2016 Croydon tram derailment
 The derailed tram at Sandilands Junction | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Location within Greater London  2016 Croydon tram derailment (London Borough of Croydon) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date | 9 November 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 06:07 GMT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Close to Sandilands tram stop, Croydon, London | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 51°22′27″N 0°04′31″W / 51.374205°N 0.075410°WCoordinates: 51°22′27″N 0°04′31″W / 51.374205°N 0.075410°W | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rail line | Tramlink | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operator | FirstGroup for Tramlink | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type of incident | Derailment | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cause | Excessive speed on curve due to driver error (microsleep). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trains | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Passengers | 69 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crew | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deaths | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Injuries | 62 (19 serious) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.jpg)
On 9 November 2016, a tram operated by Tramlink, a light rail tram system serving Croydon and surrounding areas in South London, England, derailed and overturned on a sharp bend approaching a junction.[1][2] There were seven fatalities with 62 other people injured; nineteen of them sustained serious injuries. The tram was carrying 69 passengers.[3] It was the first tram incident in the United Kingdom in which passengers were killed since 1959.[1]
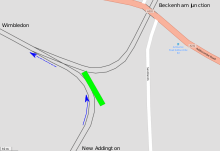
The tram was running from New Addington to Wimbledon via Croydon, and was on the approach to Sandilands tram stop soon after 6:00 a.m.[4] The second interim report into the accident indicated that although the speed limit approaching the junction was 20 km/h (12 mph), the tram had been travelling at an estimated speed of 73 kilometres per hour (45 mph).[5] Driver error was found to be the cause of the accident.[3]
Accident

The accident took place in the dark and during heavy rain at 06:07,[6] on a sharp left curve approaching the points where the route from New Addington (on which the tram was operating) converges with the line from Beckenham Junction and Elmers End.[4][7][8] The curve is located in a cutting, which comes almost immediately after the line emerges from a series of three tunnels on a 1-mile (1.6 km) straight section of track after leaving Lloyd Park tram stop. It has been described as a "sharp bend",[9] and has a 20 km/h (12 mph) speed restriction.
The tram entered the curve at a speed of approximately 73 kilometres per hour (45 mph)[5] and derailed, overturning on its right side and coming to a stand 25 metres (27 yd) beyond the point of derailment, damaging the side of the tram and ejecting several passengers through broken windows.[5] The tram involved was No. 2551, a Bombardier CR4000 constructed in 1998 by Bombardier Transportation, a two-section articulated unit with a maximum design speed of 80 km/h (50 mph).[5]
The emergency services confirmed that 51 people were injured, and initially stated that five had been killed.[9][10] The death toll later rose to seven.[11] The victims, six men and a woman, were between 19 and 63 years old.[12] Sixteen of the survivors were described as having serious or life-threatening injuries.[5][13] The final casualty figures were seven killed and 62 injured, 19 seriously. One person was uninjured.[3]
It was the deadliest tram accident in the United Kingdom since an accident at Dover in 1917 killed eleven and injured 60,[14][15] and the first in the United Kingdom in which passengers were killed since three people died in an accident in Glasgow in 1959.[1] It is also the deadliest accident on any rail network in the UK since the 2001 Great Heck rail crash.[15]
Aftermath
The injured were taken to St George's Hospital in Tooting, and to Croydon University Hospital.[9] As well as the 51 people taken to hospital, seven more made their own way to hospital for treatment. Twenty-two ambulances,[2] eight fire engines, and over 70 firefighters from the London Fire Brigade were sent to the scene.[16] Assistance was given by Croydon Council, the Red Cross, Salvation Army and railway chaplains.[17]
FirstGroup, which operates the tram service on behalf of Transport for London (TfL), said it was "shocked and saddened by what happened."[16] An extra minute was added to the two-minute Armistice Day silence at Croydon Cenotaph.[16] TfL later made an offer to cover the funeral expenses of the victims.[18]
During the night of 10–11 November, the tram was righted in preparation for removal from the accident site,[19] and it was removed on the morning of 12 November. The tram had suffered serious damage to its right side, onto which it had overturned.[20][21]
After the accident, no services operated on the line between East Croydon and Addington Village, Harrington Road or Elmers End. Partial tram services ran between East Croydon and Wimbledon, between New Addington and Addington Village, and between Beckenham Junction and Harrington Road. Full services were reinstated on 18 November.[22][23]
It was found that the speed restriction sign for the bend at Sandilands was not visible to drivers until the tram had travelled for 90 to 120 metres (98 to 131 yd) past the point where braking would need to have been initiated to reach the required speed at the sign, drivers "were expected to know this from their knowledge of the route"[5]. At Sandilands, an additional speed restriction was imposed before the curve, and chevron signs were installed to give better warning of the curve.[5] Chevron signs were also installed at three other locations on the Croydon Tramlink system.[24] Following recommendations made in the first interim report into the accident, tram systems in the United Kingdom introduced stepped speed reductions where there was a required reduction in speed of 30 kilometres per hour (19 mph) or more. This affected systems in Blackpool, Edinburgh, the West Midlands and Nottingham.[5]
In March 2017, it was reported that Tramtrack Croydon Ltd and TfL had admitted liability for the accident. Victims and survivors would not have to sue for compensation for losses caused by the accident.[25] In August 2017 TfL confirmed they would be altering Tramlink timetables to take account of reduced speed limits.[26]
In November 2017, two days of strikes by tram drivers were announced following the installation of fatigue monitoring devices. The devices shine an infrared light into the driver's face and are capable of generating an alert and vibrating the driver's chair if eye movements indicate a lack of attention. Some drivers have raised concerns about health and safety issues, and have described the device as a "spy in the cab".[27]
On 22 January 2018, the Office of Rail and Road (ORR) organised a safety summit in Manchester to discuss the findings of the Rail Accident Investigation Branch (RAIB) report on the investigation into the accident.[28]
Investigations
British Transport Police
The 42-year-old tram driver was arrested by the British Transport Police on suspicion of manslaughter.[11][29] After questioning, he was released on bail until May 2017.[29] According to The Metro, one aspect of the police investigation is whether or not the tram driver fell asleep; and The Guardian reports that some passengers said the driver had blacked out at the controls.[30][31] In November 2017, it was reported that a file was being prepared for the Crown Prosecution Service, who would decide whether or not a trial would take place.[27]
A former driver suggested, to The Times, that a blackout was a possibility, due to the erratic shift patterns that the drivers had to adhere to. He also said that the vending machine at the tram depot was stocked only with energy drinks, and that "Nobody is ever fully awake; I was always in a bit of a daze and that is because the way the shifts work doesn't allow the drivers to get a regular sleep pattern."[32] Following this, multiple sources reported on a video apparently showing a different driver struggling to stay awake at the controls.[33][34] The driver concerned was suspended pending an investigation into the matter.[35]
Victoria Derbyshire programme
In April 2017, the BBC Two programme Victoria Derbyshire reported that its own investigation into drivers falling asleep at the controls of trams on the Tramlink network revealed four such cases. Six drivers claimed that the dead-man's vigilance device fitted to the trams was not fit for purpose. Tramlink stated that the devices were "fully functional".[36]
Office of Rail and Road
The ORR opened its own investigation into the accident, concentrating on whether or not safety rules were followed.[18] They have confirmed that British trams are not fitted with any safety protection systems that would apply the brakes automatically if they are going too fast.[9][37] The ORR expects to make an announcement about its investigation early in 2018.[38]
Rail Accident Investigation Branch
The RAIB also investigatied the accident, with data from the tram's on-board event recorder being analysed.[39] The RAIB stated that initial indications suggested that the tram was travelling at a significantly higher speed than permitted.[4] Rail magazine reported that the tram's electro-magnetic track brakes had not been activated.[40] Following the accident, The Guardian reported that on 31 October there had been passenger allegations made on Facebook of a tram travelling round the curve at excessive speed. The Evening Standard reported an earlier passenger complaint describing the tram as "tipping" on the curve.[2][15] The driver of the tram involved in the incident of 31 October was not the one involved in the accident on 9 November.[41]
The interim report was released a week later on 16 November 2016. At the time of the accident it was dark and it was raining heavily. There was no evidence of any track defects, or obstructions on the track, that could have contributed to the derailment. Initial investigation did not indicate any malfunction of the tram's braking system.[6] Initial findings were that the tram, with about 60 people on board, was travelling at approximately 70 kilometres per hour (43 mph) at the time of the accident—far exceeding the speed restriction of 20 kilometres per hour (12 mph).[42] The RAIB interim report noted that "a tram approaching the Sandilands Junction area from Lloyd Park at 80 kilometres per hour (50 mph) would need to brake at its full service rate of 1.3 m/s² for approximately 180 metres before the speed restriction board in order to be travelling at 20 km/h (12.5 mph) when the board was reached." The On Tram Data Recorder (OTDR) indicated that some braking had occurred within this distance but only sufficient to reduce the tram's speed from 80 kmph (50mph) to 70 kmph (43.5mph).
A recommendation was made that a further speed limit should be introduced prior to the one for the curve at Sandilands Junction before the line reopened to traffic.[6] The recommendation was accepted and three further speed restrictions were put in place before the line reopened.[21][23] The report also found that a number of passengers with fatal or serious injuries had been ejected from the tram through broken bodyside and door windows.[6] In November 2016, Rail magazine called for the RAIB to complete its investigation and release the final report "much more rapidly than has become the norm".[40]
A second interim report was released on 20 February 2017.[5] In April 2017, it was reported that there had been three cases of speeding on the section of line which included the accident site in the period November 2016–April 2017. In one case, a tram was reported to be travelling at 64 kilometres per hour (40 mph) in a 40 kilometres per hour (25 mph) zone.[36] Within the second interim report the RAIB notes that drivers of trams approaching the curve can be expected to sight the curve and the speed restriction sign from 90 metres with full beam headlights and 60 metres with dipped beam headlights. Although the report states that the tram's braking system was not capable of slowing the tram sufficiently between the point where the speed restriction sign became visible and the point at which the speed restriction is enforced it also says "There was no sign to indicate to drivers where they should begin to apply the brake for the Sandilands curve; they were expected to know this from their knowledge of the route".[5]
In the light of the first interim report the UK government Office for Rail and Road (ORR) requested that all operators of light rail tramway systems apply a system of stepped speed restrictions where reductions in speed greater than 30km/h are required by changes in the characteristics of the track.[5]
In August 2017, the RAIB gave an update on the progress of the investigation. It stated that the Final Report was being written, with the intention to publish it before the first anniversary of the accident.[43] In September 2017, a further update was published, stating that it was hoped to publish the Final Report by the end of 2017, subject to factors outside the control of the RAIB.[44]
The final report was published on 7 December 2017. Driver error was found to be the cause of the accident. The most likely scenario being that the driver had a microsleep episode approaching the bend.[45] Fifteen recommendations were made.[3] Key findings of the RAIB investigation were that the tram's windows, which were made of toughened glass, were not strong enough to contain passengers inside the tram. All the fatalities had been ejected through the right side windows. Laminated glass would not have broken, improving the survivability of the accident. Regulations applying to trams were similar to those applying to buses. If railway regulations had applied, laminated glass would have been fitted. The tram's operators had not considered it possible for a tramcar to overturn. There had been insufficient reporting of previous incidents by drivers, who feared that they would be disciplined rather than such reports being seen as an opportunity to learn a safety lesson (a "blame culture" rather than a "just culture"). The system for dealing with complaints from passengers was not fit for purpose. The investigation also found that trams were not as safe as the ORR previously thought, having a higher accident rate than other rail transport and also buses and coaches.[38]
Transport for London
Transport for London (TfL) opened an investigation into the accident. It is expected to publish its report in early 2018. TfL stated that all recommendations from the RAIB final report will be implemented.[38]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Several killed and more than 50 injured as tram overturns in Croydon". ITV. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 Ross, Alice; Gayle, Damien; Topham, Gwyn (10 November 2016). "Croydon tram crash: police examine reports of incident in previous week". The Guardian. Retrieved 11 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 "Overturning of a tram at Sandilands junction, Croydon 9 November 2016" (PDF). RAIB. Retrieved 7 December 2017.
- 1 2 3 "Investigation into a fatal accident involving a tram near Sandilands Junction, Croydon, 9 November 2016". Rail Accident Investigation Branch.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Report IR1/2017 February 2017. Rail Accident Investigation: Interim Report 2. Fatal accident involving the derailment of a tram at Sandilands Junction, Croydon 9 November 2016" (PDF). Rail Accidents Investigation Branch. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 "Fatal accident involving the derailment of a tram at Sandilands Junction, Croydon – 9 November 2016" (PDF). Rail Accident Investigation Branch. 16 November 2016. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ↑ "BBC London Live: Latest updates". BBC London. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon Tram Derails: Several Feared Dead After Crash". LBC. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 "Croydon tram: Five dead and 50 injured after derailment". BBC London. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ Tom Powell (9 November 2016). "Croydon tram derailment: Several feared dead and dozens injured after tram overturns at Sandilands". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- 1 2 "BTP | Updated statement on tram derailment – Croydon". media.btp.police.uk. "British Transport Police". Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash: Who were the victims?". BBC News. 13 November 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash: Driver held on suspicion on manslaughter". BBC News. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ↑ Horn, J. V. (1955). "Chapter VI. The tramways during the First World War". The Story of the Dover Corporation Tramways, 1897–1936. London: The Light Railway Transport League.
- 1 2 3 Davis, Barney; Watts, Matt; Sleigh, Sophia. "Croydon tram crash: first victim named as Crystal Palace fan, 19 who was on his way to work". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Croydon tram crash: Crane to lift carriages from site". BBC. Retrieved 11 November 2016.
- ↑ Clinnick, Richard; Browne, Stefanie; Stephen, Paul (23 November 2016). "Croydon tram speeding at 70kph on 20kph curve". Rail. Peterborough: Bauer Consumer Media (814): 6–7. ISSN 0953-4563.
- 1 2 "Croydon tram crash: Funeral costs offer from Transport for London". BBC News. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ↑ Gillett, Francesca. "Croydon tram crash: Giant crane arrives as work begins to move wreckage". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 11 November 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash: Carriages being removed from site". BBC News. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- 1 2 "Croydon tram crash: Driver was 'three times over speed limit'". BBC News. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ↑ "Status Updates Tram". Transport for London. Retrieved 17 November 2016.
- 1 2 "Croydon tram line services resume". BBC News. Retrieved 18 November 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash victims 'ejected through windows'". BBC News Online. Retrieved 20 February 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash survivor's life 'now a nightmare'". BBC News Online. 15 March 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- ↑ Booth, Samantha (30 August 2017). "The timetable for Croydon trams is to change because of lower speed limits after fatal crash". Croydon Advertiser. Local World. Retrieved 31 August 2017.
- 1 2 "Croydon tram bosses install infra-red beams to shine on drivers' faces to check they are awake - drivers to strike in protest". Evening Standard. 1 November 2017. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- ↑ "ORR organises Croydon tram safety summit". Office of Rail and Road. 19 January 2018. Retrieved 22 January 2018.
- 1 2 "Croydon tram driver bailed as first victim is named". Sky News. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ↑ Morley, Nicole. "Crowdfunding page launched for victims of Croydon tram crash that killed 7". Metro. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- ↑ Siddique, Haroon; Gayle, Damien; Rawlinson, Kevin (9 November 2016). "Croydon tram driver 'blacked out' in crash that killed seven, claim passengers". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- ↑ Kolirin, Lianne (14 November 2016). "Tram drivers left 'in a daze' by erratic shifts". The Times (72067). p. 17. ISSN 0140-0460.
- ↑ "Croydon tram driver suspended after video of man 'asleep' at controls". The Guardian. 19 November 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
- ↑ "Probe into driver 'falling asleep'". London Evening Standard. 18 November 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
- ↑ "Croydon line tram driver suspended over Sun footage". BBC News. 19 November 2016. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
- 1 2 Thomas, Ed; Titheradge, Noel. "Croydon tram crash: Drivers 'fell asleep' on fatal line". BBC News Online. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- ↑ "Dozens injured after tram overturns in Croydon". Sky News. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 Matthews, Tom (8 December 2017). "Croydon tram crash: The key things we've learned from the RAIB report into the causes of the disaster". Croydon Advertiser. Local World. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- ↑ "There will be disruption 'for days' on Croydon trams after crash". Croydon Advertiser. 9 November 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- 1 2 Harris, Nigel (23 November 2016). "Croydon, HS2 and NR costs...". Rail. Peterborough: Bauer Consumer Media (814): 3. ISSN 0953-4563.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash: Bosses were warned of 'speeding trams'". BBC News. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ↑ Gwyn Topham (16 November 2016). "Croydon tram going three times speed limit when it derailed, say investigators". The Guardian. Retrieved 16 November 2016.
- ↑ "Fatal tram accident in Croydon". Rail Accident Investigation Branch. 3 August 2017. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ↑ "Fatal tram accident in Croydon". Rail Accident Investigation Branch. 25 September 2017. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- ↑ "Croydon tram crash: Report says driver 'probably dozed off'". BBC. Retrieved 7 December 2017.
External links

- Final report of the Rail Accident Investigation Branch