NATO Accessory Rail
The NATO Accessory Rail (or NAR), defined by the new modernization agreement Standardization Agreement 4694, is a new rail interface system standard for mounting accessory equipments such as telescopic sights, tactical lights, laser aiming modules, night vision devices, reflex sights, foregrips, bipods and bayonets to small arms such as rifles and pistols.[1]

STANAG 4694, was approved by the NATO Army Armaments Group (NAAG), Land Capability Group 1 Dismounted Soldier (LCG1-DS) on 8 May 2009. It will be forwarded to the NATO Standardization Agency and then onto individual NATO nations, which will test the NATO Accessory Rail system for final ratification.[2]
The NATO Accessory Rail is backwards-compatible with the STANAG 2324/MIL-STD 1913 Picatinny rail, which dates back to 3 February 1995,[3] and was designed in conjunction with weapon specialists like Aimpoint, Beretta, Colt Firearms, FN Herstal and Heckler & Koch. The Heckler & Koch G28 designated marksman rifle features NATO Accessory Rails.[4]
Technical specifications
According to the NATO Army Armaments Group the differences between the MIL-STD 1913 Picatinny rail and the STANAG 4694 are:
- A metric reference drawing.
- Additional new measurements and tolerances.
- Adjustments of some measurements.
- Tighter straightness tolerances (approximately 50%).
Another notable change is the recommendation that while in the Picatinny rail system the V-angles are used for the alignment and reference of the accessory, NATO recommends using the top surface instead. Initial NATO tests had shown that the Picatinny rail system did not provide good repeatability. Using the top surface as a reference and alignment of the grabbers provided excellent repeatability.
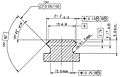 STANAG 4694 "NATO Accessory Rail" metric reference drawing (dimensions in millimetres).
STANAG 4694 "NATO Accessory Rail" metric reference drawing (dimensions in millimetres).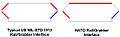 STANAG 4694 "NATO Accessory Rail" Rail - Grabber interfaces.
STANAG 4694 "NATO Accessory Rail" Rail - Grabber interfaces.
Further plans
Further plans are underway to develop a NATO standard to provide electrical power to rail mounted accessories in the future.[5] Currently, Wilcox Industries, in cooperation with Surefire, is working on the creation of a railed forend for an AR-15 that will power battery-reliant accessories such as tactical lights and laser sights. Accessories are intended to be powered by one central battery pack or via their proprietary vertical grip, the Universal Control Grip.[6]
See also
- Rail Integration System, generic term for a system for attaching accessories to small firearms
- Weaver rail mount, early system used for scope mounts, still has some popularity in the civilian market
- Picatinny rail (MIL-STD-1913), improved and standardized version of the Weaver mount. Used for both for scope mounts, and for accessories (such as extra sling mounts, vertical grips, bipods etc.) Major popularity in the civilian market.
- Warsaw Pact rail, is a rail mount system to connect telescopic sights to rifles
- UIT rail, an older standard used for mounting slings particularly on competition firearms
- KeyMod - open standard design to replace MIL-STD-1913 for mounting accessories (except for scope mounts)
- M-LOK - free licensed competing standard to KeyMod
- Zeiss rail, a ringless scope mounting standard
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to NATO Accessory Rail. |
- Weapons & Sensors, NATO Army Armaments Group
- NATO countries finalise plans for a standard rail adaptor system
- Military Standard 1913 - Dimensioning of accessory mounting rail for small arms weapons Archived 2010-11-26 at the Wayback Machine
- Heckler & Koch G28
- Powered Rail Presentation to Intl Infantry & Joint Service Small Arms System Symposium, May 20, 2009 Archived September 24, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- Wilcox Industries Develops a "Power Rail" For ARs