< Fractals < Mathematics
The doubling map
How to find the period of angle under doubling map
- visual
- numerical
- read period from denominator of decimal fraction ( reduced rational fraction m/n )
- find period/preperiod in the binary expansion ( binary sequence)
- string matching algorithms, for instance, naive or brute-force search, Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithm[1]
- discrete Fourier transform
- read it from the itinerary of angle under doubling map
Period of binary expansion of reduced rational fraction m/n is equal to the multiplicative order of 2 modulo n:
 orbit of angle 5/31 under doubling map
orbit of angle 5/31 under doubling map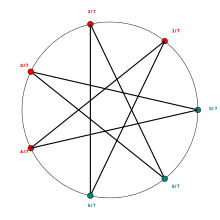 rotation with rational angle 3 over 7
rotation with rational angle 3 over 7
C version
double precision: forward and inverse doubling map
/*
doubling map
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dyadic_transformation
2*t mod 1
how to invert doubling map
Inverse of doubling map is multivalued function: 2 preimages
t/2 and (t+1)/2
to choose proper preimage one needs extra information from forward iteration = itinerary
itinerary : list of symbols
for coding the orbits of a given dynamical system
by partitioning the space X and forming an itinerary
http://www.maths.qmul.ac.uk/~sb/cf_chapter4.pdf
see also how to convert proper decimal fraction to binary fraction
commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Binary_decomposition_of_dynamic_plane_for_f0(z)_%3D_z%5E2.png
---------- git --------------------
cd existing_folder
git init
git remote add origin git@gitlab.com:adammajewski/doubling_map.git
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit"
git push -u origin master
*/
#include <stdio.h> // printf
#include <math.h> // fabs
#define iMax 8 //
int main(){
double t0 ;
double t ;
double ti; // final t after iMax iterations
double tr; //
double dt;
int itinerary[iMax]= {0};
int i;
t0 = (double) 1/7;
t = t0;
// check the input : it should be 0.0 <= t < 1.0
if (t>1.0) {printf("t is > 1.0\n"); return 1;}
if (t<0.0) {printf("t is < 0.0\n"); return 1;}
printf("forward iteration of doubling map\n");
for(i=0; i<iMax; i++){
printf("t%d = %f", i, t);
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dyadic_transformation
t = t*2.0; // doubling
if (t>1.0) {
itinerary[i]= 1;
t = t - 1.0;
printf(" wrap\n");} // modulo 1
else printf("\n");
}
printf("t%d = %f\n", i, t);
//
ti = t;
printf("\nbackward iteration of doubling map = halving map \n");
//
for(i=iMax; i>0; i--){ // reverse counting
printf("t%d = %f", i, t);
if (itinerary[i-1]==1) { // i-1 !!!
t = t + 1.0;
printf(" unwrap\n");} // modulo 1
else printf("\n");
t = t/2.0; // halving
}
printf("t%d = %f\n", i, t);
tr = t;
//
printf("\n\nresults \n");
printf("t0 = %f\n", t0);
printf("t%d = %f\n", iMax, ti);
dt = fabs(t0- tr);
printf("tr = %f\n", tr);
printf("dt = fabs(t0- tr) = %f\n", dt );
printf("\nitinerary:\n");
for(i=0; i<iMax; i++) printf("itinerary[%d] = %d \n", i, itinerary[i]);
printf("\ndecimal %f has binary expansion = 0.", t0);
for(i=0; i<iMax; i++) printf("%d", itinerary[i]);
printf("\n");
if (dt < 0.0000000001) printf("program works good !\n");
else printf("program fails !\n");
return 0;}
arbitrary precision
// gcc d.c -lgmp -Wall
#include <stdio.h>
#include <gmp.h>
// a multiple precision integer, as defined by the GMP library. The C data type for such integers is mpz_t
int print_z(mpz_t z, int base, char *s){
printf("%s= ", s);
mpz_out_str (stdout, 10, z);
printf (" for base = %d\n", base);
return 0;
}
// rop = (2*op) mod 1
// wikipedia : dyadic_transformation or doubling map
void mpq_doubling(mpq_t rop, const mpq_t op)
{
mpz_t n; // numerator
mpz_t d; // denominator
mpz_inits(n, d, NULL);
//
mpq_get_num (n, op); //
mpq_get_den (d, op);
// n = (n * 2 ) % d
mpz_mul_ui(n, n, 2);
mpz_mod( n, n, d);
// output
mpq_set_num(rop, n);
mpq_set_den(rop, d);
mpz_clears(n, d, NULL);
}
int main ()
{
int i;
//
unsigned long int e = 89; // exponent is also a period of doubling map
unsigned long int b = 2;
// arbitrary precision variables from GMP library
mpz_t n ; // numerator of q
mpz_t d ; // denominator of q
mpq_t q; // rational number q = n/d
// init and set variables
mpz_init_set_ui(n, 1);
// d = (2^e) -1
// http://fraktal.republika.pl/mset_external_ray.html
mpz_init(d);
mpz_ui_pow_ui(d, b, e) ; // d = b^e
mpz_sub_ui(d, d, 1); // d = d-1
// q = n/d
mpq_init (q); //
mpq_set_num(q,n);
mpq_set_den(q,d);
mpq_canonicalize (q); // It is the responsibility of the user to canonicalize the assigned variable before any arithmetic operations are performed on that variable.
// print
//print_z(d, 10, "d ");
//print_z(n, 10, "n ");
gmp_printf ("q = %Qd\n",q); //
//
for (i=0; i<(1+2*e) ; i++){
mpq_doubling(q, q);
gmp_printf ("q = %Qd\n",q); //
}
// clear memory
mpq_clear (q);
mpz_clears(n, d, NULL);
return 0;
}
C++ version
/*
based on :
mndcombi.cpp by Wolf Jung (C) 2010.
http://mndynamics.com/indexp.html
which is the part of Mandel 5.5
multiplatform C++ GUI program using QT
on the same licence as above
"The function is computing the preperiod and period (of n/d under doubling map)
and setting the denominator to 2^preperiod*(2^period - 1) if possible.
So 1/5 becomes 3/15 and 2/10 becomes 3/15 as well.
The period is returned as the value of the function,
n and d are changed ( Arguments passed to function by reference)
and the preperiod is returned in k." (Wolf Jung)
Question : if result is >=0 why do not use unsigneg char or unsigned int for type of result ???
*/
int normalize(unsigned long long int &n, unsigned long long int &d, int &k)
{ if (!d) return 0; // d==0 error
n %= d;
while (!(n & 1) && !(d & 1)) { n >>= 1; d >>= 1; }
int p;
unsigned long long int n0, n1 = n, d1 = d, np;
k = 0;
while (!(d1 & 1)) { k++; d1 >>= 1; if (n1 >= d1) n1 -= d1; }
n0 = n1;
for (p = 1; p <= 65 - k; p++)
{ twice(n1, d1);
if (n1 == n0) break; }
if (k + p > 64) return 0; // more then max unsigned long long int
np = 1LL;
np <<= (p - 1);
np--; np <<= 1;
np++; //2^p - 1 for p <= 64
n0 = np;
d >>= k; n1 = d;
if (n1 > n0) { n1 = n0; n0 = d; }
while (1) { d1 = n0 % n1; if (!d1) break;
n0 = n1; n1 = d1; } //gcd n1
n /= d/n1;
n *= np/n1;
d = np << k;
return p;
}
Lisp version
(defun give-period (ratio-angle)
"gives period of angle in turns (ratio) under doubling map"
(let* ((n (numerator ratio-angle))
(d (denominator ratio-angle))
(temp n)) ; temporary numerator
(loop for p from 1 to 100 do
(setq temp (mod (* temp 2) d)) ; (2 x n) modulo d = doubling)
when ( or (= temp n) (= temp 0)) return p )))
Maxima CAS version
DoublingMap(r):=
block([d,n],
n:ratnumer(r),
d:ratdenom(r),
mod(2*n,d)/d)$
/*
Tests :
GivePeriod (1/7)
3
GivePeriod (1/14)
0
GivePeriod (1/32767)
15
GivePeriod (65533/65535)
16
Gives 0 if :
* not periodic ( preperiodic )
* period >pMax
*/
GivePeriod (r):=
block([rNew, rOld, period, pMax, p],
pMax:100,
period:0,
p:1,
rNew:DoublingMap(r),
while ((p<pMax) and notequal(rNew,r)) do
(rOld:rNew,
rNew:DoublingMap(rOld),
p:p+1
),
if equal(rNew,r) then period:p,
period
);
Haskell version
Haskell version[2]
Conversion from an integer type (Int or Integer) to anything else is done by "fromIntegral". The target type is inferred automatically
-- by Claude Heiland-Allen
-- import Data.List (findIndex, groupBy)
-- type N = Integer
-- type Q = Rational
period :: Q -> N
period p =
let Just i = (p ==) `findIndex` drop 1 (iterate double p)
in fromIntegral i + 1
Real quadratic map
Complex quadratic map
- "Critically preperiodic polynomials are typically parameterized by the angle θ of the external ray landing at the critical value rather than by the critical value." MARY WILKERSON[3]
checking the period using position of parameter = periodicity checking
Finding period of the orbit
/* mndynamo.cpp by Wolf Jung (C) 2007-2015. Defines classes:
mndynamics, mndsiegel, mndcubesiegel, mndquartsiegel, mndexposiegel,
mndtrigosiegel, mndexpo, mndtrigo, mndmatesiegel, mndmating, mndsingpert,
mndherman, mndnewtonsiegel, mndnewton, mndcubicnewton, mndquarticnewton
These classes are part of Mandel 5.13, which is free software; you can
redistribute and / or modify them under the terms of the GNU General
Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
version 3, or (at your option) any later version. In short: there is
no warranty of any kind; you must redistribute the source code as well.
*/
uint mndynamics::period(double &a, double &b, int cycle) // = 0
{ //determine the period, if cycle then set a, b to periodic point.
uint j; double x, y, x0, y0; critical(a, b, x, y);
for (j = 1; j <= 1000; j++)
{ if (x*x + y*y <= bailout) f(a, b, x, y); else return 0; }
x0 = x; y0 = y;
for (j = 1; j <= 1024; j++)
{ if (x*x + y*y <= bailout) f(a, b, x, y); else return 0;
if ( (x - x0)*(x - x0) + (y - y0)*(y - y0) < 1e-16)
{ if (cycle) { a = x; b = y; }
return j;
}
}
return 10000;
}
 critical orbit with 3-period cycle
critical orbit with 3-period cycle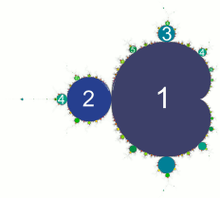 periodic components of M set
periodic components of M set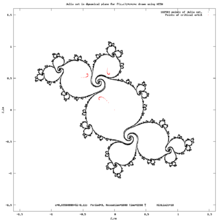 Drawing Julia set and critical orbit. Computing period
Drawing Julia set and critical orbit. Computing period Computing period for drawing Mandelbrot set
Computing period for drawing Mandelbrot set
Methods :
- direct period detection from iterations
- the spider algorithm
- "methods based on interval arithmetic when implemented properly are capable of finding all period-n cycles for considerable large n." (ZBIGNIEW GALIAS )[4]
- Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm [5]
Finding period is used to :
Period of critical orbit
Finding period of critical orbit using forward iteration of critical point :
Maxima CAS
/*
b batch file for maxima
*/
kill(all);
remvalue(all);
/* =================== functions ============ */
/*
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Fractals/Iterations_in_the_complex_plane/qpolynomials
complex quadratic polynomial
*/
f(z,c):=z*z+c;
/* iterated map */
fn(p, z, c) :=
if p=0 then z
elseif p=1 then f(z,c)
else f(fn(p-1, z, c),c);
/*
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Fractals/Mathematics/Period#Complex_quadratic_map
period of c under complex quadratic polynomial f
*/
GivePeriod(c):=block(
[z: 0.0,
k2Max:200, /* to big values couse bind stack overflow */
k1Max:100,
ER:2.0,
dMax:0.0003, /* if too low then gives smaller period then */
period:0 /* no period found = (period > k2Max) or ..... ???? */
],
/* to remove non periodic points , iterate and do not use it */
for k1:1 thru k1Max do
(z: f(z,c),
if (cabs(z)>ER) then (period : -1, /* escaping */
go(exit))
),
/* after k1Max iterations z SHOULD BE inside periodic orbit */
zOld:z,
for k2:1 thru k2Max do
( z: f(z,c),
if (cabs(z)>ER) then (period : -1, go(exit)), /* escaping */
if (cabs(zOld-z)<dMax) then (period : k2, go(exit)) /* periodic */
),
exit,
return(period)
)$
/*
Tests :
good
G(0)
G(-1.75)
G(-1.77)
G(-1.778)
G(-0.155+0.75*%i) period = 3
G(-1.7577+0.0138*%i) period = 9
G(-0.615341000000000 +0.423900000000000*%i); period = 7
G(-1.121550281113895 +0.265176187855967*%i); period = 18)
Tuning :
0 period ( when true period > k2Max
G(-1.119816337988403 +0.264371090395906*%i);
gives 0 when k2Max =100
gives 108 when dMax = 0.003
but true period = 162 ( set k2Max = 200 and dMax= 0.0003
-------------------
G(0.37496784+%i*0.21687214);
http://fraktal.republika.pl/period.html
gives 0
*/
G(c):=GivePeriod(c);
compile(all);
/* -------- input value ------ */
c : 0.25 +0.5 * %i$
/* ============== compute =============== */
p:GivePeriod(c)$
p;
c
Comparison of 2 functions for finding a period :
/*
gcc p.c -Wall -lm
time ./a.out
numerical approximation of period of limit cycle
Adam Majewski
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
long double ER2 = 4.0L;
unsigned int jMax = 1000; // iteration max = Max period
// mndynamics::period(double &a, double &b, int cycle)
// mndynamo.cpp by Wolf Jung (C) 2007-2014
// part of Mandel 5.10 which is free software; you can
// redistribute and / or modify them under the terms of the GNU General
// Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
// version 3, or (at your option) any later version. In short: there is
// no warranty of any kind; you must redistribute the source code as well.
/*
void mndlbrot::f(double a, double b, double &x, double &y) const
{ double u = x*x - y*y + a; y = 2*x*y + b; x = u; }
*/
unsigned int GivePeriodJung(long double cx, long double cy, long double ER2, unsigned int jMax, long double precision2, long double Zp[2])
{ //determine the period, then set Zp to periodic point.
// bailout = ER2 = (EscapeRadius)^2
unsigned int j;
// unsigned int jMax = 500000;
long double x=0.0L;
long double y=0.0L; // z
long double x0, y0; // z0 inside periodic orbit
long double t; // temp
//long double precision = 1e-16;
// iterate until z fall into periodic cycle ( = limit cycle)
for (j = 1; j <= jMax; j++)
{
if (x*x + y*y <= ER2)
{t = x*x - y*y + cx;
y = 2*x*y + cy;
x = t;}
else return 0; //escaping = definitely not periodic
}
// after jMax iterations z SHOULD BE inside periodic orbit
x0 = x; y0 = y; // z = z0
// find a period
for (j = 1; j <= jMax; j++)
{
if (x*x + y*y <= ER2)
{t = x*x - y*y + cx;
y = 2*x*y + cy;
x = t;}
else return 0; // escaping = definitely not periodic
if ( (x - x0)*(x - x0) + (y - y0)*(y - y0) < precision2) // periodic
{ Zp[0] = x;
Zp[1] = y;
return j; // period = j
}
}
return (2*jMax+3); // (not escaping after 2*jMax = maybe periodic but period > jMax) or
// (maybe escaping but slow dynamics, so need more iterations then 2*jMax)
}
int SameComplexValue(long double Z1x,long double Z1y,long double Z2x,long double Z2y, long double precision)
{
if (fabsl(Z1x-Z2x)<precision && fabs(Z1y-Z2y)<precision)
return 1; /* true */
else return 0; /* false */
}
/*-------------------------------*/
// this function is based on program:
// Program MANCHAOS.BAS
// http://sprott.physics.wisc.edu/chaos/manchaos.bas
// (c) 1997 by J. C. Sprott
//
unsigned int GivePeriodS(long double Cx,long double Cy, unsigned int iMax, long double precision, long double Zp[2])
{
long double Zx2, Zy2, /* Zx2=Zx*Zx; Zy2=Zy*Zy */
ZPrevieousX,ZPrevieousY,
ZNextX,ZNextY;
unsigned int i;
unsigned int period = iMax+3; // not periodic or period > iMax
/* dynamic 1D arrays for x, y of z points */
long double *OrbitX; // zx
long double *OrbitY; // zy
int iLength = iMax; // length of arrays ; array elements are numbered from 0 to iMax-1
// creates dynamic arrays and checks if it was done properly
OrbitX = malloc( iLength * sizeof(long double) );
OrbitY = malloc( iLength * sizeof(long double) );
if (OrbitX == NULL || OrbitY ==NULL)
{
printf("Could not allocate memory \n");
return 1; // error
}
Zp[0] = 0.0;
Zp[1] = 0.0;
/* starting point is critical point */
ZPrevieousX=0.0;
ZPrevieousY=0.0;
OrbitX[0] =0.0;
OrbitY[0] =0.0;
Zx2=ZPrevieousX*ZPrevieousX;
Zy2=ZPrevieousY*ZPrevieousY;
/* iterate and save points to the array */
for (i=0;i<iMax ;i++)
{
ZNextY=2*ZPrevieousX*ZPrevieousY + Cy;
ZNextX=Zx2-Zy2 +Cx;
Zx2=ZNextX*ZNextX;
Zy2=ZNextY*ZNextY;
if ((Zx2+Zy2)>ER2) return 0; /* basin of atraction to infinity */
//if (SameComplexValue(ZPrevieousX,ZPrevieousY,ZNextX,ZNextY,precision))
// return 1; /* fixed point , period =1 */
ZPrevieousX=ZNextX;
ZPrevieousY=ZNextY;
/* */
OrbitX[i] = ZNextX;
OrbitY[i] = ZNextY;
};
/* find */
for(i=iMax-2;i>0;i--)
if (SameComplexValue(OrbitX[iMax-1],OrbitY[iMax-1],OrbitX[i],OrbitY[i],precision))
{
Zp[0] = OrbitX[i];
Zp[1] = OrbitY[i];
period = iMax-i-1; // compute period
break; // the loop
}
// free memmory
free(OrbitX);
free(OrbitY);
return period ;
}
unsigned int GivePeriodReal(long double Cx,long double Cy)
{
// check
if ( -0.75L<Cx && Cx<0.25L ) return 1;
if ( -1.25L<Cx && Cx<-0.75L ) return 2;
if ( -1.368089448988708L<Cx && Cx<-1.25L ) return 4; // numerical approximation = maybe wrong
if ( -1.394040000725660L<Cx && Cx<-1.368089448988708L ) return 8; // numerical approximation = maybe wrong
return 0; // -1.36809742955000002314
}
int main()
{
// THE REAL SLICE OF THE MANDELBROT SET
long double CxMin = -1.4011551890L; // The Feigenbaum Point = the limit of the period doubling cascade of bifurcations
long double CxMax = -0.74L;
long double Cx;
long double Cy = 0.0L;
long double PixelWidth = (CxMax-CxMin)/10000.0L;
long double precisionS = PixelWidth / 100.0L;
long double precisionJ = 1e-16;
unsigned int periodS, periodJ, periodR;
long double Zp[2]; // periodic z points on dynamic plane
unsigned int iMax = 1000000; // iteration max = Max period
// text file
FILE * fp; // result is saved to text file
fp = fopen("data2p10pz.txt","w"); // create new file,give it a name and open it in binary mode
fprintf(fp," periods of attracting orbits ( c points ) on real axis of parameter plane = real slice of the Mandelbrot set \n");
fprintf(fp," from Cmin = %.20Lf to Cmax = %.20Lf \n", CxMin, CxMax);
fprintf(fp," dC = CxMax-CxMin = %.20Lf \n", CxMax- CxMin);
fprintf(fp," PixelWidth = %.20Lf \n", PixelWidth);
fprintf(fp," precisionS = %.20Lf ; precisionJ = %.20Lf\n", precisionS, sqrtl(precisionJ));
fprintf(fp," iMaxS = %u ; iMaxJ = %u\n", iMax, 2*jMax);
fprintf(fp," \n\n\n");
// go along real axis from CxMin to CxMax using linear scale
Cx = CxMin;
while (Cx<CxMax)
{
// compute
periodR = GivePeriodReal(Cx,Cy);
periodS = GivePeriodS(Cx, Cy, iMax, precisionS, Zp);
periodJ = GivePeriodJung(Cx, Cy, ER2, jMax, precisionJ, Zp);
// check and save
if (periodR>0)
{
if (periodJ==periodS && periodS==periodR ) // all periods are the same and real period is known
fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; period = %u ; \n", Cx, periodS );
else fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; period = %u ; periodS = %u ; periodJ = %u ; difference !!! \n", Cx, periodR, periodS, periodJ );
}
else // PeriodR==00
{
if (periodJ==0 && periodS==0 )
fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; period = %u ; \n", Cx, periodS );// all periods are the same and real period is known
else { if (periodS==periodJ)
fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; periodJ = periodS = %u ; \n", Cx, periodS );
else fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; periodS = %u ; periodJ = %u ; difference !!! \n", Cx, periodS, periodJ );
}
}
// info message
printf("c = %.20Lf \n",Cx);
// next c point
Cx += PixelWidth;
}
fclose(fp);
printf(" result is saved to text file \n");
return 0;
}
Non-linear scale shows bigger periods ( along real slice of Mandelbrot set ) :
/*
gcc p.c -Wall -lm
time ./a.out
numerical approximation of limit cycle's period
along real slice of Mandelbrot set
Adam Majewski
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
// part of THE REAL SLICE OF THE MANDELBROT SET where period doubling cascade is
long double CxMin = -1.4011552; // 1890L; // > The Feigenbaum Point = the limit of the period doubling cascade of bifurcations
long double CxMax = 0.26L;
long double Cx;
long double Cy = 0.0L; // constant value
long double PixelWidth ; // = (CxMax-CxMin)/10000.0L;
//long double precisionS ; //precisionS = PixelWidth / 100.0L;//= PixelWidth / 100.0L;
long double f= 4.669201609102990671853203820466L; // The Feigenbaum delta constant
long double precisionJ = 1e-20;
unsigned int periodJ, periodR;
long double Zp[2]; // periodic z points on dynamic plane
long double ER2 = 4.0L;
unsigned int jMax = 5000000; // iteration max = Max period
unsigned int iNoPeriod;
//unsigned int iMax ; //= 2*jMax; // 1000000; // iteration max = Max period
// mndynamics::period(double &a, double &b, int cycle)
// mndynamo.cpp by Wolf Jung (C) 2007-2014
// part of Mandel 5.10 which is free software; you can
// redistribute and / or modify them under the terms of the GNU General
// Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
// version 3, or (at your option) any later version. In short: there is
// no warranty of any kind; you must redistribute the source code as well.
/*
void mndlbrot::f(double a, double b, double &x, double &y) const
{ double u = x*x - y*y + a; y = 2*x*y + b; x = u; }
code with small changes
*/
unsigned int GivePeriodJung(long double cx, long double cy, long double ER2, unsigned int jMax, long double precision2, long double Zp[2])
{ //determine the period, then set Zp to periodic point.
// bailout = ER2 = (EscapeRadius)^2
unsigned int j;
// unsigned int jMax = 500000;
long double x=0.0L;
long double y=0.0L; // z
long double x0, y0; // z0 inside periodic orbit
long double t; // temp
//long double precision = 1e-16;
// iterate until z fall into periodic cycle ( = limit cycle)
for (j = 1; j <= jMax; j++)
{
if (x*x + y*y <= ER2)
{t = x*x - y*y + cx;
y = 2*x*y + cy;
x = t;}
else return 0; //escaping = definitely not periodic
}
// after jMax iterations z SHOULD BE inside periodic orbit
x0 = x; y0 = y; // z = z0
// find a period
for (j = 1; j <= jMax; j++)
{
if (x*x + y*y <= ER2)
{t = x*x - y*y + cx;
y = 2*x*y + cy;
x = t;}
else return 0; // escaping = definitely not periodic
if ( (x - x0)*(x - x0) + (y - y0)*(y - y0) < precision2) // periodic
{ Zp[0] = x;
Zp[1] = y;
return j; // period = j
}
}
return (iNoPeriod); // (not escaping after 2*jMax = maybe periodic but period > jMax) or
// (maybe escaping but slow dynamics, so need more iterations then 2*jMax)
}
// http://classes.yale.edu/Fractals/MandelSet/MandelScalings/CompDiam/CompDiam.html
unsigned int GivePeriodReal(long double Cx,long double Cy)
{
long double Cx0= 0.25L;
long double Cx1= -0.75L;
long double Cx2= -1.25L;
long double Cx3= -1.368089448988708L; // numerical approximation = maybe wrong
long double Cx4= -1.394040000725660L; // numerical approximation = maybe wrong
if ( Cx1<Cx && Cx<Cx0 ) return 1;
if ( Cx2<Cx && Cx<Cx1 ) return 2;
if ( Cx3<Cx && Cx<Cx2 ) return 4; // numerical approximation = maybe wrong
if ( Cx4<Cx && Cx<Cx3 ) return 8; // numerical approximation = maybe wrong
return 0; // -1.36809742955000002314
}
// try to have the same number of the pixels = n
// inside each hyperbolic component of Mandelbrot set along real axis
// width of components
long double GivePixelWidth(unsigned int period, unsigned int n)
{
long double w ;
unsigned int k;
switch ( period )
{ // A SCALING CONSTANT EQUAL TO UNITY IN 1D QUADRATIC MAPS M. ROMERA, G. PASTOR and F. MONTOYA
case 0 : w=(CxMax-CxMin)/n; break;
case 1 : w=1.000000000000L/n; break; // exact value
case 2 : w=0.310700264133L/n; break; // numerical approximation , maybe wrong
case 4 : w=0.070844843095L/n; break; // w(2*p) = w(p)/f ; f = Feigenbaum constant
case 8 : w=0.015397875272L/n; break;
case 16 : w=0.003307721510L/n; break;
case 32 : w=0.000708881730L/n; break;
case 64 : w=0.000151841994935L/n; break;
case 128 : w=0.000032520887170L/n; break;
case 256 : w=0.00000696502297L/n; break;
case 512 : w=0.000001491696694L/n; break;
case 1024 : w=0.000000319475846L/n; break;
case 2048 : w=0.000000068421948L/n; break;
case 4096 : w=0.000000015L/n; break;
case 8192 : w=0.000000004L/n; break;
case 16384 : w=0.000000001L/n; break;
default : if (period == 2*jMax+3) w=(CxMax-CxMin)/10.0L; // period not found or period > jMax
else { k=period/16384; w = 0.000000001L; while (k>2) { w /=f; k /=2;}; w /=n;} // feigenbaum scaling
}
return w;
}
int main()
{
PixelWidth = (CxMax-CxMin)/1000.0L;
precisionJ = PixelWidth/10000000.0L;
iNoPeriod = 2*jMax+3;
// text file
FILE * fp; // result is saved to text file
fp = fopen("data64_50ff.txt","w"); // create new file,give it a name and open it in binary mode
fprintf(fp," periods of attracting orbits ( c points ) on real axis of parameter plane = real slice of the Mandelbrot set \n");
fprintf(fp," from Cmax = %.20Lf to Cmin = %.20Lf \n", CxMax, CxMin);
fprintf(fp," dC = CxMax-CxMin = %.20Lf \n", CxMax- CxMin);
fprintf(fp," non-inear scale with varied step = PixelWidth \n");
fprintf(fp," precisionJ = %.20Lf\n", sqrtl(precisionJ));
fprintf(fp," jMax = %u\n", 2*jMax);
fprintf(fp," \n\n\n");
// go along real axis from CxMin to CxMax using linear scale
Cx = CxMax;
while (Cx>CxMin)
{
// compute
//periodR = GivePeriodReal(Cx,Cy);
periodJ = GivePeriodJung(Cx, Cy, ER2, jMax, PixelWidth/10000000.0L, Zp);
// check and save
if (periodJ == iNoPeriod)
fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; periodJ = %u ; PixelWidth = %.20LF Period not found : error !!! \n", Cx, periodJ, PixelWidth );
else fprintf(fp," c = %.20Lf ; periodJ = %u ; PixelWidth = %.20LF \n", Cx, periodJ, PixelWidth );
printf("c = %.20Lf ; period = %u \n",Cx, periodJ); // info message
// next c point
PixelWidth =GivePixelWidth( periodJ, 50);
Cx -= PixelWidth;
}
fclose(fp);
printf(" result is saved to text file \n");
return 0;
}
References
- ↑ math stackexchange question: period-of-a-finite-binary-sequence
- ↑ lavaurs' algorithm in Haskell with SVG output by Claude Heiland-Allen
- ↑ Subdivision rule constructions on critically preperiodic quadratic matings by Mary Wilkerson
- ↑ Rigorous Investigations Of Periodic Orbits In An Electronic Circuit By Means Of Interval Methods by Zbigniew Galias
- ↑ Mandelbrot set drawing by Milan
See also
This article is issued from
Wikibooks.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.