shaped, spherical, oblong or irregular. The size ranges from 7 centimetres (2.8 in) to 12 centimetres (4.7 in), depending on the cultivar. When ripe, the fruit is brown or yellowish, with red highlights and a varying degree of reticulation, depending again on the variety. The flesh varies from juicy and very aromatic to hard with a repulsive taste.[5] The flavor is sweet and pleasant, akin to the taste of 'traditional' custard.
Distribution and habitat
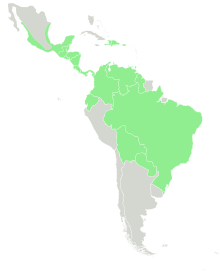
Possibly a native of the Caribbean[6] and Central America,[1] Annona reticulata is now pantropical[6] and can be found growing between altitudes of 0 metres (0 ft) to 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) in areas of Central America that have alternating seasons.[5] It is cultivated in many tropical countries, and also occurs as feral populations in many parts of the world, including Southeast Asia, Taiwan, India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Australia, and Africa.
Cultivated and naturalized[6] in many parts of the world including Southeast Asia, Taiwan, India, Australia, and Africa.
- Native
- Nearctic:
- Central Mexico: Veracruz
- Neotropic:
- Central America: Belize, Chiapas, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama
- Caribbean: The Bahamas, Dominican Republic, Guadeloupe, Haiti, Martinique, Puerto Rico, Trinidad, Jamaica, Cuba
- Northern South America: Guyana, Venezuela
- Brazil: Acre, Amazonas, Bahia, Mato Grosso, Minas Gerais, Para, Rio Grande do Sul, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo
- Western South America: Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, El Salvador, Paraguay[1][7]
References
- 1 2 3 "Annona reticulata". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ↑ Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). "PLANTS Profile, Annona reticulata L." The PLANTS Database. United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ↑ "Annona cherimola". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- ↑ "Annona squamosa". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Mahdeem, H. (5 July 1998). "Annona reticulata". Neglected Crops. Department of Horticulture & Landscape Architecture, Purdue University. Archived from the original on 11 May 2008. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- 1 2 3 Aluka. "Entry for Annona reticulata Linn. [family ANNONACEAE]". African Plants. Ithaka Harbors, Inc. doi:10.5555/AL.AP.UPWTA.1_232 (inactive 2018-09-23). Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ↑ Bioversity International. "Result set for: Annonaceae Annona reticulata". New World Fruits Database. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Annona reticulata. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Annona reticulata |
- Dr. Kiran Kharat article - Induction of mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human breast cancer cells (T-47D) by Annona reticulata L. leaves methanolic extracts
- Custard apple with pictures of the fruit and the tree
- Prospects and potential of fatty acid methyl esters of some non-traditional seed oils for use as biodiesel in India
- Photos
- Purdue Crop Index page
- "Species Annona reticulata". UniProt Consortium. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- Mahdeem, H. (5 July 1998). "Annona reticulata". hort.purdue.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2008.