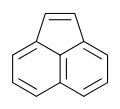
Acenaphthylene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acenaphthylene | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Tricyclo[6.3.1.04,12]dodeca-1(12),2,4,6,8,10-hexaene | |||
| Other names
Cyclopenta[de]naphthalene, Acenaphthalene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.380 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C12H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 152.20 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Yellow crystals | ||
| Density | 0.8987 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 91.8 °C (197.2 °F; 364.9 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Solubility in ethanol | very soluble | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | very soluble | ||
| Solubility in benzene | very soluble | ||
| Solubility in chloroform | soluble | ||
| Hazards | |||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R22 R36 R37 R38 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S36 S37 S39 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
acenaphthene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Acenaphthylene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The molecule resembles naphthalene with positions 1 and 8 connected by a C2H2 unit. It is a yellow solid. Unlike many polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, it has no fluorescence.
Occurrence
Acenaphthylene occurs as about 2% of coal tar. It is produced industrially by dehydrogenation of acenaphthene.[1]
Reactions
Hydrogenation gives the more saturated compound acenaphthene. It functions as a ligand for some organometallic compounds.[2]
Toxicity
The no-observed-effect-level of acenaphthylene after repeated 28-day oral administration to both male and female rats was found to be 4 mg/kg/day.[3]
References
- ↑ Karl Griesbaum, Arno Behr, Dieter Biedenkapp, Heinz-Werner Voges, Dorothea Garbe, Christian Paetz, Gerd Collin, Dieter Mayer, Hartmut Höke “Hydrocarbons” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_227
- ↑ Yukihiro Motoyama; Chikara Itonaga; Toshiki Ishida; Mikihiro Takasaki; Hideo Nagashima (1925). "Catalytic Reduction of Amides to Amines with Hydrosilanes Using a Triruthenium Cluster as the Catalyst". Organic Syntheses. 82: 188. ; Collective Volume, 11, p. 1
- ↑ Tanabe, S.; et al. (2017). "Toxicity of repeated 28-day oral administration of acenaphthylene in rats". Fundamental Toxicological Sciences. 4 (6): 247–259. doi:10.2131/fts.4.247. Retrieved November 6, 2017.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.