Xeroderma pigmentosum
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a genetic disorder in which there is a decreased ability to repair DNA damage such as that caused by ultraviolet (UV) light.[1] Symptoms may include a severe sunburn after only a few minutes in the sun, freckling in sun exposed areas, dry skin and changes in skin pigmentation.[1] Nervous system problems, such as hearing loss, poor coordination, loss of intellectual function and seizures, may also occur.[1] Complications include a high risk of skin cancer, with about half having skin cancer by age 10 without preventive efforts, and cataracts.[1] There may be a higher risk of other cancers such as brain cancers.[1]
| Xeroderma pigmentosum | |
|---|---|
| Other names | DeSanctis-Cacchione syndrome[1][2] |
 | |
| An eight-year-old girl from Guatemala with xeroderma pigmentosum[3] | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Severe sunburn after only a few minutes in the sun, freckling in sun-exposed areas, dry skin, changes in skin pigmentation[1] |
| Complications | Skin cancer, brain cancer, cataracts[1] |
| Usual onset | Becomes visible ~6 months of age[2] |
| Causes | Genetic disorder (autosomal recessive)[1] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing[4] |
| Differential diagnosis | Trichothiodystrophy, Cockayne syndrome, cerebrooculofacioskeletal syndrome, erythropoietic protoporphyria[5] |
| Treatment | Avoiding the sun, retinoid creams, vitamin D[4][5] |
| Prognosis | Life expectancy is shortened by about 30 years[6] |
| Frequency | 1 in 250,000 (US)[7] |
XP is autosomal recessive, with at least nine specific mutations able to result in the condition.[1][5] Normally, the damage to DNA which occurs in skin cells from exposure to UV light is repaired by nucleotide excision repair.[1] In people with xeroderma pigmentosum, this damage is not repaired.[1] As more abnormalities form in DNA, cells malfunction and eventually become cancerous or die.[1] Diagnosis is typically suspected based on symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing.[4]
There is no cure for XP.[5] Treatment involves completely avoiding the sun.[5] This includes protective clothing, sunscreen and dark sunglasses when out in the sun.[5] Retinoid creams may help decrease the risk of skin cancer.[5] Vitamin D supplementation is generally required.[4] If skin cancer occurs, it is treated in the usual way.[5] The life expectancy of those with the condition is about 30 years less than normal.[6]
The disease affects about 1 in 20,000 in Japan, 1 in 250,000 people in the United States and 1 in 430,000 in Europe.[7] It occurs equally commonly in males and females.[8] Xeroderma pigmentosum was first described in 1870s by Moritz Kaposi.[4][8] In 1882, Kaposi coined the term xeroderma pigmentosum for the condition, referring to its characteristic dry, pigmented skin.[8] Individuals with the disease have been referred to as "children of the night" or "moon children".[9][10]
Signs and symptoms
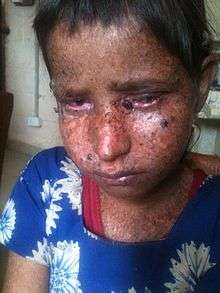
Signs and symptoms of xeroderma pigmentosum may include:
- Severe sunburn when exposed to only small amounts of sunlight. These often occur during a child's first exposure to sunlight.
- Development of many freckles at an early age
- Rough-surfaced growths (solar keratoses), and skin cancers
- Eyes that are painfully sensitive to the sun and may easily become irritated, bloodshot and clouded
- Blistering or freckling on minimum sun exposure
- Telangiectasia (spider veins)
- Limited growth of hair on chest and legs
- Scaly skin
- Xeroderma (dry skin)
- Irregular dark spots on the skin
- Corneal ulcerations
Genetics
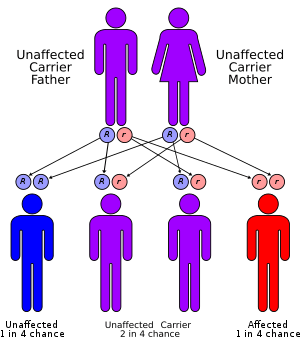
One of the most frequent defects in xeroderma pigmentosum is an autosomal recessive genetic defect in which nucleotide excision repair (NER) enzymes are mutated, leading to a reduction in or elimination of NER.[11] If left unchecked, damage caused by ultraviolet light can cause mutations in individual cell's DNA. The causes of the neurological abnormalities are poorly understood and are not connected with exposure to ultraviolet light. The most current theories suggest that oxidative DNA damage is generated during normal metabolism in the central nervous system, and that some types of this damage must be repaired by NER.[12]
Since DNA repair is under genetic control, it can mutate. Many genetic disorders such as xeroderma pigmentosum (XP; MIM 278700) are caused by mutations in genes that repair damaged DNA. XP affects the mechanism that repairs UV damage in skin cell DNA. Those affected with the autosomal recessive disorder XP are extremely sensitive to UV light produced by the sun and develop pigmented spots, tumors, and skin cancer with minimal exposure. Individuals with XP are about 1,000 times more likely to develop skin cancer than individuals without the disorder.
The molecular defects in XP cells result in a greatly elevated induction of mutations in sun-exposed skin of affected individuals. This increased mutation frequency probably accounts for the pigmentation changes and the skin cancers. Examination of mutations in the p53 gene in tumors from XP patients reveal p53 mutations characteristic of UV exposure in the majority of tumors[13] As with all genetic disorders, genetic counseling and psychological support is appropriate for the families to discuss probability of occurrence in future pregnancies, feelings of isolation and concern about career prospects. There is no cure for xeroderma pigmentosum. The most common fate for individuals with XP is early death from cancer.
XP repair proteins
The XPA protein acts during NER as a scaffold for assembly of other DNA repair proteins at sites of DNA damage to ensure appropriate excision of the damage.[14]
The XPB (ERCC3) protein is employed in unwinding the DNA double helix after DNA damage is initially recognized. Mutations in the XPB(ERCC3) gene can lead to XP or XP combined with Cockayne syndrome.[15]
The XPC protein forms a complex with RAD23B protein to form the initial damage recognition factor in global genomic nucleotide excision repair (GG-NER).[16] This complex recognizes a wide variety of damages that thermodynamically destabilize DNA duplexes.
The XPD (ERCC2) protein, in combination with the XPB helicase-containing transcription/repair complex TFIIH, is employed in unwinding the DNA duplex after damage is initially recognized. Mutations in the XPD(ERCC2) gene cause a variety of syndromes; XP, trichothiodystrophy (TTD), or a combination of XP and Cockayne syndrome (XPCS).[17][18] Both trichothiodystrophy and Cockayne syndrome display features of premature aging, suggesting an association between deficient DNA repair and premature aging (see DNA damage theory of aging).
XPE is a heterodimeric protein composed of two subunits. The larger subunit DDB1 primarily functions as a core component of CUL4A- and CUL4B-based E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes. Substrates that are ubiquitinnated by these complexes include proteins employed in DNA repair.[19]
The XPF (ERCC4) protein together with the ERCC1 protein forms a complex usually designated ERCC1-XPF. This complex separates the DNA helix for a short distance on either side of the site of damage. It then acts as a endonuclease to incise the damaged DNA strand on the 5’ side of the damaged site.[20] Mutant cells with deficient ERCC1-XPF are not only defective in NER, but also in the repair of double-strand breaks and inter-strand crosslinks.
The XPG protein is an endonuclease that incises DNA during NER at the 3’ side of the damaged nucleotide. Mutations in the XPG (ERCC5) gene can lead to XP alone, or in combination with Cockayne syndrome (CS), or in combination with infantile lethal cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome.[21]
Diagnosis
Types
There are seven complementation groups, plus one variant form:
| Type | Diseases Database | OMIM | Gene | Locus | Also known as / description |
| Type A, I, XPA | 29877 | 278700 | XPA | 9q22.3 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group A - the classical form of XP |
| Type B, II, XPB | 29878 | 133510 | XPB | 2q21 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group B |
| Type C, III, XPC | 29879 | 278720 | XPC | 3p25 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group C |
| Type D, IV, XPD | 29880 | 278730 278800 | XPD ERCC6 | 19q13.2-q13.3, 10q11 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group D or De Sanctis-Cacchione syndrome (can be considered a subtype of XPD) |
| Type E, V, XPE | 29881 | 278740 | DDB2 | 11p12-p11 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group E |
| Type F, VI, XPF | 29882 | 278760 | ERCC4 | 16p13.3-p13.13 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group F |
| Type G, VII, XPG | 29883 | 278780 133530 | RAD2 ERCC5 | 13q33 | Xeroderma pigmentosum group G and COFS syndrome type 3 |
| Type V, XPV | 278750 | POLH | 6p21.1-p12 | Xeroderma pigmentosum variant - these patients have mutation in a gene that codes for a specialized DNA polymerase called polymerase-η (eta). Polymerase-η can replicate over the damage and is needed when cells enter S-phase in the presence of a DNA-replication. |
Treatment
The most obvious, and often important part of treatment, is avoiding exposure to sunlight. This includes wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen (physical and chemical).[22] Keratosis can also be treated using cryotherapy or fluorouracil.[3]
Prognosis
In the United States of America, the probability of survival of individuals with the disease at age of 40 years amounts to 70 %. [23]
History
Xeroderma pigmentosum was first described in 1874 by Hebra and Moritz Kaposi. In 1882, Kaposi coined the term xeroderma pigmentosum for the condition, referring to its characteristic dry, pigmented skin.
The 1968 paper about XP by James Cleaver demonstrated the link between UV-induced DNA damage, faulty DNA repair and cancer.[24]
Popular culture
Because people with XP need to strictly avoid sunlight, but can go outside at night, they have been called children of the dark, children of the night, and vampire children. These terms can be considered derogatory.[25]
XP has been a plot element in several fictional works. One of the common themes in films about XP is whether teens with XP will risk sun exposure in pursuit of a romantic partner.[26]
A CBS television movie aired in 1994, Children of the Dark, was based on the story of the real-life couple Jim and Kim Harrison, whose two daughters have XP.[27][28]
The 2012 documentary Sun Kissed explores the XP problem on the Navajo Indian Reservation, and links it to the genetic legacy of the Long Walk of the Navajo, when the Navajo people were forced to move to a new location.[29][30][31]
A 2018 romance movie Midnight Sun tells the story of a young woman with XP and the impact it has on her life.
Research directions
Research into XP has had two main results: better understanding the disease itself, and also better understanding the normal biological mechanisms involved in DNA repair.[24] Research into XP has produced insights that have been translated into treatments and prevention for cancer.[24]
See also
References
- "Xeroderma pigmentosum". Genetics Home Reference. U.S. Library of Medicine. 26 June 2018. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- "Xeroderma pigmentosum". dermnetnz.org. Retrieved 25 February 2020.
- Halpern J, Hopping B, Brostoff JM (October 2008). "Photosensitivity, corneal scarring and developmental delay: Xeroderma Pigmentosum in a tropical country". Cases Journal. 1 (1): 254. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-254. PMC 2577106. PMID 18937855.
- "Xeroderma Pigmentosum". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). 2017. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- "Xeroderma pigmentosum". Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2018. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- Ahmad S, Hanaoka F (2008). Molecular Mechanisms of Xeroderma Pigmentosum. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 17. ISBN 9780387095998.
- Lehmann AR, McGibbon D, Stefanini M (November 2011). "Xeroderma pigmentosum". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 6: 70. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-6-70. PMC 3221642. PMID 22044607.
- Griffiths C, Barker J, Bleiker T, Chalmers R, Creamer D (2016). Rook's Textbook of Dermatology, 4 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118441190.
- Salway JG (2011). Medical Biochemistry at a Glance. John Wiley & Sons. p. 313. ISBN 9781118292402.
- "Moon children". The Guardian. 1999.
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T (2006). DNA repair and mutagenesis. Washington: ASM Press. p. 1118. ISBN 978-1-55581-319-2.
- Brooks PJ (July 2008). "The 8,5'-cyclopurine-2'-deoxynucleosides: candidate neurodegenerative DNA lesions in xeroderma pigmentosum, and unique probes of transcription and nucleotide excision repair". DNA Repair. 7 (7): 1168–79. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.03.016. PMC 2797313. PMID 18495558.
- Daya-Grosjean L, Sarasin A (April 2005). "The role of UV induced lesions in skin carcinogenesis: an overview of oncogene and tumor suppressor gene modifications in xeroderma pigmentosum skin tumors". Mutation Research. 571 (1–2): 43–56. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.11.013. PMID 15748637.
- Sugitani N, Sivley RM, Perry KE, Capra JA, Chazin WJ (August 2016). "XPA: A key scaffold for human nucleotide excision repair". DNA Repair. 44: 123–135. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.05.018. PMC 4958585. PMID 27247238.
- Oh KS, Khan SG, Jaspers NG, Raams A, Ueda T, Lehmann A, Friedmann PS, Emmert S, Gratchev A, Lachlan K, Lucassan A, Baker CC, Kraemer KH (November 2006). "Phenotypic heterogeneity in the XPB DNA helicase gene (ERCC3): xeroderma pigmentosum without and with Cockayne syndrome". Human Mutation. 27 (11): 1092–103. doi:10.1002/humu.20392. PMID 16947863.
- Sugasawa K, Ng JM, Masutani C, Iwai S, van der Spek PJ, Eker AP, Hanaoka F, Bootsma D, Hoeijmakers JH (August 1998). "Xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein complex is the initiator of global genome nucleotide excision repair". Molecular Cell. 2 (2): 223–32. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80132-x. PMID 9734359.
- Andressoo JO, Hoeijmakers JH, Mitchell JR (December 2006). "Nucleotide excision repair disorders and the balance between cancer and aging". Cell Cycle. 5 (24): 2886–8. doi:10.4161/cc.5.24.3565. PMID 17172862.
- van de Ven M, Andressoo JO, van der Horst GT, Hoeijmakers JH, Mitchell JR (November 2012). "Effects of compound heterozygosity at the Xpd locus on cancer and ageing in mouse models". DNA Repair. 11 (11): 874–83. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.08.003. PMID 23046824.
- Iovine B, Iannella ML, Bevilacqua MA (December 2011). "Damage-specific DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1): a protein with a wide range of functions". The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 43 (12): 1664–7. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2011.09.001. PMID 21959250.
- Sijbers AM, de Laat WL, Ariza RR, Biggerstaff M, Wei YF, Moggs JG, Carter KC, Shell BK, Evans E, de Jong MC, Rademakers S, de Rooij J, Jaspers NG, Hoeijmakers JH, Wood RD (September 1996). "Xeroderma pigmentosum group F caused by a defect in a structure-specific DNA repair endonuclease". Cell. 86 (5): 811–22. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80155-5. hdl:1765/3110. PMID 8797827.
- Barnhoorn S, Uittenboogaard LM, Jaarsma D, Vermeij WP, Tresini M, Weymaere M, Menoni H, Brandt RM, de Waard MC, Botter SM, Sarker AH, Jaspers NG, van der Horst GT, Cooper PK, Hoeijmakers JH, van der Pluijm I (October 2014). "Cell-autonomous progeroid changes in conditional mouse models for repair endonuclease XPG deficiency". PLoS Genetics. 10 (10): e1004686. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004686. PMC 4191938. PMID 25299392.
- Nussbaum R, McInnes R, Willard H (2016-01-01). Genetics in Medicine. Elsevier. ISBN 978-14377-0696-3.
- Kraemer, Kenneth H. (1 February 1987). "Xeroderma Pigmentosum". Archives of Dermatology. 123 (2): 241. doi:10.1001/archderm.1987.01660260111026. Retrieved 21 June 2020.
- Kraemer KH, DiGiovanna JJ (March 2015). "Forty years of research on xeroderma pigmentosum at the US National Institutes of Health". Photochemistry and Photobiology. 91 (2): 452–9. doi:10.1111/php.12345. PMC 4355260. PMID 25220021.
- Almeida, Craig A.; Barry, Sheila A. (2011-08-26). Cancer: Basic Science and Clinical Aspects. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781444357394.
- Walsh, Katie (23 March 2018). "No spark in sick teen romance - Baltimore Sun". Baltimore Sun. Tribune New Service. Retrieved 2018-07-08.
- Holder K (1994-05-01). "Family in Twilight for Sun-Sensitive Girls : Health: Two daughters have a rare genetic intolerance that leaves victims vulnerable to skin cancers, blindness and neurological damage after exposure to sunlight". Associated Press. Retrieved 2017-09-14.
- Voros D (1994-04-15). "Review: 'Children of the Dark'". Variety. Retrieved 2017-09-14.
- "A Rare Genetic Disorder Is Stalking the Children of the Navajo Nation In POV's 'Sun Kissed,' Premiering Thursday, Oct. 18, 2012, on PBS". 7 June 2012. Retrieved 2018-06-29.
- Ziff D. "Hiding From the Sun". The Alberquerque Journal. Retrieved 2018-06-29.
- Bender A (2013-03-06). "Rare disease suddenly arises on Navajo Reservation". People's World. Retrieved 2018-06-29.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Xeroderma pigmentosum. |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |