N-Acetylmuramic acid
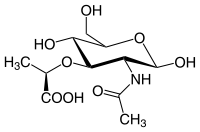
N-Acetylmuramic acid, or MurNAc, is the ether of lactic acid and N-acetylglucosamine with the chemical formula C
11H
19NO
8. It is part of a biopolymer in the bacterial cell wall, which is built from alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc), cross-linked with oligopeptides at the lactic acid residue of MurNAc. This layered structure is called peptidoglycan.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.092 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H19NO8 | |
| Molar mass | 293.272 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
MurNAc is a monosaccharide derivative of N-acetylglucosamine.
Clinical significance
N-Acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) is part of the peptidoglycan polymer of bacterial cell walls. MurNAc is covalently linked to N-acetylglucosamine and may also be linked through the hydroxyl on carbon number 4 to the carbon of L-alanine. A pentapeptide composed of L-alanyl-D-isoglutaminyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine is added to the MurNAc in the process of making the peptidoglycan strands of the cell wall.
Synthesis is inhibited by fosfomycin.[1]
References
- Grif K, Dierich MP, Pfaller K, Miglioli PA, Allerberger F (2001). "In vitro activity of fosfomycin in combination with various antistaphylococcal substances". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 48 (2): 209–217. doi:10.1093/jac/48.2.209. PMID 11481290.