α-Vetivone
α-Vetivone is an organic compound that is classified as a sesquiterpene (derived from three isoprene units). It is a major component of the oil of vetiver, which is used to prepare certain high value perfumes.
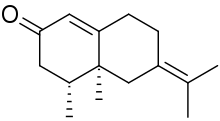 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4R,4aS)-6-Isopropylidene-4,4a-dimethyl-4,4a,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-2(3H)-naphthalenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.217 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H22O | |
| Molar mass | 218.335 |
| Appearance | colourless solid |
| Density | 0.962 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 270.5 °C (518.9 °F; 543.6 K) |
| practically insoluble | |
| Solubility in ethanol | soluble |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | soluble |
| Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
α-Vetivone is isolated by steam distillation of the roots of the grass Vetiveria zizanioides. Two other components of this distillate are the sesquiterpenes khusimol and β-vetivone shown below.[1]
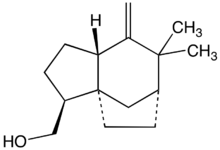 Structure of khusimol, another fragrant component of the oil of vetiver.
Structure of khusimol, another fragrant component of the oil of vetiver.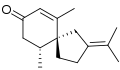 Structure of β-vetivone, another fragrant component of the oil of vetiver.
Structure of β-vetivone, another fragrant component of the oil of vetiver.
References
- Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragrances" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim: 2002. Published online: 15 January 2003; doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.