Vaballathus
Lucius Julius Aurelius Septimius Vaballathus Athenodorus (Palmyrene: ![]()
| Vaballathus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Augustus of Syria, Cappadocia and Aegyptus | |||||||||
.jpg) Vaballathus as King on the observe of a Palmyrene Antoninianus, 271 AD. | |||||||||
| King of Kings of Palmyra | |||||||||
| Reign | 267–272 AD | ||||||||
| Predecessor | Odaenathus | ||||||||
| Successor | Position abolished | ||||||||
| Emperor of the Palmyrene Empire | |||||||||
| Reign | 272 | ||||||||
| Predecessor | Maeonius | ||||||||
| Successor | Septimius Antiochus | ||||||||
| Born | c. 259 Palmyra, Syria | ||||||||
| Died | After 274 Rome, Roman Empire | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| House | House of Odaenathus | ||||||||
| Father | Odaenathus | ||||||||
| Mother | Zenobia | ||||||||
| Religion | Palmyrene paganism | ||||||||
Early life
Lucius Julius Aurelius Septimius Vaballathus was born and raised in the city of Palmyra, an oasis settlement in the Syrian Desert in 259 to the king of kings of Palmyra, Odaenathus, and his second wife, queen consort of Palmyra, Zenobia. Vaballathus is the Latinized form of his Palmyrene name, Wahballāt, "Gift of Allāt". As the Arabian goddess Allāt came to be identified with Athena, he used Athenodorus as the Greek form of his name.[1] He had a half-brother, Hairan I, born from his father and another woman, who reigned as co-king of kings with his father, and a lesser-known brother, Hairan II. He also might have had other brothers, who were mentioned in (and only known from) the Augustan History, Herennianus and Timolaus.[2] Herennianus may be Hairan; while Timolaus is probably a fabrication.[3]
As King
Succession to the throne
In 267, his father Odaenathus and half-brother Hairan I were murdered by a relative, perhaps a cousin of Odaenthus's, named Maeonius. Maeonius ruled as a usurper and crowned himself emperor but was almost immediately killed, as no inscription or evidence for his rule exists. With Odaenathus and his oldest son dead, the succession came to his younger son, Vaballathus. The young Vaballathus was made king (rex consul imperator dux Romanorum, "illustrious King of Kings" and corrector totius orientis) of the Palmyrene Empire at eight years old. Being too young to rule, his mother Zenobia ruled as queen regent and was the de facto ruler of Palmyra.
Reign

Initially the Roman emperor Aurelian recognized Vaballathus' rule, perhaps because he was engaged in conflict with the Gallic Empire in the west and hesitated to incite open warfare with the Palmyrene Empire. This mutual recognition is testified by early coins issued by Zenobia under Vaballathus's name, but also acknowledging Aurelian as emperor. In the coins, Aurelian is shown wearing a radiate crown that signifies his supremacy as emperor, and Vaballathus was crowned with a laurel wreath.[4] The Alexandrian minted coins showed Aurelian in his first year and Vaballathus in his fourth year[5] with Vaballathus adopting honorary titles possibly inherited from his father Odaenathus. Although the Palmyrene Empire was centred in Palmyra, Vaballathus and Zenobia probably spent most of their reign in Antioch,[6] Syria's administrative capital.[7] The relationship between the Roman Empire and the newly established Palmyrene empire deteriorated, and a series of Palmyrene conquests, done under the protective show of subordination to Rome,[8] began around 270.
In October of 270,[9] a Palmyrene army of 70,000 invaded Egypt,[10][11] and declared Zenobia, Vaballathus's mother, the Queen of Egypt.[12] The Roman general Tenagino Probus was able to regain Alexandria in November, but was defeated and escaped to the fortress of Babylon, where he was besieged and killed by Zabdas, a Palmyrene general, who continued his march south and secured Egypt.[13] Afterward, in 271, Zabbai, another Palmyrene general serving Zenobia, started the operations in Anatolia, and was joined by Zabdas in the spring of that year.[14] The Palmyrenes subdued the Asian province of Galatia,[15] and occupied the regional capital of Ancyra, marking the greatest extent of the Palmyrene expansion.[16]
Aurelian disappeared from Palmyrene coinage, while Zenobia and Vaballathus adopted the titles of Augusta and Augustus, respectively. Vaballathus was named in coins "King, Emperor, Dux Romanum leader of the Romans"[17] and an open rebellion against Rome started.
Defeat
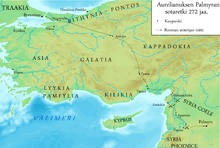
In 272, the Emperor Aurelian crossed the Bosporus and advanced quickly through Anatolia.[11] While the Roman general Marcus Aurelius Probus regained Egypt from Palmyra, the emperor continued his march and reached Tyana.[18] Tyana fell from Palmyrene control; Aurelian up to that point had destroyed every city that resisted him, but he allegedly spared Tyana. Whatever the reason for his clemency, it paid off, as many more cities submitted to him upon seeing that the emperor would not exact revenge upon them.
Passing through Issus, Aurelian defeated Zenobia in the Battle of Immae near Antioch.[19] The Palmyrene armies retreated to Antioch, then later Emesa, while Aurelian advanced and took the former.[20] The defeat at Emesa forced the Palmyrene armies to evacuate to the capital.[21] The Romans began a siege, and tried to breach the city defences several times but were repelled,[22] however, the situation worsened, so Zenobia, Vaballathus's mother, left the city and headed east to ask the Sasanian Empire for help.[23] The Romans followed the queen, arrested her near the Euphrates, and brought her back to the emperor. Soon after, the Palmyrene citizens asked for peace, and the city fell.

The end of Vaballathus's nominal rule came after losing the Siege of Palmyra. Vaballathus, his mother and her council were taken to Emesa and put on trial. Most of the high-ranking Palmyrene officials were executed,[24] while Zenobia and Vaballathus's fates remain uncertain. Although Aurelian had most of his prisoners executed, he most likely spared the queen and her son to parade her in his planned triumph.[25]
According to Zosimus, Vaballathus died on the way to Rome, but this theory has been neither confirmed nor disproved. Other sources have implied that after shipping the defeated Zenobia and Vaballathus to Rome, Aurelian allowed both of the rebels to live, but only after they had been marched through the streets of the imperial city in accordance with Roman traditions of celebrating military victories with a triumphal procession. This would have been humiliating, but better than death. This theory is supported by Aurelian's similar treatment of the Tetrici, Tetricus I and Tetricus II of the Gallic Empire, long-time enemies of Rome whom the emperor allowed to retire following their defeat at the Battle of Châlons in 274.
The fate of Palmyra, however took a turn for the worse. In 273, a revolution was started by Septimius Apsaios[26] declaring a relative of Zenobia, Septimius Antiochus, as Augustus.[27] Aurelian marched to Palmyra, razing it. Buildings were smashed, citizens clubbed and massacred and Palmyra's holiest temples pillaged.[28] The city was reduced and disappeared from historical records from that time,[29] thus ending the ascendancy of Palmyra over Roman Asia Minor.
Ancestors
| Ancestors of Vaballathus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- Butcher 2003, p. 284.
- Southern 2008, p. 10.
- Watson 2004, p. 58.
- Southern 2015, p. 168.
- Southern 2015, p. 167.
- Teixidor 2005, p. 205.
- Nakamura 1993, p. 141.
- Watson 2014, p. 79.
- Watson 2014, p. 62.
- Southern 2008, p. 133.
- Bryce 2014, p. 303.
- Bryce 2014, p. 304.
- Watson 2014, p. 63.
- Watson 2014, p. 64.
- Watson 2014, p. 64.
- Watson 2002, p. 80.
- Ando 2012, p. 210.
- Watson 2002, p. 71.
- Bryce 2014, p. 309.
- Watson 2002, p. 74.
- Bryce 2014, p. 310.
- Stoneman 1994, p. 175.
- Watson 2004, p. 77.
- Ware 1838, p. 24.
- Watson 2004, p. 79, 84.
- Smith II 2013, p. 180.
- Smith II 2013, p. 181.
- Ball 2002, p. 81.
- Pollard 2000, p. 299.
Sources cited
- Butcher, Kevin (2003). Roman Syria and the Near East. Getty Publications. ISBN 978-0-89236-715-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Southern, Pat (2008). Empress Zenobia: Palmyra's Rebel Queen. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4411-7351-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sommer, Michael (2017). Palmyra: A History. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-351-34715-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Vabalathus. |
- Coinage of Vabalathus
- Long, Jacqueline F. "Vaballathus and Zenobia (270-272 A.D.)". De Imperatoribus Romanis.