Emden
Emden (German: [ɛmdn̩]) is an independent city and seaport in Lower Saxony in the northwest of Germany, on the river Ems. It is the main city of the region of East Frisia and, in 2011, had a total population of 51,528.
Emden | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Emden 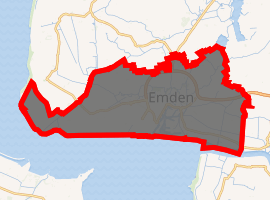
| |
 Emden  Emden | |
| Coordinates: 53°22′1″N 07°12′22″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Lower Saxony |
| District | Urban district |
| Government | |
| • Lord Mayor | Tim Kruithoff (Ind.) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 112.33 km2 (43.37 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1 m (3 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 50,195 |
| • Density | 450/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 26721, 26723, 26725 |
| Dialling codes | 04921, 04927 (Knock) |
| Vehicle registration | EMD |
| Website | www.emden.de |
History
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

The exact founding date of Emden is unknown, but it has existed at least since the 8th century. Older names for Emden are Amuthon, Embda, Emda, Embden and Embderland. Town privilege and the town's coat of arms, the Engelke up de Muer (The Little Angel on the Wall) was granted by Emperor Maximilian I in 1495.
In the 16th century, Emden briefly became an important centre for the Protestant Reformation under the rule of Countess Anna von Oldenburg who was determined to find a religious "third way" between Lutheranism and Catholicism. In 1542 she invited the Polish noble John Laski (or Joahannes a Lasco) to become pastor of a Protestant church at Emden;[2]:xi and for 7 years he continued to spread the new religion around the area of East Frisia. However, in 1549 following pressure from the Emperor Charles V, the Countess was forced to ask Laski to leave for England and the experiment came to an end. Nevertheless, the legacy was important for the reformation in the Netherlands.
At the end of the 16th century Emden experienced a period of great prosperity. Due to the Spanish blockade of Flemish and Brabant ports at the start of the Dutch Revolt, Emden became the most important transshipment port on the North Sea. Thousands of Protestant refugees came from Flanders and the Duchy of Brabant to the Protestant city Emden to escape persecution by the Spanish rulers of the Low Countries. During this period, the predominantly Calvinist Emden came into conflict with the Lutheran counts of East Friesland. The Emden Revolution in 1595 resulted in Emden becoming a distinct city-state.[3] With the support of the Dutch Republic, Emden became a free government city under the protection of the Dutch Republic. The Brabantian dialect became the official language of trade and civil administration.
Emden was a very rich city during the 17th century, due to large numbers of Dutch and Flemish immigrants such as Diederik Jansz. Graeff. It was a centre of reformed Protestantism at that time. The political theorist Johannes Althusius served as Syndic from 1604 to 1638.[2]:xii
In 1744 Emden was annexed by Prussia. In 1752 Frederick the Great chartered the Emden Company to trade with Canton, but the company was ruined when Emden was captured by French forces in 1757 during the Seven Years' War. [The city was recaptured by Anglo-German forces in 1758 and for the rest of the conflict was used as a major supply base by the British to support the ongoing war in Westphalia.
During the Napoleonic French era, Emden and the surrounding lands of East Frisia were part of the short-lived Kingdom of Holland.
Industrialization started at around 1870, with a paper mill and a somewhat bigger shipyard. At the end of the 19th century, a big canal, the Dortmund-Ems Canal was constructed, which connected Emden with the Ruhr area. This made Emden the "seaport of the Ruhr area", which lasted until the 1970s. Coal from the south was transported to the North Sea port, and imported iron ore was shipped via the canal towards Rhine and the Ruhr. The last iron ore freighter was moored in the port of Emden in 1986.
In 1903, a large shipyard (Nordseewerke, "North Sea Works") was founded which in operation until 2010.
The city centre was almost completely wiped out as a result of Allied bombing raids during the Second World War, destroying nearly all historic buildings. The RAF first bombed Emden on 31 March 1940. The most severe bombing took place on 6 September 1944, when roughly 80 percent of all houses in the city centre were destroyed. In the collective memory of the city, this date still plays an important role. The shipyard area was largely untouched – the British targeted the civilian areas, apparently in response to the bombing of Coventry by the Luftwaffe.[4] The reconstructed city was opened on 6 September 1962, exactly 18 years after the bombing.
Climate
| Climate data for Emden (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
9.0 (48.2) |
13.5 (56.3) |
17.0 (62.6) |
19.7 (67.5) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.4 (65.1) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
4.8 (40.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) |
-0.0 (32.0) |
1.7 (35.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7.2 (45.0) |
10.1 (50.2) |
12.7 (54.9) |
12.7 (54.9) |
10.0 (50.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
3.3 (37.9) |
0.1 (32.2) |
5.6 (42.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 66.8 (2.63) |
47.6 (1.87) |
60.9 (2.40) |
39.9 (1.57) |
55.8 (2.20) |
79.1 (3.11) |
80.3 (3.16) |
71.3 (2.81) |
81.5 (3.21) |
75.6 (2.98) |
74.3 (2.93) |
67.9 (2.67) |
801 (31.54) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 53.0 | 70.7 | 122.7 | 179.5 | 216.6 | 204.4 | 211.3 | 186.2 | 143.3 | 112.7 | 54.3 | 51.5 | 1,606.2 |
| Source: Météoclimat | |||||||||||||
Economy
The main industries in Emden are automobile production and shipbuilding. Volkswagen runs a large production plant which builds the Volkswagen Passat car and which employs around 10,000 people. Emden harbor is also one of the three main ports for car shipping in Europe (together with Zeebrugge in Belgium and Bremerhaven in Germany). More than 850,000 cars were imported and exported in 2005. The Nordseewerke shipyard, a subsidiary of ThyssenKrupp, employs around 1,400 dockers and specializes in conventional submarines. It also produces different kinds of cargo ships as well as ships for special purposes such as icebreakers, dredgers and other ships of that type.
Another important economic sector is tourism, mainly as a day trip destination for tourists staying in the surrounding villages on the North Sea coastline.
A university of applied sciences (Fachhochschule) was opened in 1973. At present, around 4.240 students are enrolled, most of them studying for technical degrees.
The airline Ostfriesische Lufttransport has its headquarters in Emden.[5]
Sports
The highest playing association football club is BSV Kickers Emden. The capacity of the stadium is 7,200, due to safety objections of the German Football Association. In 1994, some 12,000 spectators followed a match against the reserves squad of Hamburger SV, which remains the record. In that season, Kickers Emden finished top of the 3rd League, but were not promoted to the Second League as they lost the promotion round.
Since Emden is not only located close to the North Sea, but also to the river Ems and various small rivers and canals, boat sports are very popular among inhabitants and tourists.
Notable people

- Jacob Emden, also known as Ya'avetz (June 4, 1697 – April 19, 1776), leading German rabbi and talmudist.
- Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser, (ca. 1540-1596), sailor in Portuguese and Dutch service
- Johannes Althusius (1563–1638), legal scholar, Calvinist political theorist, city counsel and politician
- Johann Heinrich Alting, (1583-1644), reformed theologian
- Martin Hermann Faber (1586 – 1648), painter, architect, and cartographer
- Ludolf Bakhuizen, (1630-1708), major Marinemaler
- Eduard Norden, (1868-1941), philologist and religious historian
- Claude France (1893–1928), actor
- Hans Boelsen, (1894-1960), general lieutenant in the Second World War
- Henri Nannen, (1913–1996), publisher and publicist, founder of Stern magazine
- Hans-Joachim Hespos, (born 1938), composer
- Helma Sanders-Brahms, (1940-2014), film director and actress
- Karl Dall (born 1941), presenter, singer and comedian
- Wolfgang Petersen (born 1941), film director and producer
- Otto Waalkes (born 1948), comedian, comic artist, singer and actor
- Eva Herman, (born 1958), book author and former television presenter
- Jan van Koningsveld, (born 1969), mental calculator
- Heidi Hartmann, (born 1971), boxing champion
- Stefan Lampadius, (born 1976), actor and filmmaker
- Ferydoon Zandi (born 1979), football player
Ships and places named after the city


Three German light cruisers were named after the city, two of which served in World War I and the third in World War II. Today, the fifth navy ship named after the city is in service.
- SMS Emden (1906), a light cruiser in the Kaiserliche Marine, Bay of Bengal, Battle of Cocos
- Emden (1911), schooner, renamed Duhnen, then Brigantine Yankee; made four circumnavigations
- SMS Emden (1916), a light cruiser in the Kaiserliche Marine
- Emden (1925), a light cruiser in the Kriegsmarine, used in the invasion of Norway and Denmark
- F210 Emden (1979), Bremen-class frigate of the German Navy
A deep sea spot in the Pacific Ocean close to the Philippines is named after the first Emden ship, and is therefore called Emdentief in German. The spot (10,400 m deep) was sounded in the 1920s (in 1920, 1923 or 1928—sources vary).
In addition, the village of Emden, Illinois in the United States was named after Jacob Emden[6] due to the large number of emigrants from Emden to the village in northwestern Logan County, Illinois. Another namesake city in the USA is the unincorporated town of Embden, North Dakota (the b added to correct the pronunciation).[7]
See also
References
- Landesamt für Statistik Niedersachsen, LSN-Online Regionaldatenbank, Tabelle 12411: Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes, Stand 31. Dezember 2018.
- Carney, Frederick S. (1995). Politica:Translator's Introduction. Liberty Fund. ISBN 9780865971158.
- Mentzer, Raymond (1994). Sin and the Calvinists: Morals, Control and the Consistory in Reformed Tradition. Truman State University Press. p. 22. ISBN 1931112185.
- "You have no chance – Airminded". Airminded. 2 February 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
Why are we doing so? It is not revenge, though we do not forget Warsaw, Belgrade, Rotterdam, London, Plymouth and Coventry. We are bombing Germany, city by city, and ever more terribly, in order to make it impossible for you to go on with the war. That is our object. We shall pursue it remorselessly. City by city: Lübeck, Rostock, Cologne, Emden, Bremen, Wilhelmshaven, Duisburg, Hamburg -- and the list will grow longer and longer.
- "Imprint". (Archive) Ostfriesische Lufttransport. Retrieved on 4 August 2011. "Gorch-Fock-Str. 103 26721 Emden Germany".
- Emdenil.com Archived 29 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- Wick, Douglas A. (1988). "Embden (Cass County)". North Dakota Place Names. Bismarck, ND: Hedemarken Collectibles. ISBN 0962096806. OCLC 18941733. Retrieved 12 May 2012.
- "Emder Städtepartnerschaften". emden.de (in German). Emden. Retrieved 30 November 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Emden (Lower Saxony). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Emden. |
- Official website
- Kunsthalle Emden (in German)
- Johannes a Lasco Library (in German)
- Kickers Emden (in German)
- Chess (in German)
- Current weather data and forecast for Emden (in German)
- Cruisers EMDEN, Frigates EMDEN – 5 warships named EMDEN until today (in German)
- "Google map gives German harbour to Netherlands". BBC. 23 February 2011.—BBC article about an error in Google maps
- . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
