Nitrogen oxide
Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
- NO
x (Pron. "knocks"), = NO + the free radical NO2, defined as such due to the rapid gas-phase inter-conversion between NO and NO2. NO2 dimerises to liquid N2O4 under pressure. - NOy = the sum of all oxidized odd-Nitrogen species (e.g. NOx + HNO3 + HONO + etc.)
- NOz = NOy - NOx
- Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrogen(IV) oxide
- Nitrous oxide (N2O), nitrogen(−I,III) oxide
- Nitrosylazide (N4O), nitrogen(−I,0,I,II) oxide
- Oxatetrazole (N4O)
- Dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3), nitrogen(II,IV) oxide
- Dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), nitrogen(IV) oxide
- Dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5), nitrogen(V) oxide
- Nitrate radical (NO3),nitrogen(VI) oxide
- Trinitramide (N(NO2)3 or N4O6), nitrogen(0,IV) oxides
Anions
- Dinitramide (N(NO2)3−)
- Nitrite (NO−
2) - Nitrate (NO−
3) - Trioxodinitrate (N2O32-)
- Peroxonitrite (ONO−
2) - Hyponitrite (N2O22-)
- Nitroxylate (NO−)
Cations
- Nitronium (NO+
2) - Nitrosonium (NO+
)
Atmospheric sciences
In atmospheric chemistry,
- NO
x (or NOx) refers to the sum of NO and NO2.[1][2] - NO
y (or NOy) = the sum of all oxidised atmospheric odd-nitrogen. - NO
z (or NOz) = NOy - NOx
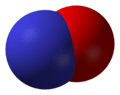
Nitric oxide, NO 
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 
Nitrous oxide, N2O 
Dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3 
Dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4 
Dinitrogen pentoxide, N2O5 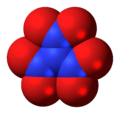
Trinitramide, N4O6
See also
- Nitrogen oxide sensor
- Sulfur nitrides, which are valence isoelectronic with nitrogen oxides
References
- United States Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7602
- Seinfeld, John H.; Pandis, Spyros N. (1997), Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-17816-0
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative
Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.