Abrolhos Archipelago
| Native name: Arquipélago de Abrolhos | |
|---|---|
 Sueste Island | |
 Abrolhos Archipelago  Abrolhos Archipelago | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Atlantic Ocean |
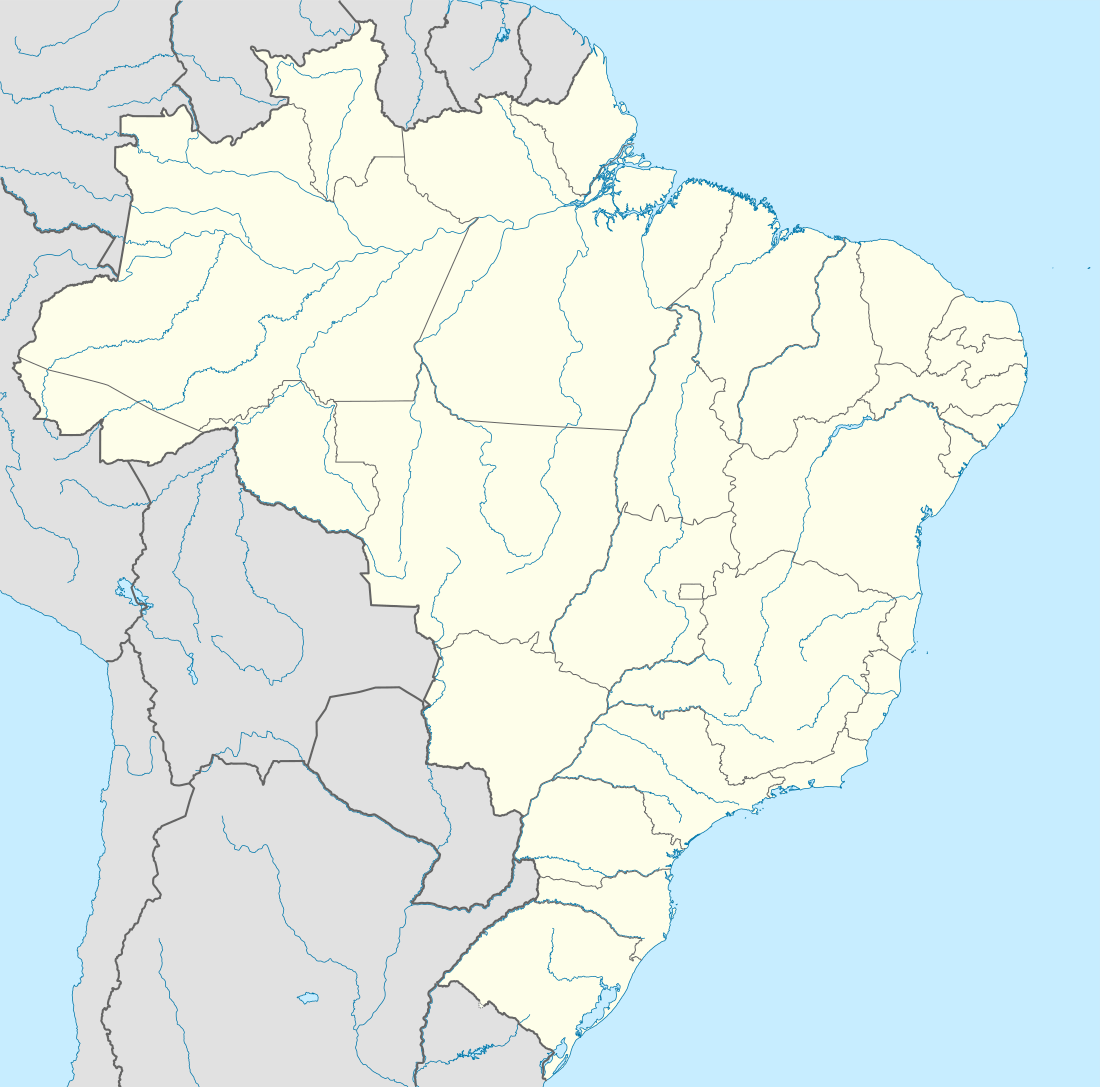
| Coordinates | 17°55′34″S 38°56′07″W / 17.92611°S 38.93528°WCoordinates: 17°55′34″S 38°56′07″W / 17.92611°S 38.93528°W |
| Archipelago | Arquipélago de Abrolhos |
| Total islands | 5 |
| Major islands | Santa Bárbara |
| Area | 50.0 km2 (19.3 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
|
Brazil | |
| Region | Southeast |
| State | Bahia |
| Administration | 1st Naval District of the Brazilian Navy |
| Demographics | |
| Population | uninhabited |
| Additional information | |
| Official website | Abrolhos website |
 Abrolhos Lighthouse | |
 Abrolhos Light Brazil | |
| Location |
Ihla de Santa Bárbara Abrolhos Archipelago Brazil |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 17°57′53″S 38°41′39″W / 17.964737°S 38.694086°W |
| Year first constructed | 1861 |
| Foundation | concrete base |
| Construction | cast iron tower |
| Tower shape | cylindrical tower with double balcony and lantern |
| Markings / pattern | white and black horizontal bands tower |
| Height | 22 feet (6.7 m) |
| Focal height | 60 metres (200 ft) |
| Current lens | two meso-radial lenses |
| Range | 51 nautical miles (94 km; 59 mi)[1] |
| Characteristic | Fl W 6s. |
| Racon |
Q |
| Admiralty number | G0306 |
| NGA number | 18200 |
| ARLHS number | BRA-001 |
| Brazil number | BR-1848[2] |
The Abrolhos Archipelago (Portuguese: Arquipélago de Abrolhos) are a group of 5 small islands with coral reefs off the southern coast of Bahia state in the northeast of Brazil, between 17º25’—18º09’ S and 38º33’—39º05’ W. Caravelas is the nearest town.[3] Their name comes from the Portuguese: abrolho ("Abre Olhos" meaning: Open your eyes),[4] a rock awash or submerged sandbank that is a danger to ships. There is a conspicuous shipwreck in the group.
History
These islets were surveyed by Baron Roussin. As part of the instructions for the second survey voyage of HMS Beagle, the Admiralty noted "the great importance of knowing the true position of the Abrolhos Banks, and the certainty that they extend much further out than the limits assigned to them by Baron Roussin", and asked Captain Robert FitzRoy to take soundings and establish the position of the reefs.[5] The work was carried out from 27 to 30 March 1832, giving Charles Darwin the opportunity to examine the wildlife and geology of the islands.[6]
Features
Islands
- Ilha de Santa Bárbara, the largest island. There is a Brazilian Navy military outpost and a lighthouse.
- Ilha Siriba, the only island open to visitors
- Ilha Redonda
- Ilha Guarita
- Ilha Sueste
Submerged banks
- Parcel dos Abrolhos, a large submerged reef extending from north to south east of the archipelago. Located 5 kilometres (3.1 miles) to the east of Santa Barbara Island, its limits are not well defined.[7]
- Parcel das Paredes, located to the northwest of the archipelago and the largest feature of the wider Abrolhos.[8]
- Sebastiao Gomes Reef, Coroa Vermelha Reef and Viçosa Reef, located to the southwest of the Parcel das Paredes.
- Timbebas Reef, located to the north near the coast.
Wildlife
The extensive reefs of the island group are an area of rich marine fauna. The uninhabited islets are a breeding ground for pelagic birds.[9]
The Abrolhos Marine National Park (Portuguese: Parque Nacional Marinho dos Abrolhos) is a Marine Park located in the Abrolhos Archipelago since 1983. It is strictly forbidden to disembark on Ilha Guarita and Ilha Suest.[10]
Gallery
View of Ilha de Santa Barbara. |
 View of Ilha Redonda in the Abrolhos Archipelago. |
 A humpback whale in the waters of the Abrolhos area. |
Southern right whales are recovering and visiting Abrolhos in small numbers.[11] |
See also
Notes
- ↑ List of Lights, Pub. 110: Greenland, The East Coasts of North and South America (Excluding Continental U.S.A. Except the East Coast of Florida) and the West Indies (PDF). List of Lights. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency.
- ↑ "Bahia". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- ↑ O Arquipélago dos Abrolhos Archived 2011-09-10 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Daehnhardt, Rainer. (1998) Segredos de História Luso-Alemã, (Portuguese/German), Publicações Quipu, p. 77
- ↑ FitzRoy 1839, pp. 24–26
- ↑ Keynes 2001, pp. 48–61.
- ↑ Enroute Prostar Sailing Directions 2004 East Coast of South America, p. 63
- ↑ Coral community structure and sedimentation at different distances from the coast of the Abrolhos Bank, Brazil, Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, ISSN 1982-436X, vol.59 no.2, São Paulo 2011
- ↑ Parque Nacional Marinho dos Abrolhos
- ↑ Brazil Govt. - Parque Nacional Marinho dos Abrolhos
- ↑ Baleia jubarte
References
- FitzRoy, Robert (1839), Narrative of the surveying voyages of His Majesty's Ships Adventure and Beagle between the years 1826 and 1836, describing their examination of the southern shores of South America, and the Beagle's circumnavigation of the globe. Proceedings of the second expedition, 1831-36, under the command of Captain Robert Fitz-Roy, R.N., II, London: Henry Colburn, retrieved 2011-12-31
- Keynes, Richard (2001), Charles Darwin's Beagle Diary, Cambridge University Press, retrieved 2011-12-31
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Abrolhos Islands. |