Typhoon Mujigae
Typhoon Mujigae (pronounced [mu.dʑi.ɡɛ]), known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Kabayan, was the strongest storm to strike the province of Guangdong in the month of October.[1] The storm affected the Philippines, southern China and northern Vietnam during early October 2015 as a strong typhoon. The typhoon originated from a weak tropical disturbance near Palau on September 28. The system subsequently developed into the twenty-second named storm of the annual typhoon season on October 1.
| Typhoon (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
 Typhoon Mujigae over the Leizhou Peninsula on October 4 | |
| Formed | September 30, 2015 |
| Dissipated | October 5, 2015 |
| Highest winds | 10-minute sustained: 155 km/h (100 mph) 1-minute sustained: 215 km/h (130 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 950 hPa (mbar); 28.05 inHg |
| Fatalities | 29 total |
| Damage | $4.26 billion (2015 USD) |
| Areas affected | Philippines, Vietnam, China |
| Part of the 2015 Pacific typhoon season | |
Meteorological history
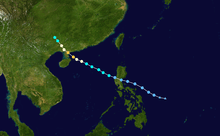
Early on September 30, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued a tropical cyclone formation alert for an area of convection east of the Philippines. The system had a consolidating center and rainbands, and moved to the west-northwest.[2] At 18:00 UTC on September 30, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) classified the system as a tropical depression about 160 km (100 mi) east of the Philippine island of Samar.[3] Early the next day, the JTWC initiated advisories on the system as Tropical Depression 22W,[4] and the PAGASA designated it with the local name Tropical Depression Kabayan.[5] All three agencies later classified Kabayan as a tropical storm, with the JMA naming it Mujigae.[6][7][8] The system was located in a region of light vertical wind shear.
By October 2, Mujigae made landfall over Aurora province and the JTWC later downgraded the system to a tropical depression.[9] Soon, the storm left the Philippine Area of Responsibility. Later on the same day, Mujigae reemerged into the South China Sea, where weak vertical wind shear and warm sea surface temperature favored development and reorganization of the system. The JTWC upgraded it back to a tropical storm whilst the JMA upgraded its intensity to severe tropical storm strength.[10][11] The next day, due to radial outflow, Mujigae began a phase of rapid deepening, with convection wrapping around a developing eye, as it moved towards western Guangdong, China, prompting the JMA and the JTWC to classify Mujigae as a typhoon.[12][13]
The JTWC upgraded Mujigae to a Category 4-equivalent typhoon. At that time the storm was about 350 km (215 mi) south-southwest of Hong Kong. Later on the same day, Mujigae made landfall for the second time near Zhanjiang, China.
Preparations and impact
Philippines
The city of Iba, on the western side of Luzon Island in the northern Philippines, was deluged with at least 175 mm (6.9 in) of rain in just 24 hours. Manila was spared the worst of it but still got approximately 50 mm (2.0 in) during that same time. A coast guard spokesman said search-and-rescue ships were scouring the sea west of Pangasinan, Ilocos and Zambales after two cargo ships bound for Japan had picked up nine fishermen of the Philippines, of which are all conscious from a capsized boat. According to the NDRRMC, damages amounted to ₱46.86 million (US$1 million).[14] Two people were reported dead in Central Luzon from the Office of Civil Defense (OCD).[15]
China
In Hainan and coastal Guangdong province, around 60,000 fishing boats were recalled to harbor to shelter from the storm. Three were reported dead in Foshan as a tornado struck from the rainbands of Mujigae and a fisherman died at sea off Zhanjiang.[16] Mujigae killed 27 people and caused a total of ¥27.032 billion (US$4.26 billion) in economic losses.[17]
Retirement
Due to the high damage toll caused by the storm in China, the name Mujigae was retired at the Fourth Joint Session of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee and WMO/ESCAP Panel on Tropical Cyclones during 2016. On February 2017, they chose the name Surigae to replace Mujigae.[18]
See also
- Typhoon Utor
- Typhoon Vicente (2012)
- Typhoon Son-Tinh (2012)
- Typhoon Rammasun (2014)
References
- "Typhoon Mujigae reportedly the most powerful storm in history to hit China in Oct... Brings "rare tornadoes" many injured". The Big Wobble. October 5, 2015.
- Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert. Joint Typhoon Warning Center (Report). September 30, 2015. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- RSMC Tokyo — Typhoon Center (November 12, 2015). Typhoon Best Track 2015-11-12T08:00:00Z (Report). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- Annual Tropical Cyclone Report 2015 (PDF) (Report). Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 2016. p. 40. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 16, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- Final Report re Effects of Tropical Storm "Kabayan" (I.N. Mujigae) (PDF) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. October 2015. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- "TS 1522 MUJIGAE (1522) UPGRADED FROM TD". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 2, 2015. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
- "Tropical Storm 22W (Twentytwo) Warning Nr 003". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on October 1, 2015. Retrieved October 1, 2015.
- https://www.webcitation.org/6bxSLjRxn?url=http://gwydir.demon.co.uk/advisories/WTPH20-RPMM_201510011200.htm
- "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 22W (Twentytwo) Warning Nr 04". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on October 2, 2015. Retrieved October 2, 2015.
- "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 22W (Mujigae) Warning Nr 06". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on October 2, 2015. Retrieved October 2, 2015.
- "STS 1522 MUJIGAE (1522) UPGRADED FROM TS". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 3, 2015. Retrieved October 2, 2015.
- "Typhoon 22W (Mujigae) Warning Nr 011". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Archived from the original on October 3, 2015. Retrieved October 3, 2015.
- "TY 1522 MUJIGAE (1522) UPGRADED FROM STS". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on October 3, 2015. Retrieved October 3, 2015.
- "FINAL REPORT re Effects of Tropical Storm KABAYAN (MUJIGAE)" (PDF). NDRRMC. October 14, 2015. Retrieved October 14, 2015.
- "Kabayan leaves 2 dead, 31 missing". PhilStar. Retrieved October 5, 2015.
- "Typhoon Mujigae batters South China, kills 7". Xinhuanet. October 5, 2015.
- "Member Report: China" (PDF). CMA. China Meterelogical Agency. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- http://www.typhooncommittee.org/48th/docs/final/TC48FINAL.pdf
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Typhoon Mujigae (2015). |
- JMA General Information of Typhoon Mujigae (1522) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data of Typhoon Mujigae (1522) (in Japanese)
- 22W.MUJIGAE from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory