Tarmoola Gold Mine
The Tarmoola or King of the Hills gold mine is located 29 km north-west of Leonora, Western Australia. The mine was placed in care and maintenance from September 2004, when a pit wall failure forced its closure. It is owned by Saracen Mineral Holdings Limited.[2]
| Location | |
|---|---|
 Tarmoola Gold Mine Location in Australia | |
| Location | Leonora |
| State | Western Australia |
| Country | Australia |
| Coordinates | 28°39′58″S 121°10′01″E |
| Production | |
| Production | 20,000 oz est.[1] |
| Financial year | 2016-17 |
| History | |
| Opened | 1990 |
| Owner | |
| Company | Red 5 |
| Website | http://red5limited.com |
| Year of acquisition | 2018 |
The Tarmoola mine was developed and opened in May 1990 by Mt Edon Gold Mines Australia NL. It is now known as King of the Hills, the original name for the area from its discovery in 1897, and is owned and operated by Saracen Mineral Holdings Limited. Saracen commenced underground mining operations at King of the Hills in July 2016.[3][4]
History
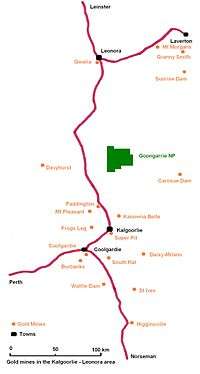
The mine, opened in May 1990,[5] was discovered and developed by Mount Edon Mines until April 1997,[6] when it was taken over by jointly by Camelot Resources and Teck Corporation through Reachwest Pty Ltd for A$158 million.[7]
Camelot Resources was renamed Pacmin Mining in June 1998[8] and took control of all assets of the two companies in Australia.[9] Pacmin was then taken over by Sons of Gwalia in October 2001 for A$210 million,[10][11] the mine thereby becoming part of the company's Leonora operations, together with the Gwalia mine. This merger also secured the Carosue Dam mine for Sons of Gwalia.[12][13]
In February 2004, a pit wall failure caused disruptions to the mine, leading to its eventual closure in September 2004.[2]
In retrospect, the purchase of Pacmin and Tarmoola was seen as very expensive, especially in the light of gold reserve write downs and operational difficulties at the mine.[14][15]
Sons of Gwalia went into administration on 30 August 2004, following a financial collapse, with debts exceeding $800 million after suffering from falling gold reserves and hedging losses.[16] Sons of Gwalia was Australia's third-largest gold producer and also controlled more than half the world's production of tantalum.[17]
St Barbara purchased the mine from insolvent Sons of Gwalia in March 2005 but has not reopened the mine since.[18] The company placed the mine on the market in 2007, seeing little value in operating the mine because of high costs of production. St Barbara estimated that it would cost A$700 per ounce to mine at Tarmoola, at an average grade of 1.1 g/t.[19] However, the sale of Tarmoola did not eventuate.[20]
St Barbara has been reviewing the option of underground mining at Tarmoola in 2009 and processing the ore at Gwalia.[21]
King of the Hills has since been sold to Red 5 Limited; production restarted in January 2018 with Pit N Portal as the contractor.
Production
Production of the mine:
| Year | Production | Grade | Cost per ounce |
| 1995-96[7] | 58,369 ounces | ||
| 2000[22] | 230,357 ounces | 2.27 g/t | A$287 |
| 2001[22] | 194,540 ounces | 1.80 g/t | A$379 |
| 2002 1[22] | 150,484 ounces | 1.41 g/t | A$375 |
| 2002-03 2[12] | 237,036 ounces | A$470 | |
| 2003-04 2[23] | 165,802 ounces | A$476 | |
| 2004-05 | |||
| 2005–present | inactive | ||
- 1 2002 results for January to November only.
- 2 Combined result for the Leonora operations, consisting of Gwalia and Tarmoola. The Gwalia mine closed in December 2003.
Sources
- The Australian Mines Handbook: 2003-2004 Edition, Louthean Media Pty Ltd, Editor: Ross Louthean
- Western Australian Mineral and Petroleum Statistics Digest 2008 Page 34: Principal Mineral and Petroleum Producers - Gold
References
- "Quarterly report: December 2016" (pdf). Saracen Mineral Holdings Limited. 24 January 2017. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- St Barbara annual report 2005 accessed: 7 February 2010
- Fairclough, M.C.; Brown, J.C. (1998). "Tarmoola Gold Deposit". In Berkman, Donald Alexander; Mackenzie, David H. (eds.). Geology of Australian and Papua New Guinean mineral deposits (PDF). Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. pp. 173–178. ISBN 978 1 875776 53 5. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- "Quarterly report: September 2016" (pdf). Saracen Mineral Holdings Limited. 25 October 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- Klaus Eckhof - Project Geologist and Business Development Manager of Mount Edon www.goldinvest.de, published: 18 January 2007, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Mr Tony Brennan - Managing Director of Mount Edon Gold Mines Limited deltacapital.com.au, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Joint Takeover Bid For Australian Mine The New York Times, published: 23 January 1997, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Tarmoola Joint Venture acclaimexploration.com.au, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Establishment of Pacific Mining Corporation Camelot ASX announcement, published: 13 March 1998, accessed: 8 February 2010
- PACMIN MINING CORPORATION LIMITED (PML) delisted.com.au, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Intention to Make Takeover Bid for PacMin Mining Corporation SGW ASX announcement, published: 23 August 2001, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Sons of Gwalia annual report 2003 accessed: 12 January 2010
- MINEDEX website - Tarmoola search result Archived 11 September 2008 at the Wayback Machine accessed: 8 February 2010
- ASX to probe Sons of Gwalia collapse ABC Australia, published: 5 September 2004, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Gwalia sweats on review metalsplace.com, published: 8 August 2004, accessed: 8 February 2010
- Ernst &Young agrees to $125m Sons of Gwalia settlement The West Australian, published: 4 September 2009, accessed: 4 September 2009
- Sons of Gwalia's gold hedging had big holes The Sydney Morning Herald, published: 4 September 2004, accessed: 4 September 2009
- St Barbara Mines Limited - Lodgement of Open Briefing Archived 15 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine published: 28 June 2005, accessed: 3 September 2009
- St Barbara offloads Tarmoola goldmine The Sydney Morning Herald, published: 9 November 2009, accessed: 8 February 2010
- St Barbara considers underground gold mine at Tarmoola The Australian, published: 14 April 2007, accessed: 8 February 2010
- St Barbara website - Leonora accessed: 8 February 2010
- The Australian Mines Handbook: 2003-2004 Edition, page 128
- Sons of Gwalia fourth quarter report 2004 accessed: 12 January 2010
External links
- St Barbara website - Leonora operations
- MINEDEX website
- How sons of Lalor built, then sank, Sons of Gwalia The Sydney Morning Herald - Article on the collapse of Sons of Gwalia