Aniene
| Aniene | |
|---|---|
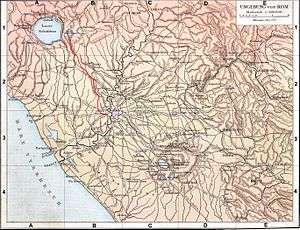 An 1886 German map of the settlements, roads, and aqueducts around ancient Rome. The Anio is the principal left-hand tributary of the Tiber, joining it just north of Rome. | |
| Country | Italy |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source |
Filettino 1,075 m (3,527 ft) |
| River mouth |
Tiber (Rome, ponte Salario) 41°56′30″N 12°30′07″E / 41.941745°N 12.50181°ECoordinates: 41°56′30″N 12°30′07″E / 41.941745°N 12.50181°E |
| Length | 99 km (62 mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 1,414 km2 (546 sq mi) |
The Aniene (pronounced [aˈnjɛːne]; Latin: Anio), formerly known as the Teverone,[1] is a 99-kilometer (62 mi) river in Lazio, Italy. It originates in the Apennines at Trevi nel Lazio and flows westward past Subiaco, Vicovaro, and Tivoli to join the Tiber in northern Rome. It thus formed the principal valley east of ancient Rome and was an important water source as the city's population expanded. The falls at Tivoli were noted for their beauty.[1] Historic bridges across the river include the Ponte Nomentano, Ponte Salario, and Ponte di San Francesco, all of which were originally fortified with towers.
History
The confluence of the Aniene and Tiber was controlled by Antemnae, a Latin settlement on a hill just to its south. Rome's foundation myths numbered them among the Sabines seized by Romulus but that his wife Hersilia convinced him to make its people Roman citizens after their defeat and annexation around 752 BC.[2]
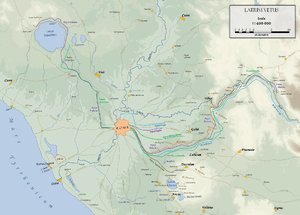

In antiquity, three principal aqueducts of Rome—the Aqua Anio Vetus, Aqua Anio Novus and Aqua Claudia—had their sources in the Aniene valley. Together with the Aqua Marcia, they were regarded as the "four great aqueducts of Rome."[3] The Aqua Anio Vetus (Latin for "Old Anio aqueduct") was constructed around 270 BC.[1] The Aqua Anio Novus ("New Anio aqueduct") was begun under Caligula around AD 38 and completed under Claudius in 48.[1] A third aqueduct, the Aqua Marcia, was constructed by Q. Marcius Rex between 144 and 140 BC using the proceeds from the destructions of Corinth and Carthage in 146 BC.
The emperor Nero created three lakes on the river for his villa at Subiaco. The largest of these dams was the highest dam in classical antiquity and remained in use until its destruction by a flood in 1305.[4][5][6][7] Trajan eventually connected the Anio Novus to two of these lakes.
The former site of Antemnae is now the ruins of Forte Monte Antenne, which was erected by the Kingdom of Italy between 1877 and 1891.
References
- 1 2 3 4 EB (1878).
- ↑ Livy. From the Founding of the City. (I,11).
- ↑ Blackman, Deane R. "The Volume of Water Delivered by the Four Great Aqueducts of Rome." Papers of the British School at Rome 46 (1978): 52-72. https://www.jstor.org/stable/40310747.
- ↑ Smith (1970), pp. 60–61.
- ↑ Smith (1971), p. 26.
- ↑ Schnitter (1978), p. 28.
- ↑ Hodge (1992), p. 87.
Sources
- "Anio", Encyclopædia Britannica, 9th ed., Vol. II, New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1878, p. 57 .
- Hodge, A. Trevor (1992), Roman Aqueducts & Water Supply, London: Duckworth, ISBN 0-7156-2194-7
- Schnitter, Niklaus (1978), "Römische Talsperren", Antike Welt, 8 (2): 25–32
- Smith, Norman (1970), "The Roman Dams of Subiaco", Technology and Culture, 11 (1): 58–68, doi:10.2307/3102810
- Smith, Norman (1971), A History of Dams, London: Peter Davies, ISBN 0-432-15090-0
See also
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aniene. |

- Simbruina Stagna History and Art of Subiaco (Italian site)
