Plastic SCM
Plastic SCM is a cross-platform commercial distributed version control tool developed by Códice Software Inc. It is available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and other operating systems. It includes a command-line tool, native GUIs, diff and merge tool and integration with a number of IDEs. It is a full version control stack not based on Git (although it can communicate with it).
| Developer(s) | Codice Software |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 31 October 2006 |
| Stable release | 8.0
/ January 30, 2019 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS |
| Platform | .NET / Mono |
| Size | 93 MB (Windows installer) |
| Type | Revision control |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | www |
Features
Plastic SCM is a full version control stack platform. It includes these components:
Some of its features include:
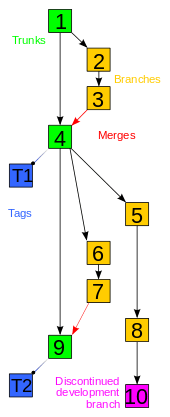
- Support for heavy branching and merging: According to its creators, Plastic can handle unlimited branching and complex merge scenarios[4]
- Visual Branch Explorer: A timeline to represent branches, merges and changes in repositories, implemented in all of its GUIs[5]
- ACL-based security: Every object in the system can be secured with access control lists[6]
- Built-in 3-way merge and side-by-side diff including language-aware support and history of a specific method or function[7]
- Directory versioning and support for versioning renames
- Revision history for branched, renamed, moved, copied, and deleted files
- Blame/Annotate
- Centralized operation (SVN/Perforce style)
- Distributed operation (Git/Mercurial style)
- Atomic commits—the server assures that changesets are committed in the repository entirely
- Shelving—users can save and restore work in progress for task switching
- Support for ASCII, Unicode, binary, symbolic link (on Unix), Mac-specific, and UTF-16 files
- Support for Mac OS X, Windows and Linux platforms
- Server-side and client-side event triggers[8]
- High-latency network support: The network protocol used by Plastic is optimized for high-speed/high-latency networks[9]
- Gluon: GUI and workflow for non-developers (specially focused on game development)[10]
- Locking: Binary files and assets that can't be merged can use locking instead of branching/merging[11]
Design
Plastic is a client/server system although in current terms of version control it can also be defined as a distributed revision control system, due to its ability to have very lightweight servers on the developer computer and push and pull branches between servers (similar to what Git and Mercurial do). Developers work on files in their client workspaces, and check in changed files together in changesets.
Storage
Plastic SCM has 2 different families of storage for all its data and metadata:
- Jet: An ad-hoc storage designed for high-performance, released with version 6.0. It is now the default storage.
- Relational databases: Traditionally Plastic supported storing all data and metadata in relational databases: MySQL, SQL Server, SQLite, SQL Server Compact Edition, Firebird, Firebird Embedded, Postgresql and Oracle. Relational databases are still supported although Jet is now the default option.[12]
Modes of operation
Plastic can work in 2 modes:
- Centralized: With workspaces (working copies) connected directly to a server. Users perform checkin operations without the need for an additional push step.
- Distributed: Users host their own repositories on their computers and push/pull to a central server.[13]
Differences with Git
Plastic SCM is not based on Git although it can act as a Git server and a Git client. Differences can be summarized as: improvements in merge, native support for large files and projects, optional file-locking, can work distributed and centralized. There are differences in the branching structure too: while in Git branches are just pointers, in Plastic branches are containers. Plastic versions directories and files identifying them with "item ids" which is good for move/rename tracking, while Git relies on diffs to rebuild the renames/moves and doesn't version directories.[14]
Interoperability with other version control systems
Git
Plastic can interoperate with Git in the following ways:
- GitSync: Every Plastic client can push and pull from a Git repository.[15]
- GitServer: A Plastic server can act as a Git server, so any git client can push/pull to a Plastic server.
- Fast-import/export support: Fast-export and fast-import commands are available to export Plastic repositories to Git intermediate format and import from Git intermediate format.[16]
Perforce
Plastic can do bi-directional sync with Perforce depots to ease migration[17]
Other version controls
Import/export from other systems is achieved through Git's fast-import/export format.
Availability, release cycle and supported platforms
Plastic SCM is available to download from the plasticscm.com website. Major releases are published yearly as pre-built executables for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux.[18]
Minor releases are available on a weekly basis.
Licensing and terms of use
Plastic SCM is free for individuals (Personal Edition), non-profit organizations and open-source projects (Community Edition).
Cloud Edition is a commercial version for teams that do not need an on-premise server. Customers pay per active monthly user and cloud storage. The subscription includes all the Plastic SCM software.
Team Edition is a commercial version for teams under 15 users that need an on-premise server. The subscriptions are monthly or annual and includes all the Plastic SCM software.
Enterprise Edition is a commercial version for teams over 15 users, typically used by corporations. It can be purchased in perpetual edition mode or with a monthly or annual subscription.[19]
History
Codice Software started in August 2005 backed by an angel investor and the founders.[20] The goal was to create a version control stronger than SVN in branching and merging and more affordable for SME than the commercial alternatives available at the time. In October 2006, they released the first version of Plastic SCM and was officially presented in Tech Ed 2006 in Barcelona.[21][22]
In 2007, Codice was the first Spanish SME to achieve CMMI L2 using SCRUM.[23]
Plastic SCM was featured by Novell as one of the companies using Mono commercially.[24]
Plastic SCM 2.0 was launched on March 2008.[25]
In 2009, Codice secures its first round of VC backed by Bullnet Capital, a Spanish firm specializing in tech companies.[26]
Plastic SCM was a Jolt Award finalist in the Change and Configuration Management category, announced in December 2008.[27]
Plastic SCM 3.0 was launched in July 2010[28] and it featured Xdiff/Xmerge: their first approach to track moved code in diffs and merges.
In December 2010, Plastic SCM announces "method history", a feature that allows the user to calculate the history of a given method/function instead of the history of a full file.[29]
In 2011, Francisco Monteverde joined the company as CEO while Pablo Santos, founder, was appointed as CTO and President of the board.[30]
Plastic SCM 4.0 was launched on November 23, 2011[31][32] and introduced a major change in the internal design: versioning and merge tracked was moved from a per-file approach to a per-changeset approach, which helped improving later Git-interop.[33]
Since 4.0, Plastic started to be more oriented towards game development, specially considering the weaknesses of Git in terms of big repositories and files.[34]
Version 4.1 was launched in April 2012.[35]
In 2013, Codice launches SemanticMerge, a tool that diffs and merges based on code structure and not text.[36] The technology was later integrated inside Plastic. Semantic builds on top of the previous work done on the Xdiff/Xmerge tool. Later that year Semantic added Java support to complement the initial .NET offering.[37] Pablo Santos introduced cross-file diff and merge detection in QCon 2013 in San Francisco.[38]
In 2013, Plastic SCM started natively supporting the Git network protocol, which virtually converts any Plastic installation into a Git client.[39]
Plastic SCM 5.0 is launched in September 2013.[40] It features built-in semantic diff, refactor detection[41] and method history.[42] Other features are path based security, client changelists and improved cloaked rules.
Version 5.4 later expands some of these features and add a few more: encrypted servers, JavaCLI (a Java client to support HP-UX and Solaris scripting), multi-core file upload and download, Plastic Gluon (developed in collaboration with Telltale [43]), a GUI for artists in game development, WAN optimized data transfer, submodules, transformable workspaces. Plastic 5.4 evolves as Plastic's primary version and in December 2014 a new native GUI for Linux is launched replacing the previous cross-platform one.[44] 5.4 includes a new native MacOS GUI too.
In January 2016, Plastic Cloud was launched as a cloud repo hosting system.[45]
In March 2016, Plastic Cloud Edition was launched, a new version designed for teams who do not need an on-premise server.[46]
Version 6.0 was finally released in January 2017.[47] It features a new data storage system called Jet, full backwards compatibility up to 5.0 and floating licenses support. 6.0 continues evolving during 2017.
Plastic SCM 7.0 was launched in March 2018[48] including a new Branch Explorer design, new web-based administration interface, and improvements in MacOS and Linux GUIs.
The mergebots feature was launched in September 2018. Mergebots are a way to implement DevOps with server-side agents that detect when branches have to be merged after testing them on a CI system.[49] Plastic SCM 8.0 was released in January 2019.
See also
- List of revision control software
- Comparison of revision control software
Notes
- XDIFF AND XMERGE
- WebUI: redesigned web interface for Plastic
- webadmin – introducing the new server admin tool
- mergeMachine
- Branch Explorer
- SECURITY
- Semantic Version Control
- TRIGGERS GUIDE
- Optimized network channel for high latency
- Gluon: Version Control for Artists
- PLASTIC SCM ADMINISTRATOR'S GUIDE: Chapter 7: Configuring exclusive checkout (Lock)
- The story of Jet: Plastic's super-fast repo storage
- Plastic SCM – DVCS at Enterprise Level
- Plastic SCM vs Git — 2018 edition
- GitSync for Plastic SCM with Native Git Protocols and Visual Studio 2012 Support
- PLASTIC SCM HIGHLIGHTS FOR GIT USERS
- [reference: https://www.plasticscm.com/perforce Plastic SCM for Perforce teams]
- Miguel de Icaza on Plastic SCM UI on Linux and Mac OS X
- Major PlasticSCM Updates
- LinkedIn: Pablo Santos
- SIMO 2006
- Plastic SCM – DVCS at Enterprise Level Plastic SCM – DVCS at Enterprise Level
- Codice Software shows off new SCM tool
- Companies using Mono
- Plastic SCM 2.0 set for parallel development projects
- Innova.- La entidad de capital riesgo Bullnet Capital entra en el accionariado de la vallisoletana Códice Software
- Embarcadero products are Jolt Award finalists in several categories
- Codice includes XMerge/XDiff 2.0 in Plastic SCM release
- Announcing the method history
- Francisco Monteverde se convierte en el nuevo CEO de Códice Software
- Plastic SCM 4.0 Launch: new features in Plastic SCM 4.0 by Pablo Santos
- Codice Software Launches Plastic SCM 4.0; Challenges Git and Perforce in DVCS
- Plastic internals: de 3.0 a 4.0
- Codice Software Unveils Plastic SCM 4.0 for Game Development, Successful Collaboration With Digital Legends Entertainment
- Plastic SCM Pays Attention to Detail in Source Code Management
- A Merge Tool that Understands Functions
- Codice Add Java Support to their Code-Aware Merging Tool
- InfoQ - QCon San Francisco 2013 - Refactoring in the DVCS Age - Enter Semantic Merge
- GitSync for Plastic SCM with Native Git Protocols and Visual Studio 2012 Support
- Two new Plastic SCM versions are out today
- Semantic Version Control
- Plastic SCM features
- How Telltale Games handles version control
- Native Linux GUI – gtkplastic
- Plastic Cloud is now out!
- Plastic SCM Cloud Edition
- Release 6.0.16.804
- Release 7.0.16.2047
- Add a mergebot to your repo!
References
- Krill, Paul (2008-03-24), "Plastic SCM 2.0 set for parallel development projects", InfoWorld, retrieved 2012-03-14
- Feinman, Jeff (2009-12-01), "Codice branches out with new version of SCM tool", SD Times, retrieved 2012-03-14
- Norfolk, David (2007-07-30), "Codice Software shows off new SCM tool", The Register, retrieved 2012-03-14
- Serignese, Katie (2010-07-15), "Codice includes XMerge/XDiff 2.0 in Plastic SCM release", SD Times, retrieved 2012-03-14
- McConnel, Toni (2010-04-27), "ESC — Embed-X incorporates first Agile dev framework for critical software processes", EE Times, retrieved 2012-03-14
- Santos, Pablo (2007-08-02), "SCRUM Meets CMMi", Dr. Dobb's Journal, retrieved 2012-03-14