Reims
Reims (/riːmz/ REEMZ, also US: /ræ̃s/,[2] French: [ʁɛ̃s] (![]()
Reims | |
|---|---|
Subprefecture and commune | |
 Clockwise from top: southwest aerial view, Reims Cathedral, Stade Auguste-Delaune, Place Royale, Hôtel de Ville, Museum of Fine Arts, Porte de Mars | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
Location of Reims 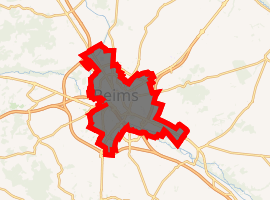
| |
 Reims 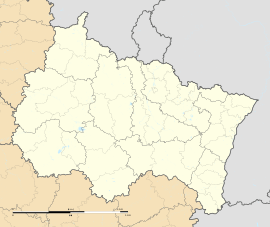 Reims | |
| Coordinates: 49°15′46″N 4°02′05″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Grand Est |
| Department | Marne |
| Arrondissement | Reims |
| Canton | Reims-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 |
| Intercommunality | CU Grand Reims |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2014–2020) | Arnaud Robinet (LR) |
| Area 1 | 46.9 km2 (18.1 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 182,460 |
| • Density | 3,900/km2 (10,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 51454 /51100 |
| Elevation | 80–135 m (262–443 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Founded by the Gauls, Reims became a major city during the period of the Roman Empire.[3] Reims later played a prominent ceremonial role in French monarchical history as the traditional site of the coronation of the kings of France. The royal anointing was performed at the Cathedral of Reims, which housed the Holy Ampulla of chrism allegedly brought by a white dove at the baptism of Frankish king Clovis I in 496. For this reason, Reims is often referred to in French as la cité des sacres ("the Coronation City").
The Cathedral, the Palace of Tau and the former Abbey of Saint-Remi have been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1991.
History

Before the Roman conquest of northern Gaul, Reims had served as the Remi tribe's capital, founded circa 80 BC. In the course of Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul (58–51 BC), the Remi allied themselves with the Romans, and by their fidelity throughout the various Gallic insurrections secured the special favour of the imperial power.[4] At its height in Roman times the city had a population in the range of 30,000–50,000 or perhaps up to 100,000.[5] Reims was first called Durocortorum[6] in Latin, which is hypothesized to derive from a Gaulish name meaning "Door of Cortoro-".[7] The city later took its name from the Remi tribe[8] (Rēmi or Rhēmi).[9] The modern French name is derived from the accusative case of the latter, Rēmos.[10]

Christianity had become established in the city by 260, at which period Saint Sixtus of Reims founded the Diocese of Reims (which would be elevated to an archdiocese around 750). The consul Jovinus, an influential supporter of the new faith, repelled the Alamanni who invaded Champagne in 336; but the Vandals captured the city in 406 and slew Bishop Nicasius;[4] and in 451 Attila the Hun put Reims to fire and sword.

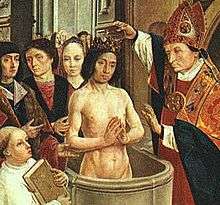
In 496—ten years after Clovis, King of the Salian Franks, won his victory at Soissons (486)—Remigius, the bishop of Reims, baptized him using the oil of the sacred phial–purportedly brought from heaven by a dove for the baptism of Clovis and subsequently preserved in the Abbey of Saint-Remi.[4] For centuries the events at the crowning of Clovis I became a symbol used by the monarchy to claim the divine right to rule.
Meetings of Pope Stephen II (752–757) with Pepin the Short, and of Pope Leo III (795–816) with Charlemagne (died 814), took place at Reims; and here Pope Stephen IV crowned Louis the Debonnaire in 816. King Louis IV gave the city and countship of Reims to the archbishop Artaldus in 940. King Louis VII (reigned 1137–1180) gave the title of duke and peer to William of Champagne, archbishop from 1176 to 1202, and the archbishops of Reims took precedence over the other ecclesiastical peers of the realm.[4]
By the 10th century Reims had become a centre of intellectual culture. Archbishop Adalberon (in office 969 to 988), seconded by the monk Gerbert (afterwards (from 999 to 1003) Pope Silvester II), founded schools which taught the classical "liberal arts". (Adalberon also played a leading role in the dynastic revolution which elevated the Capetian dynasty in the place of the Carolingians.)[4]

The archbishops held the important prerogative of the consecration of the kings of France – a privilege which they exercised (except in a few cases) from the time of Philippe II Augustus (anointed 1179, reigned 1180–1223) to that of Charles X (anointed 1825). The Palace of Tau, built between 1498 and 1509 and partly rebuilt in 1675, would later serve as the Archbishop's palace and as the residence of the kings of France on the occasion of their coronations, with royal banquets taking place in the Salle du Tau.[4]

Louis VII granted the city a communal charter in 1139. The Treaty of Troyes (1420) ceded it to the English, who had made a futile attempt to take it by siege in 1360; but French patriots expelled them on the approach of Joan of Arc, who in 1429 had Charles VII consecrated in the cathedral. Louis XI cruelly suppressed a revolt at Reims, caused in 1461 by the salt tax.
.jpg)
During the French Wars of Religion the city sided with the Catholic League (1585), but submitted to King Henri IV after the battle of Ivry (1590).[4] At about the same time, the English College had been "at Reims for some years."[11]
The city was stricken with plague in 1635, and again in 1668, followed by an epidemic of typhus in 1693–1694.[12] The construction of the Hôtel de Ville dates back to the same century.

The Place Royale was built in the 18th century. Some of the 1792 September Massacres took place in Reims.
In the invasions of the War of the Sixth Coalition in 1814, anti-Napoleonic allied armies captured and re-captured Reims. "In 1852, the Eastern Railways completed the Paris-Strasbourg main line with branch lines to Reims and Metz."[13] In 1870–1871, during the Franco-Prussian War, the victorious Germans made it the seat of a governor-general and impoverished it with heavy requisitions.[4] In 1874 the construction of a chain of detached forts started in the vicinity, the French Army having selected Reims as one of the chief defences of the northern approaches to Paris.[lower-alpha 1] In the meantime, British inventor and manufacturer Isaac Holden had opened plants at Reims and Croix, which "by the 1870s [...] were producing almost 12 million kilograms of combed wool a year [...] and accounted for 27 percent of all the wool consumed by French industry."[14]

On 30 October 1908, Henri Farman made the first cross-country flight from Châlons to Reims.[15] In August 1909 Reims hosted the first international aviation meet, the Grande Semaine d'Aviation de la Champagne. Major aviation personages such as Glenn Curtiss, Louis Blériot and Louis Paulhan participated.

Hostilities in World War I greatly damaged the city. German bombardment and a subsequent fire in 1914 did severe damage to the cathedral. The ruined cathedral became one of the central images of anti-German propaganda produced in France during the war, which presented it, along with the ruins of the Ypres Cloth Hall and the University Library in Louvain, as evidence that German aggression targeted cultural landmarks of European civilization.
_-_German_officers_sign_unconditional_surrender_in_Reims%2C_France._(Bottom)_-_Allied_force_leaders_at_the_signing._-_NARA_-_195337.jpg)
From the end of World War I to the present day an international effort to restore the cathedral from the ruins has continued. The Palace of Tau, Church of Saint-Jacques and the Abbey of Saint-Remi also were protected and restored. The collection of preserved buildings and Roman ruins remains monumentally impressive.
During World War II the city suffered additional damage. On the morning of 7 May 1945, at 2:41, General Eisenhower and the Allies received the unconditional surrender of the German Wehrmacht in Reims. General Alfred Jodl, German Chief-of-Staff, signed the surrender at the Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF) as the representative for German President Karl Dönitz.
The British statesman Leslie Hore-Belisha died of a cerebral haemorrhage while making a speech at the Hôtel de Ville in February 1957.
Climate
Reims has an oceanic climate (Köppen Cfb), influenced by its inland position. This renders that although the maritime influence moderates averages, it nevertheless is prone to hot and cold extremes in certain instances. Reims has a relatively gloomy climate due to the said maritime influence and the dominance of low-pressure systems for much of the year. In spite of this, the amount of precipitation is fairly limited.
| Climate data for Reims (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.6 (61.9) |
21.6 (70.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
29.4 (84.9) |
32.4 (90.3) |
38.3 (100.9) |
41.1 (106.0) |
39.3 (102.7) |
35.5 (95.9) |
27.5 (81.5) |
21.0 (69.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
41.1 (106.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5.8 (42.4) |
7.1 (44.8) |
11.3 (52.3) |
14.7 (58.5) |
18.8 (65.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
24.7 (76.5) |
24.3 (75.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
15.6 (60.1) |
9.7 (49.5) |
6.3 (43.3) |
15.1 (59.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.0 (37.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7.0 (44.6) |
9.5 (49.1) |
13.5 (56.3) |
16.4 (61.5) |
18.8 (65.8) |
18.5 (65.3) |
15.1 (59.2) |
11.4 (52.5) |
6.6 (43.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
10.6 (51.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.1 (32.2) |
0.1 (32.2) |
2.6 (36.7) |
4.2 (39.6) |
8.1 (46.6) |
10.8 (51.4) |
12.9 (55.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
9.8 (49.6) |
7.2 (45.0) |
3.4 (38.1) |
1.1 (34.0) |
6.1 (43.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.3 (−8.1) |
−21.0 (−5.8) |
−12.8 (9.0) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
1.2 (34.2) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−8.6 (16.5) |
−11.5 (11.3) |
−19.6 (−3.3) |
−22.3 (−8.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 46.4 (1.83) |
41.2 (1.62) |
51.0 (2.01) |
47.6 (1.87) |
61.8 (2.43) |
56.8 (2.24) |
59.0 (2.32) |
58.7 (2.31) |
48.5 (1.91) |
52.4 (2.06) |
47.6 (1.87) |
56.2 (2.21) |
627.2 (24.69) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 10.3 | 9.4 | 10.9 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 9.5 | 8.1 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 9.0 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 114.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 58.2 | 83.9 | 127.9 | 173.7 | 202.1 | 213.6 | 233.0 | 217.7 | 162.3 | 112.6 | 68.1 | 46.9 | 1,700 |
| Source: Météo Climat[16][17] | |||||||||||||
Administration
Reims functions as a subprefecture of the department of Marne,[4] in the administrative region of Grand Est. Although Reims is by far the largest commune in its department, Châlons-en-Champagne is the prefecture.
Economy
Rue de Vesle is the main commercial street (continued under other names), traversing the city from southwest to northeast through the Place Royale.[4]
Cityscape
Architecture

Reims Cathedral is an example of French Gothic architecture.

The Basilica of Saint-Remi, founded in the 11th century "over the chapel of St. Christophe where St. Remi was buried",[18] is "the largest Romanesque church in northern France, though with later additions."[18]
The Church of Saint-Jacques dates from the 13th to the 16th centuries. A few blocks from the cathedral, it stands as of 2009 in a neighbourhood of shopping and restaurants. The churches of Saint-Maurice (partly rebuilt in 1867), Saint-André,[4] and Saint-Thomas (erected from 1847 to 1853, under the patronage of Cardinal Gousset, now buried within its walls[4]) also draw tourists.
The Protestant Church of Reims, built in 1921–1923 over designs by Charles Letrosne, is an example of flamboyant neo-Gothic architecture.
The Hôtel de Ville, erected in the 17th century and enlarged in the 19th, features a pediment with an equestrian statue of Louis XIII (reigned 1610 to 1643).[4]
Narcisse Brunette was the architect of the city for nearly 50 years in the 19th century. He designed the Reims Manège and Circus, which "combines stone and brick in a fairly sober classical composition."[19]
Examples of Art Deco in Reims include the Carnegie library.
The Foujita Chapel, built in 1965–1966 over designs and with frescos by Japanese–French artist Tsuguharu Foujita, has been listed as a monument historique since 1992.[20]
Culture
Museums
The Palace of Tau contains such exhibits as statues formerly displayed by the cathedral, treasures of the cathedral from past centuries, and royal attire from coronations of French kings.

The Musée Saint-Remi, formerly the Abbey of Saint-Remi, contains tapestries from the 16th century donated by the archbishop Robert de Lenoncourt (uncle of the cardinal of the same name), marble capitals from the fourth century AD, furniture, jewellery, pottery, weapons and glasswork from the sixth to eighth centuries, medieval sculpture, the façade of the 13th-century musicians' House, remnants from an earlier abbey building, and also exhibits of Gallo-Roman arts and crafts and a room of pottery, jewellery and weapons from Gallic civilization, as well as an exhibit of items from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic periods. Another section of the museum features a permanent military exhibition.
The Museum of Fine Arts is housed in the former Abbey of Saint-Denis. The former Collège des Jésuites has also become a museum.
The Museum of the Surrender is the building in which on 7 May 1945, General Eisenhower and the Allies received the unconditional surrender of the German Wehrmacht.
Theaters
Venues include the Reims Opera House, built in 1873 and renovated in 1931–1932, and the Reims Manège and Circus, dating from 1865 and 1867.
The Comédie de Reims was inaugurated in 1966.
Libraries
Libraries in Reims include a Carnegie library which was built in the 1920s.
Festivals and events
Every year in June, the Fêtes Johanniques commemorate the entrance of Joan of Arc into Reims in 1429 and the coronation of Charles VII of France in the cathedral.
A Christmas market is held on the parvis of Reims Cathedral (Place du Cardinal-Luçon).
Wine and food

Restaurants and bars are concentrated around Place Drouet d'Erlon in the city centre.
Reims, along with Épernay and Ay, functions as one of the centres of champagne production. Many of the largest champagne-producing houses, known as les grandes marques, have their headquarters in Reims, and most open for tasting and tours. Champagne ages in the many caves and tunnels under Reims, which form a sort of maze below the city. Carved from chalk, some of these passages date back to Roman times.
The biscuit rose de Reims is a biscuit frequently associated with Champagne wine.[21] Reims was long renown for its pain d'épices and nonnette.[22]
Sports

Between 1925 and 1969 Reims hosted the Grand Prix de la Marne automobile race at the circuit of Reims-Gueux. The French Grand Prix took place here 14 times between 1938 and 1966.
As of 2016 the football club Stade Reims, based in the city, competed in the Ligue 1, the highest tier of French football. Stade Reims became the outstanding team of France in the 1950s and early 1960s and reached the final of the European Cup of Champions twice in that era.
In October 2018, the city hosted the second Teqball World Cup.
The city has hosted the Reims Marathon since 1984.
Infrastructure
Transport
Reims is served by two main railway stations: Gare de Reims in the city centre, the hub for regional transport, and the new Gare de Champagne-Ardenne TGV 5 kilometres (3 miles) southwest of the city with high-speed rail connections to Paris, Metz, Nancy and Strasbourg. The motorways A4 (Paris-Strasbourg), A26 (Calais-Langres) and A34 intersect near Reims.
Public transport within the city consists of buses and a tramway, the latter opened in 2011.
The Canal de l'Aisne à la Marne is a waterway.
Parks and gardens
Among the parks and gardens of Reims are the Parc de Champagne, where a Monument to the Heroes of the Black Army is located, and the Promenades.
Higher education
The URCA (Université de Reims Champagne-Ardenne) was founded in 1548. This multidisciplinary university develops innovative, fundamental, and applied research. It provides more than 18 000 students in Reims (22 000 in Champagne-Ardenne) with a wide initial undergraduate studies program which corresponds to society's needs in all domains of the knowledge. The university also accompanies independent or company-backed students in continuing professional development training. The Institut d'Etudes politiques de Paris, the leading French university in social and political sciences, also known as Sciences Po, opened a new campus in the Collège des Jésuites de Reims in 2010. It hosts both the Europe-Africa and Europe-America Program[23] with more than 1500 students in the respective programs. In 2012 the first Reims Model United Nations was launched, which gathered 200 international students from all the Sciences Po campuses. Daniel Rondeau, the ambassador of France to UNESCO and a French writer, is the patron of the event. NEOMA Business School (former Reims Management School) is also one of the main schools in Reims.
Notable residents
Those born in Reims include:
- Adolphe d'Archiac (1802–1868), geologist and paleontologist
- Jean Baudrillard (1929–2007), cultural theorist and philosopher
- Nicolas Bergier (1567-1623), scholar of Roman roads
- Roger Caillois (1913–1978), intellectual
- Jean-Baptiste Colbert (1619–1683), French minister of finance from 1665 to 1683 during the reign of King Louis XIV
- Eugène Courmeaux (1817–1902), librarian of Reims, fervent republican
- Jean Del Val (1891-1975), actor
- Jean-Baptiste Drouet, Count d'Erlon (1765–1844), marshal of France and a soldier in Napoleon's army
- Paul Fort (1872–1960), poet
- Nicolas Eugène Géruzez (1799–1865), critic
- Pauline Ferrand-Prévot (born 1992), world champion cyclist
- Nicolas de Grigny (1672–1703), organist and composer
- Maurice Halbwachs (1877–1945), philosopher and sociologist
- Jean Lévesque de Burigny (1692-1785), historian
- Marie-Claire Jamet (born 1933), classical harpist
- Guillaume de Machaut (1300–1377), composer and poet (Machaut was most likely born in Reims or nearby, and spent most of his adult life there)[24]
- Henri Marteau (1874–1934), violinist and composer
- Merolilan of Rheims, Irish cleric
- Olivier Métra (1830–1889), composer, conductor
- Maurice Pézard (1876–1923), archaeologist and assyriologist
- Robert Pires (born 1973), World Cup winner, footballer for Arsenal and for Villarreal CF
- Patrick Poivre d'Arvor (born 1947), television journalist and writer
- Jean-Baptiste de la Salle (1651–1719), Catholic saint, teacher and educational reformer
- Jules de Saint-Pol (1810-1855), general
- Émile Senart (1847–1928), indologist
- Adeline Wuillème (born 8 December 1975), foil fencer
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Reims is twinned with:
|
See also
- Archbishop of Reims
- Battle of Reims
- Biscuit rose de Reims
- Champagne (province)
- Champagne
- Champagne (wine region)
- Champagne Riots
- French wine
- Reims Aviation (aircraft-maker)
Notes
- Atop the ridge of St Thierry stands a fort of the same name, which with the neighbouring work of Chenay closes the west side of the place. To the north the hill of Brimont has three works guarding the Laon railway and the Aisne canal. Farther east, on the old Roman road, stands the Fort de Fresnes. Due east, the hills of Arnay are crowned with five large and important works which cover the approaches from the upper Aisne. Fort de la Pompelle, which hosts a World War I museum featuring a rich collection of German uniforms, and Montbré close the southeast side, and the Falaise hills on the southwest are open and unguarded. The perimeter of the defences measures just under 22 miles, and the forts are at a mean distance of 6 miles (10 km) from the centre of the city.[4]
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "Reims". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Retrieved 1 October 2019.
- "Reims". Nouveau petit Larousse. 1971. p. 1638.
-

- de Planhol, X.; Claval, P. (1994). An Historical Geography of France. Cambridge University Press. p. 47. ISBN 9780521322089. Retrieved 10 October 2014.
- Félix Gaffiot (1934). Dictionnaire latin-français. p. 566.
- Jean-Paul Savignac. Dictionnaire Français-Gaulois. La Différence. p. 274.
- Auguste Longnon. Les noms de lieu de la France (in French). 1. p. 103.
- Félix Gaffiot (1934). Dictionnaire latin-français. p. 1339.
- Auguste Longnon. Les noms de lieu de la France (in French). 1. p. 98, 103.
- George Henry Tavard (1978). The Seventeenth-Century Tradition: A Study in Recusant Thought.
- R., J.-M. (2000). "Benoit R. — Vivre et mourir à Reims au Grand Siècle (1580-1720) [compte-rendu]". Population (in French): 405–406.
- Malcolm Fletcher (1990). Railways:The Pioneer Years. p. 46.
- Michael Stephen Smith (2006). The Emergence of Modern Business Enterprise in France, 1800-1930. Harvard University Press. p. 149.
- Scientific American. 21 November 1908. p. cover. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Climate normals for France 1981–2010" (in French). Météo Climat. Retrieved 16 June 2019.
- "Extreme values for Reims" (in French). Météo Climat. Retrieved 16 June 2019.
- The National Geographic Traveler: France.
- Lemoine, Bertrand; Bonfante-Warren, Alexandra (1998). Architecture in France, 1800–1900. p. 92.
- "French Culture Ministry: listing of the Foujita chapel". culture.gouv.fr. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- Clemente, Maribeth. The Riches of France: A Shopping and Touring Guide to the French Provinces. St. Martin's Press.
- Encyclopédie Méthodique: Arts et Métiers mécaniques, volume 5 (1788), p. 462.
- "Welcome | Sciences Po - College Universitaire de Reims - Campus Euro-Américain". college.sciences-po.fr. Retrieved 10 October 2014.
- Oxford Music Online
- "British towns twinned with French towns [via WaybackMachine.com]". Archant Community Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 5 July 2013. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
- Canterbury City Council – Twinning contacts. Retrieved on 14 October 2009. Canterbury.gov.uk (1 March 2011). Retrieved on 25 August 2011.
- Calderdale Council (2013). "Aachen: Twin towns: Calderdale Council". calderdale.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 28 September 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2013.
- en-db (2013). "Aachen, Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany – City, Town and Village of the world". en.db-city.com. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
Bibliography
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Reims. |
- Official website (in French)
- Tourist office website – Official site for L'Office de Tourisme de Reims, (in English and French)
- Sciences Po Paris – Euro-American campus of Reims
- Reims Model United Nations
- Joan of Arc and The Coronation Of Charles VII in Reims
- Joan of Arc's first letter to Reims — translation by Allen Williamson of the letter dictated by Joan of Arc to the city of Reims on 5 August 1429.
- Joan of Arc's second letter to Reims — letter dictated by Joan of Arc to the city of Reims on 16 March 1430, translated by Allen Williamson.