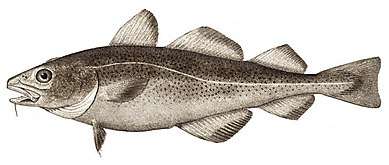
Zander
The zander (Sander lucioperca) is a species of fish from freshwater and brackish habitats in western Eurasia. It is a popular game fish and has been introduced to a variety of localities outside its native range.
| Zander | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Family: | Percidae |
| Genus: | Sander |
| Species: | S. lucioperca |
| Binomial name | |
| Sander lucioperca | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Taxonomy and etymology
The zander is closely related to perch. Zander are often called pike-perch as they resemble the pike with their elongated body and head, and the perch with their spiny dorsal fin. Zander are not, as is commonly believed, a pike and perch hybrid. In Europe, a second species (Sander volgensis) is limited to rivers in southern Russia and the basin of the Danube. These two species are suspected to hybridize occasionally where they are sympatric, as they produce fertile hybrids in captivity; no natural hybrids are known yet however, and while they are apparently hard to detect, it is suspected that the species are separated by strong prezygotic isolation. It strongly resembles, both in looks and in taste, the closely related American walleye (Sander vitreus).
Description
The zander is a common and popular game fish in Europe. It is often eaten, and it may reach 20 kg (44 lb)[2] of weight, although typical catches are considerably smaller. The IGFA All-Tackle world record zander was caught in Lago Maggiore, Switzerland in June 2016 weighing 11.48 kg (25.3 lb).[3] Zander reach an average length of 40–80 cm (15.5–31.5 in) with a maximum length of 120 cm (47 in).
Distribution and habitat
The zander is very widely distributed across Eurasia, occurring in the drainages of the Caspian, Baltic, Black, Aral, North and Aegean Sea basins. Its northern distribution limit is Finland. It has been introduced to Great Britain, southern Europe, and continental Europe west of the Elbe, Ebro, Tagus and Jucar drainages, as well as to Anatolia, North Africa, Siberia, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan.[1]
Zander inhabit freshwater bodies, preferentially large rivers and eutrophic lakes. They tolerate brackish water and will make use of coastal lakes and estuaries. Individuals living in brackish water habitats migrate upriver (for up to 250 km) for spawning.[1]
In the UK, zander were introduced into the East Anglian fens (large, partly artificial waterways) in the 20th century and spread rapidly, after the release of 97 fingerlings to the Great Ouse Relief Channel in 1963 by the former Great Ouse River Board.[4] British Waterways included zander among a "dirty dozen" non-native species most likely to harm native wildlife along rivers in Great Britain.[5]
Their success in establishing themselves is owed to a number of factors, one of which is that they are particularly well adapted to life in the slow-flowing, sparsely vegetated, rather murky waters that comprise so many of the British lowland rivers.[6] Zander thrive in water with rather low visibility, unlike pike, which often dominate the predator fish niche in clear water. However, zander need plenty of oxygen and soon disappear from eutrophic areas.
Use by humans

The zander is considered one of the most valuable food fish native to Europe. It is esteemed for its light, firm but tender meat with few bones and a delicate flavour. Although it is not generally bred for food, its adaptability makes zander fishery quite sustainable. Indeed, in some regions release of young zanders is restricted, as natural stocks already provide a sufficient supply for the market, while boosting the population of this large predator would have an adverse effect on the zander's food fishes. Zander is especially well suited for fish fillets.[7] It can also be served whole, baked, smoked or cooked. In some culinary circles, zander is appreciated even more highly than salmon. Even the offals can be cooked into consommé.
In 2004, it was revealed that some restaurants in the Minneapolis-St. Paul area of Minnesota in the United States were serving imported zander instead of the closely related North American walleye (the state fish, and a popular food in the region). While zander and walleye are almost indistinguishable by taste, the restaurants were selling the European fish under the name "walleye", which is an illegal practice. An investigation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration followed.[8]
In Ohio many restaurants were caught using juvenile Zander fillets in the 40 to 80 gram range in place of Lake Erie Yellow Perch. Shortages on the availability of Perch along with skyrocketing prices caused wholesalers and restaurants to use the juvenile Zander also known as Pike Perch fillets.
In Poland, this fish is popular and regarded as a delicacy, but the difficulty in catching it makes it expensive. It is most commonly baked with a trace of butter.
In the Serbian province of Vojvodina, zander has a long tradition in the local cuisine and is considered to be a delicacy. Its usually served baked or fried in a batter along with lemon sauce and potato and onion salad.
In Finland, as a conservation measure, the law regulates the minimum size of zander considered mature enough to be eaten. Zander is popular for its taste and its tendency to be picky with its prey, making it harder to catch than many other fish. Zander also tend to chase their prey before striking. When striking a fishing lure, it fights by pulling backwards, giving the impression that there is a big stone attached to the fishing line. Because the zander is not as good in striking as the pike, it prefers slower, even wounded fish; a lure moving too fast will not catch the zander's attention. On the other hand, anecdotal evidence suggests that zander do not attack lures that are moving too slowly either.
| Wikinews has related news: |
In July 2009 in Switzerland, a zander attacked tourists in Lake Maggiore, sending two people to the emergency room; the worst cut inflicted was about 10 centimeters long. The 70-cm 8-kg fish was later caught by the local police who cooked it and offered it to the tourists for the trouble it caused.[9] It is very unusual for zander to attack humans.
References
- Freyhof, J. & Kottelat, M. (2008). "Sander lucioperca". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T20860A9231839. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T20860A9231839.en.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- "International Angling Rules" (IGFA) Archived December 20, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Accessed 19 November 2008)
- "IGFA World Records Database". International Game Fish Association. Retrieved 2 October 2017.
- anglin-guru.info
- "Dirty dozen threaten waterways". BBC News. 14 August 2008. Retrieved 14 August 2008.
- "Foreign Fishes", The Living Countryside magazine (issue 36), p.706
- Craig, N (2012). "Fish tapeworm and sushi". Canadian Family Physician. 58 (6): 654–658. PMC 3374688. PMID 22859629.
- "Walleye or Zander? What Are You Really Eating?". KARE11TV. 7 December 2004. Retrieved 7 December 2004.
- "?" (in French). TV5. Retrieved 28 October 2010.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zander. |
- "Sander lucioperca". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 19 March 2006.
- Boyd Huppert (December 7, 2004). Walleye or Zander? What Are You Really Eating?. KARE.
- FishBase information on Zander
- International Angling Rules

.png)
