Oryza sativa
Oryza sativa, commonly known as Asian rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as rice. Oryza sativa is a grass with a genome consisting of 430Mb across 12 chromosomes. It is renowned for being easy to genetically modify, and is a model organism for cereal biology.
| Oryza sativa | |
|---|---|
_by_Augustus_Binu.jpg) | |
| Mature seed heads | |
 | |
| Inflorescence | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Oryza |
| Species: | O. sativa |
| Binomial name | |
| Oryza sativa | |
Classification
Oryza sativa contains two major subspecies: the sticky, short-grained japonica or sinica variety, and the nonsticky, long-grained indica rice variety. Japonica varieties are usually cultivated in dry fields (it is cultivated mainly submerged in Japan), in temperate East Asia, upland areas of Southeast Asia, and high elevations in South Asia, while indica varieties are mainly lowland rices, grown mostly submerged, throughout tropical Asia. Rice occurs in a variety of colors, including white, brown, black, purple, and red rices.[1] [2] Black rice (also known as purple rice) is a range of rice types, some of which are glutinous rice. Varieties include Indonesian black rice and Thai jasmine black rice.
A third subspecies, which is broad-grained and thrives under tropical conditions, was identified based on morphology and initially called javanica, but is now known as tropical japonica. Examples of this variety include the medium-grain 'Tinawon' and 'Unoy' cultivars, which are grown in the high-elevation rice terraces of the Cordillera Mountains of northern Luzon, Philippines.[3]
Glaszmann (1987) used isozymes to sort O. sativa into six groups: japonica, aromatic, indica, aus, rayada, and ashina.[4]
Garris et al. (2004) used simple sequence repeats to sort O. sativa into five groups: temperate japonica, tropical japonica and aromatic comprise the japonica varieties, while indica and aus comprise the indica varieties.[5]
Nomenclature and taxonomy
Rice has been cultivated since ancient times and oryza is a classical Latin word for rice. Sativa means "cultivated".
Gallery
 Water buffalo being used to plough rice fields in Java
Water buffalo being used to plough rice fields in Java Jumli Marshi, brown rice from Nepal
Jumli Marshi, brown rice from Nepal Traditional medicinal rice of Niyamgiri Hills, India
Traditional medicinal rice of Niyamgiri Hills, India Medicinal rice of Chhattisgarh used as immune booster
Medicinal rice of Chhattisgarh used as immune booster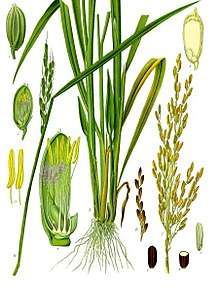 O. sativa
O. sativa Rice stem cross section magnified 400 times
Rice stem cross section magnified 400 times
See also
- Black rice
- International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants
- Japonica rice
- Maratelli rice
- Oryza glaberrima (African rice)
- Traceability of genetically modified organisms
- Domesticated plants and animals of Austronesia
References
- Oka (1988)
- Mohammadi Shad, Z; Atungulu, G. (March 2019). "Post-harvest kernel discoloration and fungi activity in long-grain hybrid, pureline and medium-grain rice cultivars as influenced by storage environment and antifungal treatment". Journal of stored products research. 81: 91–99. doi:10.1016/j.jspr.2019.02.002.
- CECAP, PhilRice and IIRR. 2000. "Highland Rice Production in the Philippine Cordillera."
- Glaszmann, J. C. (May 1987). "Isozymes and classification of Asian rice varieties". Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 74 (1): 21–30. doi:10.1007/BF00290078. PMID 24241451.
- Garris; Tai, TH; Coburn, J; Kresovich, S; McCouch, S; et al. (2004). "Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L." Genetics. 169 (3): 1631–8. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.035642. PMC 1449546. PMID 15654106.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to Oryza sativa |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oryza sativa. |
