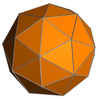
Small triambic icosahedron
In geometry, the small triambic icosahedron is a star polyhedron composed of 20 intersecting non-regular hexagon faces. It has 60 edges and 32 vertices, and Euler characteristic of −8. It is an isohedron, meaning that all of its faces are symmetric to each other, and Branko Grünbaum has conjectured that it is the only Euclidean isohedron with faces of six or more sides.[1]
| Small triambic icosahedron | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| Type | Dual uniform polyhedron | ||||||
| Index | DU30, 2/59, W26 | ||||||
| Elements (As a star polyhedron) | F = 20, E = 60 V = 32 (χ = −8) | ||||||
| Symmetry group | icosahedral (Ih) | ||||||
| Dual polyhedron | small ditrigonal icosidodecahedron | ||||||
| |||||||

Related shapes
The external surface of the small triambic icosahedron (removing the parts of each hexagonal face that are surrounded by other faces, but interpreting the resulting disconnected plane figures as still being faces) coincides with one of the stellations of the icosahedron.[2] If instead, after removing the surrounded parts of each face, each resulting triple of coplanar triangles is considered to be three separate faces, then the result is one form of the triakis icosahedron, formed by adding a triangular pyramid to each face of an icosahedron.
The dual polyhedron of the small triambic icosahedron is the small ditrigonal icosidodecahedron. As this is a uniform polyhedron, the small triambic icosahedron is a uniform dual. Other uniform duals whose exterior surfaces are stellations of the icosahedron are the medial triambic icosahedron and the great triambic icosahedron.
References
- Grünbaum, Branko (2008). "Can every face of a polyhedron have many sides?". Geometry, games, graphs and education: the Joe Malkevitch Festschrift. Bedford, Massachusetts: Comap, Inc. pp. 9–26. hdl:1773/4593. MR 2512345.
- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald; Du Val, P.; Flather, H. T.; Petrie, J. F. (1999). The fifty-nine icosahedra (3rd ed.). Tarquin. ISBN 978-1-899618-32-3. MR 0676126. (1st Edn University of Toronto (1938))
Further reading
- Wenninger, Magnus (1974). Polyhedron Models. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-09859-9. (p. 46, Model W26, triakis icosahedron)
- Wenninger, Magnus (1983). Dual Models. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-54325-8. (pp. 42–46, dual to uniform polyhedron W70)
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, (3rd edition, 1973), Dover edition, ISBN 0-486-61480-8, 3.6 6.2 Stellating the Platonic solids, pp.96-104