Romsey Abbey
Romsey Abbey is a parish church of the Church of England in Romsey, a market town in Hampshire, England. Until the dissolution it was the church of a Benedictine nunnery. It is now the largest parish church in the county, since Christchurch Priory is now in Dorset.
| Romsey Abbey | |
|---|---|
Romsey Abbey | |
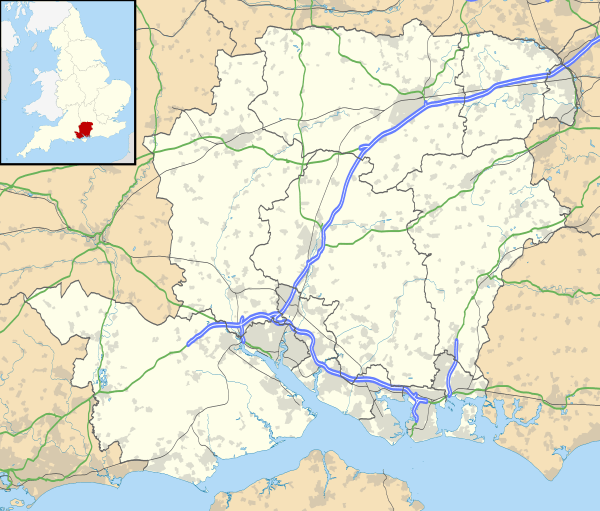 Romsey Abbey  Romsey Abbey  Romsey Abbey | |
| 50°59′23″N 1°30′5″W | |
| OS grid reference | SU3499121325 |
| Location | Romsey, Hampshire |
| Country | United Kingdom |
| Denomination | Church of England |
| Churchmanship | Broad Church |
| Website | www.romseyabbey.org.uk |
| Administration | |
| Parish | Romsey |
| Diocese | Winchester |
| Province | Canterbury |
| Clergy | |
| Vicar(s) | Rev Thomas Wharton |
| Curate(s) | Rev Nik Gower |
Background
The church was originally built during the 10th century, as part of a Benedictine foundation. The surviving church is the town's outstanding feature, which is all the more remarkable because the abbey, as a nunnery, would have been less well financially endowed than other religious establishments of the time.
History

The religious community continued to grow and a village grew around it to keep it supplied with produce. Both suffered in 993 when Viking raiders sacked the village and burnt down the original church. However, the abbey was rebuilt in stone in around 1000 and the village quickly recovered. The abbey and its religious community flourished and were renowned as a seat of learning – especially for the children of the nobility.
In Norman times a substantial, new stone abbey, primarily designed as a convent, was built on the old Anglo-Saxon foundation (circa 1130 to 1140 AD) by Henry Blois, Bishop of Winchester and Abbot of Glastonbury. Bishop Henry was the younger brother of King Stephen and his structure dominates the town to this day. By 1240 in excess of 100 nuns were living in the community.
The rule of Elizabeth Broke was filled with scandal. A commission was held against her for many charges including allowing poor dress standards for nuns, allowing nuns to go to the towns taverns, poor account keeping and an unhealthy relationship with the Chaplain.[1]
The abbey continued to grow and prosper until the Black Death struck the town in 1348-9. While it is thought that as much as half of the population of the town – which was then about 1,000 – died as a result, the number of nuns fell by over 80% to 19. 72 nuns died including Abbess Johanna. After the plague there were never more than 26 nuns in the Abbey.[1]
This so affected the area that the overall prosperity of the abbey dwindled and it was finally suppressed by Henry VIII during the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1539.

However the abbey did not suffer the fate of many other religious establishments at this time and was not demolished, although the community itself was forcibly dispersed. This was because it had, in modern terms, become "dual use" containing a church within a church – a substantial section being dedicated to St Lawrence and used solely by the townspeople.
Subsequently, the town purchased the abbey from the Crown for £100 in 1544 and then set about demolishing that very section, set aside as the church of St Lawrence, that had ensured its survival in the first place.
The abbey survives today not least due to the efforts of the Reverend Edward Lyon Berthon during the 19th century who set about restoring it to some of its former glory. It is now the largest parish church in the county and houses the tomb of Lord Mountbatten of Burma and of Sir William Petty FRS, the great English economist, scientist and philosopher. Mountbatten had been granted the lesser title of Baron Romsey in 1947 on being given his Earldom and lived locally at Broadlands House. On 27 August 1979, Mountbatten, his grandson Nicholas, and two others were assassinated by a bomb set by members of the Provisional Irish Republican Army, hidden aboard his fishing boat in Mullaghmore, County Sligo, Ireland. He was buried in the abbey following a full state funeral in Westminster Abbey.
The current vicar is the Reverend Thomas Wharton, who took up the post in September 2018.[2]
List of Abbesses
| Name | year appointed | year resigned/died | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbey founded | 907 | ||
| Abbess Ælflæda | 907 | Daughter of Edward the Elder, Abbey was built for her. | |
| Abbess Merwinna | 966 | ||
| Abbess Elwina | 992 | ||
| Abbess Æthelflæda | 1003 | ||
| Abbess Wulfynn | 1016 | ||
| Abbess Ælfgyfu | 1042 | ||
| Abbess Cristina | 1093 | Daughter of Edward the Exile | |
| Incomplete records for about a century | [3][4] | ||
| Abbes Hadewisa | 1130 | ||
| Abbess Matildis | 1150 | 1155 | |
| Abbess Princess Mary | 1155 | 1171 | Daughter of King Stephen, left to marry. |
| Abbess Juliana | 1171 | 1174 | |
| Abbess Matilad Patric | 1218 | 1219 | |
| Abbess matilda | 1218 | 1230 | |
| Abbess Matilasa de Barbfle | 1230 | 1231 | |
| Abbess Isabel de Nevil | 1237 | ||
| Abbess Cecilia | 1238 | 1247 | |
| Abbess Constancia | 1247 | 1261 | |
| Abess Amicia de Sulhere | 1261 | 1268 | |
| Abbess Alicia Walerand | 1269 | ||
| Abbess Phillipa de Stokes | 1296 | 1307 | was very infirm as Abbess.[1] |
| Abbess Clementcia de Guildford | 1307 | 1314 | Was very infirm as Abbess.[1] |
| Abbess Alicia de Wyntershulle | 1314 | 1315 | whose murder was never solved.[1] |
| Abbess Sybil Carbonel | 1315 | ||
| Abbess Johanna Icthe | 1333 | ||
| Bubonic plague | 1349 | 80% of the nuns died. | |
| Abbess Johanna Gerney | 1349 | 1351 | |
| Abbess Isabella de Camoys | 1352 | [5][6] | |
| Abbess Lucy Everard | 1396 | ||
| Abbess Felicia Aas[7] | 1405 | 1417 | |
| Abess Matilda Lovell | 1417 | ||
| Abbess Johanna Brydduys | 1462 | 1472 | |
| Abbess Elizabeth Broke | 1472 | 1502 | Her tenure was tainted by scandal. |
| Abbess Joyce Rowse | 1502 | 1515 | |
| Abbess Ann Westbroke | 1515 | 1523 | |
| Abbess Elizabeth Ryprose | 1523 | 1524 | |
| Dissolution of the Abbey | 1539 | [8] |
Bells
The church's bells were once housed in a detached campanile. After its demolition in 1625, the set of six bells was transferred to a wooden belfry on top of the central tower. They were replaced by a new set of eight in 1791; the heaviest, the tenor, weighing 26 cwt.[9] Three of the bells were recast in 1932. The bells and their eighteenth century bell frame were restored in 2007, when removing the crown reduced the weight of the tenor to 22 cwt. The Bells are now known across the region for being one of the finest rings of 8 bells.
Music
Choir
Romsey Abbey has a traditional choir of boy choristers and a back row of adult altos, tenors and basses drawn from the local area. They also have a choir of girls, a senior girls choir, a training choir of youngsters and a consort of voluntary singers and members of the congregation who sing when the choirs are on holiday. Over the years the choirs have recorded multiple CDs, sung for royalty, enjoyed choir tours to numerous UK Cathedrals, Belgium, Italy and France and have a twinning relationship with a German choir from Mülheim an der Ruhr. They have appeared numerous times on BBC Songs of Praise as well as featuring in a BBC Documentary in 2018. The current director of music is Martin Seymour.
Organs
Romsey Abbey has two organs. The main instrument was built by J W Walker & Sons in 1858 and replaced an earlier instrument by Henry Coster. The Walker Organ was rebuilt in its present position and enlarged in 1888. Major restoration work was carried out by J W Walker & Sons Ltd in 1995/96 under the supervision of the abbey's organist Jeffrey Williams, restoring the mechanical actions and overhauling all of the pipe work. 1999 saw the construction of a completely new Nave Organ with pipe work located on the South Triforium. This can be played either from a mobile console in the nave or from the main console.[10]

Organist and master of the choristers
- S.T. Cromwell ???? – 1849[11]
- Francis Wellman
- ??? Beazley
- W. Mason 1864[12] – 1865[13] (afterwards organist of Trinity Church, South Shields)
- E.W. Perren 1866[14] – 1867 (afterwards organist of St Thomas Church, Winchester)
- W. Channon Cornwall 1867[15] – 1876[16]
- William Cary Bliss 1888 – 1899[17]
- J. C. Richards ca. 1907
- R. T. Bevan ca. 1921[18]
- Charles Tryhorn 1926-1957
- Charles Piper 1957-1980
- Anthony Burns-Cox 1980–1990
- Jeffrey Williams 1990–2004
- Robert Fielding 2004–2015 [19]
- George Richford 2015–2018
- Canon Peter Gould 2019–2019 (Interim Director of Music)
- Martin Seymour 2019 - (Director of Music)[20]
Assistant organists
- Jeffrey Williams 1982–1990
- Paul Isted 1991–1996
- Timothy Rogerson 1996–2005
- David Coram 2005–2008
- James Eaton 2008–2010
- Adrian Taylor 2011–present
Titanic connection

One of the Titanic's engineering officers, Arthur (Bob) Ward, who died in the sinking, is commemorated in the Abbey with a plaque in one of the chapels.
St Swithun's, Crampmoor
The village of Crampmoor, to the east of Romsey, is within the ecclesiastical parish of Romsey.[21] St Swithun's, Crampmoor, is Romsey Abbey's daughter church. It was built in the nineteenth century to serve a rural community as both a church and a school. There were originally two other such combined use buildings in the parish; the school moved out from St Swithun's in 1927.[22]
References
- Rev. Thomas Perkins, Bell's Cathedrals: A Short Account of Romsey Abbey, A Description of the Fabric and Notes on the History of the Convent of Ss. Mary & Ethelfleda (Library of Alexandria).
- "New Vicar Appointed". Romsey Abbey. Retrieved 14 April 2019.
- Abbess Cristina at Romsey flourished 1086AD, until probably before 1093AD when her nieces were moved to Wilton Abbey.
- Abbess Eadgyth at Romsey about 1093AD.
- Born 1396AD, Abbess Isabella was the daughter of Ralph de Camoys, Governor of Windsor and his wife Joan, the daughter of Hugh le Despenser, Earl of Winchester. She was sister of Thomas de Camoys, 2nd Baron Camoys. She was appointed Abbess of Romsey 25 November 1352. She appears in the 1366 Will Of the Bishop of Edyndon, and several deeds to the Abbey. She died 1396.
- Douglas Richardson, Magna Carta Ancestry: A Study in Colonial and Medieval Families, 2nd Edition, (Douglas Richardson, 2011) page 397.
- Common Pleas, 1415 Trinity term, “Felicia Aas, abbissa de Romesey”, plaintiff, fourth entry: http://aalt.law.uh.edu/H5/CP40no618/aCP40no618fronts/IMG_0501.htm
- Henry G. D. Liveing, M.A. Records of Romsey Abbey: An account of the Benidictine House of Nunies with Notes on the Parish Church and town.(A.D. 907—1558). Compiled from Manuscript and Printed Records (WARREN AND SON, LTD., 85, HIGH STREET. 1912) page IIX-X.
- Perkins, Thomas (1907). A Short Account of Romsey Abbey. Bell’s Cathedral Guides. London: George Bell & Sons. p. 35.
- National Pipe Organ Register
- Hampshire Advertiser – Saturday 08 August 1868
- Musical Standard, Volume II, 1864
- Newcastle Journal – Saturday 16 September 1865
- Dorset County Chronicle – Thursday 11 January 1866
- Salisbury and Winchester Journal – Saturday 23 February 1867
- Glasgow Herald – Friday 24 March 1876
- Musical Times, 1920
- Dictionary of Organs and Organists. Second Edition. 1921
- Romsey Abbey News, 16 July 2015{{cite web |title=Robert Fielding |url=https://www.romseyabbey.org.uk/2015/07/farewell-robert-fielding-this-sunday/ |website=Romsey Abbey |publisher=Romsey Abbey}
- Romsey Abbey News April 2019Martin, Seymour. "Martin Seymour New Director of Music at Romsey Abbey". Romsey Abbey. Romsey Abbey.
- Map of Romsey parish – achurchnearyou.com
- St Swithun's, Crampmoor, daughter church of Romsey Abbey
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Romsey Abbey. |