Alexamenos graffito
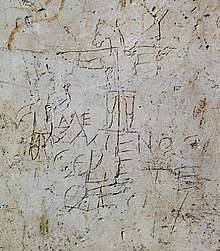
The Alexamenos graffito (also known as the graffito blasfemo, or blasphemous graffito)[1]:393 is a piece of Roman graffiti scratched in plaster on the wall of a room near the Palatine Hill in Rome, which has now been removed and is in the Palatine Hill Museum.[2] It may be the earliest surviving depiction of Jesus and, if so, competes with an engraved gem as the earliest known pictorial representation of the Crucifixion of Jesus.[3] It is hard to date, but has been estimated to have been made c. 200.[4] The image seems to show a young man worshipping a crucified, donkey-headed figure. The Greek inscription approximately translates to "Alexamenos worships [his] god,"[5] indicating that the graffito was apparently meant to mock a Christian named Alexamenos.[6]
Content

The image depicts a human-like figure affixed to a cross and possessing the head of a donkey. In the top right of the image is what has been interpreted as either the Greek letter upsilon or a tau cross.[1] To the left of the image is a young man, apparently intended to represent Alexamenos,[7] a Roman soldier/guard, raising one hand in a gesture possibly suggesting worship.[8][9] Beneath the cross is a caption written in crude Greek: ΑΛΕ ξΑΜΕΝΟϹ ϹΕΒΕΤΕ ϑΕΟΝ. ϹΕΒΕΤΕ can be understood as a variant spelling (possibly a phonetic misspelling)[2] of Standard Greek ϹΕΒΕΤΑΙ, which means "worships". The full inscription would then be read as Ᾰλεξᾰ́μενος σέβεται θεόν, "Alexamenos worships [his] God".[2][10][11] Several other sources suggest "Alexamenos worshiping a god", or similar variants, as the intended translation.[12][13][14][15]
Date
No clear consensus has been reached on when the image was made. Dates ranging from the late 1st to the late 3rd century have been suggested,[16] with the beginning of the 3rd century thought to be the most likely.[10][17][18]
Discovery and location
The graffito was discovered in 1857 when a building called the domus Gelotiana was unearthed on the Palatine Hill. The emperor Caligula had acquired the house for the imperial palace, which, after Caligula died, became used as a Paedagogium (boarding school) for the imperial page boys. Later, the street on which the house sat was walled off to give support to extensions to the buildings above, and it thus remained sealed for centuries.[19]
Interpretation
The inscription is usually taken to be a mocking depiction of a Christian in the act of worship.[20] At the time, pagans derided Christians for worshipping a man who had been crucified.[20] The donkey's head and crucifixion would both have been considered insulting depictions by contemporary Roman society. Crucifixion continued to be used as an execution method for the worst criminals until its abolition by the emperor Constantine in the 4th century, and the impact of seeing a figure on a cross is comparable to the impact today of portraying a man with a hangman's noose around his neck or seated in an electric chair.[21]
It seems to have been commonly believed at the time that Christians practiced onolatry (donkey-worship). That was based on the misconception that Jews worshipped a god in the form of a donkey, a claim made by Apion (30-20 BC – c. AD 45-48):[22]
Apion ought to have had a regard to these facts; unless he had himself had either an asse’s heart, or a dog’s impudence: of such a dog I mean as they worship. For he had no other external reason for the lies he tells of us. As for us Jews, we ascribe no honor, nor power to asses;[23]
Origen reports in his treatise Contra Celsum that the pagan philosopher Celsus made the same claim against Christians and Jews:[24]
For the sake of such a monstrous delusion, and in support of those wonderful advisers, and those wonderful words which you address to the lion, to the amphibious creature, to the creature in the form of an ass, and to others, for the sake of those divine doorkeepers..[25]
Tertullian, writing in the late 2nd or early 3rd century, reports that Christians, along with Jews, were accused of worshipping such a deity. He also mentions an apostate Jew who carried around Carthage a caricature of a Christian with ass's ears and hooves, labeled Deus Christianorum ὀνοκοίτης[26] ("The God of the Christians conceived of an ass.").[27]
It has also been suggested that both the graffito and the roughly contemporary gems with Crucifixion images are related to heretical groups outside the Church.[28]
A small minority of scholars consider the image to be not of Jesus, but of some other deity.[29]
In the image, Alexamenos is portrayed venerating an image of the crucifix, a detail that Peter Maser believed to represent actual Christian practice of veneration of icons. This practice, however, was not known to be a part of Christian worship until the 4th or 5th century.[30]
"Alexamenos fidelis"
In the next chamber, another inscription in a different hand reads ΑΛΕξΑΜΕΝΟϹ FIDELIS (Alexamenos fidēlis), Latin for "Alexamenos is faithful" or "Alexamenos the faithful".[31] This may be a riposte by an unknown party to the mockery of Alexamenos represented in the graffito.[18]
Notes
- 1 2 Bayley, Harold (1920). Archaic England: An essay in deciphering prehistory from megalithic monuments, earthworks, customs, coins, place-names, and faerie superstitions. Chapman & Hall.
- 1 2 3 Rodney J. Decker, The Alexamenos Graffito
- ↑ Schiller, 89-90, fig. 321
- ↑ "Alexamenos and pagan perceptions of Christians". uchicago.edu.
- ↑ Sight and the Ancient Senses.
- ↑ Viladesau, Richard (1992). The Word in and Out of Season. Paulist Press. p. 46. ISBN 0-8091-3626-0.
- ↑ Rodolfo Lanciani, Ancient Rome in the Light of Recent Discoveries, 1898, chapter 5 'The Palace of the Caesars'
- ↑ Thomas Wright, Frederick William Fairholt, A History of Caricature and Grotesque in Literature and Art, Chatto and Windus, 1875, p. 39
- ↑ Augustus John Cuthbert Hare, Walks in Rome, Volume 1, Adamant Media Corporation, 2005, p. 201
- 1 2 David L. Balch, Carolyn Osiek, Early Christian Families in Context: An Interdisciplinary Dialogue, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2003, p. 103
- ↑ B. Hudson MacLean, An introduction to Greek epigraphy of the Hellenistic and Roman periods from Alexander the Great down to the reign of Constantine, University of Michigan Press, 2002, p. 208
- ↑

- ↑ "Home Page – Concordia Theological Seminary". Ctsfw.edu. Archived from the original on 2008-07-04. Retrieved 2012-10-17.
- ↑ "A Sociological Analysis of Graffiti" (PDF). Sustain.ubc.ca. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-04. Retrieved 2012-10-17.
- ↑ Charles William King (1887). "Gnostics and their Remains". p. 433 note 12. Retrieved 2012-10-17.
- ↑ Hans Schwarz, Christology, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 1998, p. 207
- ↑ Schiller, 90
- 1 2 Michael Green, Evangelism in the Early Church, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2004, p. 244
- ↑ Edward L Cutts, History of Early Christian Art, Kessinger Publishing, 2004, p. 200
- 1 2

- ↑ N. T. Wright, What Saint Paul Really Said: Was Paul of Tarsus the Real Founder of Christianity?, 1997, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, p. 46
- ↑ from Against Apion book II, 7, written by Josephus.
- ↑ http://penelope.uchicago.edu/josephus/apion-2.html
- ↑ BOOK VII CHAP. XL.
- ↑ http://www.newadvent.org/fathers/04167.htm
- ↑ "Tertulliani Apologeticum".
- ↑ Tertullian, Apologeticum, 16, 1 and 12.
- ↑ Schiller, 89-90
- ↑ B. Hudson MacLean, An introduction to Greek epigraphy of the Hellenistic and Roman periods from Alexander the Great down to the reign of Constantine, University of Michigan Press, 2002, p. 208
- ↑ David L. Balch, Carolyn Osiek, Early Christian Families in Context: An Interdisciplinary Dialogue, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2003, p. 103, footnote 83
- ↑

References
- Schiller, Gertrud. Iconography of Christian Art, Vol. II,1972 (English trans from German), Lund Humphries, London, ISBN 0-85331-324-5
Further reading
- Titus Flavius Josephus, Contre Apion, II (VII), 2.80, translated by Leon Blum, LBL, 1930, 72-74.
- Norman Walker, The Riddle of the Ass's Head, and the question of a trigram, ZAW 9 (1963), 219-231.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Alexamenos graffito. |