Na+/K+-ATPase
Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase (sodium–potassium adenosine triphosphatase, also known as the Na⁺/K⁺ pump or sodium–potassium pump) is an enzyme (an electrogenic transmembrane ATPase) found in the membrane of all animal cells. It performs several functions in cell physiology.
| Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase pump | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
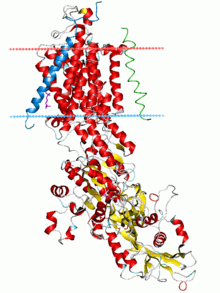 Sodium–potassium pump, E2-Pi state. Calculated hydrocarbon boundaries of the lipid bilayer are shown as blue (intracellular) and red (extracellular) planes | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 7.2.2.13 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Na+
/K+
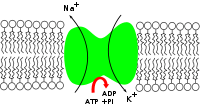
-ATPase enzyme is active (i.e. it uses energy from ATP). For every ATP molecule that the pump uses, three sodium ions are exported and two potassium ions are imported; there is hence a net export of a single positive charge per pump cycle.
The sodium–potassium pump was discovered in 1957 by the Danish scientist Jens Christian Skou, who was awarded a Nobel Prize for his work in 1997. Its discovery marked an important step forward in the understanding of how ions get into and out of cells, and it has particular significance for excitable cells such as nerve cells, which depend on this pump to respond to stimuli and transmit impulses.
All mammals have four different sodium pump sub-types, or isoforms. Each has unique properties and tissue expression patterns.[1]
Function
The Na+
/K+
-ATPase helps maintain resting potential, affects transport, and regulates cellular volume.[2] It also functions as a signal transducer/integrator to regulate the MAPK pathway, ROS, as well as intracellular calcium. In fact, all cells expend a large fraction of the ATP they produce (typically 30% and up to 70% in
nerve cells) to maintain their required cytosolic Na and K
concentrations.[3]
For neurons, the Na+
/K+
-ATPase can be responsible for up to 3/4 of the cell's energy expenditure.[4] In many types of tissue, ATP consumption by the Na+
/K+
-ATPases have been related to glycolysis. This was first discovered in red blood cells (Schrier, 1966), but has later been evidenced in renal cells,[5] smooth muscles surrounding the blood vessels,[6] and cardiac purkinje cells.[7] Recently, glycolysis has also been shown to be of particular importance for Na+
/K+
-ATPases in skeletal muscles, where inhibition of glycogen breakdown (a substrate for glycolysis) leads to reduced Na+
/K+
-ATPase activity and lower force production.[8][9][10]
Resting potential
/K+
-ATPase, as well as effects of diffusion of the involved ions maintain the resting potential across the membranes.
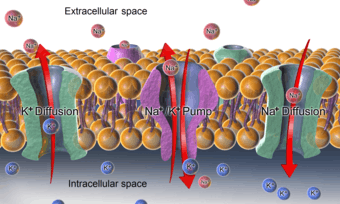
In order to maintain the cell membrane potential, cells keep a low concentration of sodium ions and high levels of potassium ions within the cell (intracellular). The sodium–potassium pump mechanism moves 3 sodium ions out and moves 2 potassium ions in, thus, in total, removing one positive charge carrier from the intracellular space (please see Mechanism for details). In addition, there is a short-circuit channel (i.e. a highly K-permeable ion channel) for potassium in the membrane, thus the voltage across the plasma membrane is close to the Nernst potential of potassium.
Reversal potential
Even if both K+ and Na+ ions have the same charge, they can still have very different equilibrium potentials for both outside and/or inside concentrations. The sodium-potassium pump moves toward an equilibrium state with the relative concentrations of Na+ and K+ for both inside and outside of cell. For instance, the concentration of K+ in cytosol is 100mM, whereas the concentration of Na+ is 10mM. On the other hand, in extracellular space, the concentration of K+ is 5mM, whereas the concentration of Na+ is 150mM.
Transport
Export of sodium from the cell provides the driving force for several secondary active transporters membrane transport proteins, which import glucose, amino acids, and other nutrients into the cell by use of the sodium gradient.
Another important task of the Na+
-K+
pump is to provide a Na+
gradient that is used by certain carrier processes. In the gut, for example, sodium is transported out of the reabsorbing cell on the blood (interstitial fluid) side via the Na+
-K+
pump, whereas, on the reabsorbing (lumenal) side, the Na+
-glucose symporter uses the created Na+
gradient as a source of energy to import both Na+
and glucose, which is far more efficient than simple diffusion. Similar processes are located in the renal tubular system.
Controlling cell volume
Failure of the Na+
-K+
pumps can result in swelling of the cell. A cell's osmolarity is the sum of the concentrations of the various ion species and many proteins and other organic compounds inside the cell. When this is higher than the osmolarity outside of the cell, water flows into the cell through osmosis. This can cause the cell to swell up and lyse. The Na+
-K+
pump helps to maintain the right concentrations of ions.
Furthermore, when the cell begins to swell, this automatically activates the Na+
-K+
pump because it changes the internal concentrations of Na+
and K+
to which the pump is sensitive.[11]
Functioning as signal transducer
Within the last decade, many independent labs have demonstrated that, in addition to the classical ion transporting, this membrane protein can also relay extracellular ouabain-binding signalling into the cell through regulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation. The downstream signals through ouabain-triggered protein phosphorylation events include activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal cascades, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, as well as activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and inositol triphosphate (IP3) receptor (IP3R) in different intracellular compartments.[12]
Protein-protein interactions play a very important role in Na+
-K+
pump-mediated signal transduction. For example, Na+
-K+
pump interacts directly with Src, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, to form a signaling receptor complex.[13] Src kinase is inhibited by Na+
-K+
pump, while, upon ouabain binding, the Src kinase domain will be released and then activated. Based on this scenario, NaKtide, a peptide Src inhibitor derived from Na+
-K+
pump, was developed as a functional ouabain-Na+
-K+
pump-mediated signal transduction.[14] Na+
-K+
pump also interacts with ankyrin, IP3R, PI3K, PLC-gamma and cofilin.[15]
Controlling neuron activity states
The Na+
/K+
pump has been shown to control and set the intrinsic activity mode of cerebellar Purkinje neurons,[16] accessory olfactory bulb mitral cells[17] and probably other neuron types.[18] This suggests that the pump might not simply be a homeostatic, "housekeeping" molecule for ionic gradients, but could be a computation element in the cerebellum and the brain.[19] Indeed, a mutation in the Na+
–K+
pump causes rapid onset dystonia-parkinsonism, which has symptoms to indicate that it is a pathology of cerebellar computation.[20] Furthermore, an ouabain block of Na+
–K+
pumps in the cerebellum of a live mouse results in it displaying ataxia and dystonia.[21] Alcohol inhibits sodium–potassium pumps in the cerebellum and this is likely how it corrupts cerebellar computation and body coordination.[22][23] The distribution of the Na+
–K+
pump on myelinated axons, in human brain, was demonstrated to be along the internodal axolemma, and not within the nodal axolemma as previously thought.[24]
Mechanism
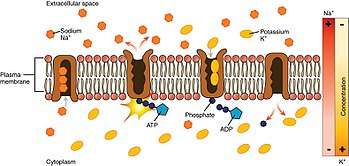
- The pump, after binding ATP, binds 3 intracellular Na+
ions.[2] - ATP is hydrolyzed, leading to phosphorylation of the pump at a highly conserved aspartate residue and subsequent release of ADP.
- A conformational change in the pump exposes the Na+
ions to the outside. The phosphorylated form of the pump has a low affinity for Na+
ions, so they are released. - The pump binds 2 extracellular K+
ions. This causes the dephosphorylation of the pump, reverting it to its previous conformational state, transporting the K+
ions into the cell. - The unphosphorylated form of the pump has a higher affinity for Na+
ions than K+
ions, so the two bound K+
ions are released. ATP binds, and the process starts again.
Regulation
Endogenous
The Na+
/K+
-ATPase is upregulated by cAMP.[25] Thus, substances causing an increase in cAMP upregulate the Na+
/K+
-ATPase. These include the ligands of the Gs-coupled GPCRs. In contrast, substances causing a decrease in cAMP downregulate the Na+
/K+
-ATPase. These include the ligands of the Gi-coupled GPCRs.
Note: Early studies indicated the opposite effect, but these were later found to be inaccurate due to additional complicating factors.
Exogenous
The Na+
-K+
-ATPase can be pharmacologically modified by administrating drugs exogenously.
For instance, Na+
-K+
-ATPase found in the membrane of heart cells is an important target of cardiac glycosides (for example digoxin and ouabain), inotropic drugs used to improve heart performance by increasing its force of contraction.
Muscle contraction is dependent on a 100- to 10,000-times-higher-than-resting intracellular Ca2+
concentration, which is caused by Ca2+
release from the muscle cells' sarcoplasmic reticulum. Immediately after muscle contraction, intracellular Ca2+
is quickly returned to its normal concentration by a carrier enzyme in the plasma membrane, and a calcium pump in sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing the muscle to relax.
According to the Blaustein-hypothesis,[26] this carrier enzyme (Na+
/Ca2+
exchanger, NCX) uses the Na gradient generated by the Na+
-K+
pump to remove Ca2+
from the intracellular space, hence slowing down the Na+
-K+
pump results in a permanently elevated Ca2+
level in the muscle, which may be the mechanism of the long-term inotropic effect of cardiac glycosides such as digoxin. The problem with this hypothesis is that at pharmacological concentrations of digitalis, less than 5% of Na/K-ATPase molecules—specifically the α2 isoform in heart and arterial smooth muscle (Kd = 32 nM) -- are inhibited, not enough to affect the intracellular concentration of Na+
. However, apart from the population of Na/K-ATPase in the plasma membrane—responsible for ion transport --, there is another population in the caveolae which acts as digitalis receptor and stimulates the EGF receptor.[27][28][29][30]
Pharmacologic regulation
In certain conditions such as in the case of cardiac disease, the Na+/K+-ATPase may need to be inhibited via pharmacological means. A commonly used inhibitor used in the treatment of cardiac disease would be Digoxin which essentially binds "to the extracellular part of enzyme i.e. that binds potassium, when it is in a phosphorylated state, to transfer potassium inside the cell"[31] After this essential binding occurs, a dephosphorylation of the alpha subunit occurs which reduces the effect of cardiac disease. It is via the inhibiting of the Na+/K+-ATPase that sodium levels will begin to increase within the cell which ultimately increases the concentration of intracellular calcium via the sodium-calcium exchanger. This increased presence of calcium is what allows for the force of contraction to be increased. In the case of patients where the heart is not pumping hard enough to provide what is needed for the body this approach allows for the temporary overcoming of this.
Discovery
Na+
/K+
-ATPase was discovered by Jens Christian Skou in 1957 while working as assistant professor at the Department of Physiology, University of Aarhus, Denmark. He published his work that year.[32]
In 1997, he received one-half of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for the first discovery of an ion-transporting enzyme, Na+
, K+
-ATPase."[33]
Genes
Additional images
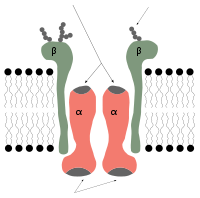
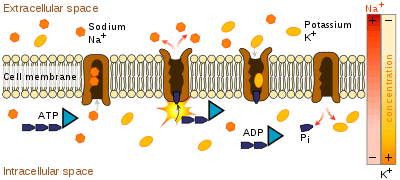 Mechanism of the sodium–potassium exchange pump.
Mechanism of the sodium–potassium exchange pump.
See also
- Thyroid hormone
- V-ATPase
References
- Clausen MV, Hilbers F, Poulsen H (June 2017). "The Structure and Function of the Na,K-ATPase Isoforms in Health and Disease". Frontiers in Physiology. 8: 371. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00371. PMC 5459889. PMID 28634454.
- Hall JE, Guyton AC (2006). Textbook of medical physiology. St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 978-0-7216-0240-0.
- Voet, Voet. "Biochemistry". Section 20-3, p. 759
- Howarth C, Gleeson P, Attwell D (July 2012). "Updated energy budgets for neural computation in the neocortex and cerebellum". Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 32 (7): 1222–32. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2012.35. PMC 3390818. PMID 22434069.
- Sanders, Martin J.; Simon, Lawrence M.; Misfeldt, Dayton S. (1983). "Transepithelial transport in cell culture: Bioenergetics of Na-,D-glucose-coupled transport". Journal of Cellular Physiology. 114 (3): 263–266. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041140303. ISSN 0021-9541. PMID 6833401.
- Lynch, R. M.; Paul, R. J. (1987-03-01). "Compartmentation of carbohydrate metabolism in vascular smooth muscle". American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology. 252 (3): C328–C334. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.3.c328. ISSN 0363-6143. PMID 3030131.
- Glitsch, H. G.; Tappe, A. (1993). "The Na+/K+ pump of cardiac Purkinje cells is preferentially fuelled by glycolytic ATP production". Pflügers Archiv : European Journal of Physiology. 422 (4): 380–385. doi:10.1007/bf00374294. ISSN 0031-6768.
- Dutka, T. L.; Lamb, G. D. (2007). "Na+-K+ pumps in the transverse tubular system of skeletal muscle fibers preferentially use ATP from glycolysis". American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology. 293 (3): C967–C977. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00132.2007. ISSN 0363-6143.
- Watanabe, Daiki; Wada, Masanobu (2019-06-24). "Effects of reduced muscle glycogen on excitation–contraction coupling in rat fast-twitch muscle: a glycogen removal study". Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 40 (3–4): 353–364. doi:10.1007/s10974-019-09524-y. ISSN 0142-4319.
- Jensen, Rasmus; Nielsen, Joachim; Ørtenblad, Niels (2019-12-10). "Inhibition of glycogenolysis prolongs action potential repriming period and impairs muscle function in rat skeletal muscle". The Journal of Physiology: JP278543. doi:10.1113/JP278543. ISSN 0022-3751.
- Armstrong CM (May 2003). "The Na/K pump, Cl ion, and osmotic stabilization of cells". PNAS. 100 (10): 6257–6262. doi:10.1073/pnas.0931278100. PMC 156359. PMID 12730376.
- Yuan Z, Cai T, Tian J, Ivanov AV, Giovannucci DR, Xie Z (September 2005). "Na/K-ATPase tethers phospholipase C and IP3 receptor into a calcium-regulatory complex". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 16 (9): 4034–45. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-04-0295. PMC 1196317. PMID 15975899.
- Tian J, Cai T, Yuan Z, Wang H, Liu L, Haas M, Maksimova E, Huang XY, Xie ZJ (January 2006). "Binding of Src to Na+/K+-ATPase forms a functional signaling complex". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 17 (1): 317–26. doi:10.1091/mbc.E05-08-0735. PMC 1345669. PMID 16267270.
- Li Z, Cai T, Tian J, Xie JX, Zhao X, Liu L, Shapiro JI, Xie Z (July 2009). "NaKtide, a Na/K-ATPase-derived peptide Src inhibitor, antagonizes ouabain-activated signal transduction in cultured cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (31): 21066–76. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.013821. PMC 2742871. PMID 19506077.
- Lee K, Jung J, Kim M, Guidotti G (January 2001). "Interaction of the alpha subunit of Na,K-ATPase with cofilin". The Biochemical Journal. 353 (Pt 2): 377–85. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3530377. PMC 1221581. PMID 11139403.
- Forrest MD, Wall MJ, Press DA, Feng J (December 2012). "The sodium–potassium pump controls the intrinsic firing of the cerebellar Purkinje neuron". PLOS ONE. 7 (12): e51169. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051169. PMC 3527461. PMID 23284664.
- Zylbertal A, Kahan A, Ben-Shaul Y, Yarom Y, Wagner S (December 2015). "Prolonged Intracellular Na+ Dynamics Govern Electrical Activity in Accessory Olfactory Bulb Mitral Cells". PLoS Biology. 13 (12): e1002319. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002319. PMC 4684409. PMID 26674618.
- Zylbertal A, Yarom Y, Wagner S (2017). "The Slow Dynamics of Intracellular Sodium Concentration Increase the Time Window of Neuronal Integration: A Simulation Study". Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience. 11: 85. doi:10.3389/fncom.2017.00085. PMC 5609115. PMID 28970791.
- Forrest MD (December 2014). "The sodium–potassium pump is an information processing element in brain computation". Frontiers in Physiology. 5 (472): 472. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00472. PMC 4274886. PMID 25566080.
- Cannon SC (July 2004). "Paying the price at the pump: dystonia from mutations in a Na+/K+ -ATPase". Neuron. 43 (2): 153–4. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.07.002. PMID 15260948.
- Calderon DP, Fremont R, Kraenzlin F, Khodakhah K (March 2011). "The neural substrates of rapid-onset Dystonia-Parkinsonism". Nature Neuroscience. 14 (3): 357–65. doi:10.1038/nn.2753. PMC 3430603. PMID 21297628.
- Forrest MD (April 2015). "Simulation of alcohol action upon a detailed Purkinje neuron model and a simpler surrogate model that runs >400 times faster". BMC Neuroscience. 16 (27): 27. doi:10.1186/s12868-015-0162-6. PMC 4417229. PMID 25928094.
- Forrest M (4 April 2015). "The Neuroscience Reason We Fall Over When Drunk". Science 2.0. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- Young EA, Fowler CD, Kidd GJ, Chang A, Rudick R, Fisher E, Trapp BD (April 2008). "Imaging correlates of decreased axonal Na+/K+ ATPase in chronic multiple sclerosis lesions". Annals of Neurology. 63 (4): 428–35. doi:10.1002/ana.21381. PMID 18438950.
- Burnier, Michel (2008). Sodium In Health And Disease. CRC Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0-8493-3978-3.
- Blaustein MP (May 1977). "Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis". The American Journal of Physiology. 232 (5): C165–73. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.1977.232.5.C165. PMID 324293.
- Schoner W, Scheiner-Bobis G (September 2008). "Role of endogenous cardiotonic steroids in sodium homeostasis". Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation. 23 (9): 2723–9. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfn325. PMID 18556748.
- Blaustein MP, Hamlyn JM (December 2010). "Signaling mechanisms that link salt retention to hypertension: endogenous ouabain, the Na+
/Ca2+
exchanger and TRPC proteins". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1802 (12): 1219–29. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.02.011. PMC 2909369. PMID 20211726. - Fuerstenwerth H (2014). "On the differences between ouabain and digitalis glycosides". American Journal of Therapeutics. 21 (1): 35–42. doi:10.1097/MJT.0b013e318217a609. PMID 21642827.
- Pavlovic D (2014). "The role of cardiotonic steroids in the pathogenesis of cardiomyopathy in chronic kidney disease". Nephron Clinical Practice. 128 (1–2): 11–21. doi:10.1159/000363301. PMID 25341357.
- https://www.pharmacorama.com/en/Sections/NAK-ATPase-Digoxin.php#:~:targetText=Cardiac%20glycosides%2C%20digoxin%2C%20digitoxin%20also,transfer%20potassium%20inside%20the%20cell.
- Skou JC (February 1957). "The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 23 (2): 394–401. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8. PMID 13412736.
- Chemistry 1997
External links
- Sodium,+Potassium+ATPase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- RCSB Protein Data Bank: Sodium–Potassium Pump
- A video by Khan Academy.