Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare,[2] but geological formations containing land animal fossils include the Forest Marble Formation in England, the Kilmaluag Formation in Scotland,[3] the Daohugou Beds in China, the Itat Formation in Russia, and the Isalo III Formation of western Madagascar.
| Middle Jurassic Epoch 174.1–163.5 million years ago | |
Ages in the Middle Jurassic -174 — – -173 — – -172 — – -171 — – -170 — – -169 — – -168 — – -167 — – -166 — – -165 — – -164 — – -163 — Ages of the Middle Jurassic. Axis scale: millions of years ago. |
| System/ Period |
Series/ Epoch |
Stage/ Age |
Age (Ma) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cretaceous | Lower/ Early |
Berriasian | younger | |
| Jurassic | Upper/ Late |
Tithonian | ~145.0 | 152.1 |
| Kimmeridgian | 152.1 | 157.3 | ||
| Oxfordian | 157.3 | 163.5 | ||
| Middle | Callovian | 163.5 | 166.1 | |
| Bathonian | 166.1 | 168.3 | ||
| Bajocian | 168.3 | 170.3 | ||
| Aalenian | 170.3 | 174.1 | ||
| Lower/ Early |
Toarcian | 174.1 | 182.7 | |
| Pliensbachian | 182.7 | 190.8 | ||
| Sinemurian | 190.8 | 199.3 | ||
| Hettangian | 199.3 | 201.3 | ||
| Triassic | Upper/ Late |
Rhaetian | older | |
| Subdivision of the Jurassic system according to the ICS, as of 2020.[1] | ||||
Paleogeography
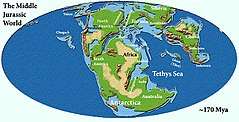
During the Middle Jurassic epoch, Pangaea began to separate into Laurasia and Gondwana, and the Atlantic Ocean formed. Eastern Laurasia was tectonically active as the Cimmerian plate continued to collide with Laurasia's southern coast, completely closing the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. A subduction zone on the coast of western North America continued to create the Ancestral Rocky Mountains.
Fauna
The Middle Jurassic is one of the key periods in the evolution of life on earth. Many groups, including dinosaurs and mammals, diversified during this time.[4][5]
Marine life
During this time, marine life (including ammonites and bivalves) flourished. Ichthyosaurs, although common, are reduced in diversity; while the top marine predators, the pliosaurs, grew to the size of killer whales and larger (e.g. Pliosaurus, Liopleurodon). Plesiosaurs became common at this time, and metriorhynchid crocodilians first appeared.
Terrestrial life
Many of the major groups of dinosaurs emerged during the Middle Jurassic, (including cetiosaurs, brachiosaurs, megalosaurs and primitive ornithopods).[4]
Descendants of the therapsids, the cynodonts, were still flourishing along with the dinosaurs. These included the tritylodonts and mammals. Mammals remained quite small, but were diverse and numerous in faunas from around the world.[6][7] Tritylodonts were larger, and also had an almost global distribution.[8] The first crown group mammals appeared in the Middle Jurassic. A group of cynodonts, the trithelodonts, were becoming rare and eventually became extinct at the end of this epoch.
Flora
Conifers were dominant in the Middle Jurassic. Other plants, such as ginkgoes, cycads, and ferns were also common.
References
- http://www.stratigraphy.org/index.php/ics-chart-timescale
- Clark, James (June 2009). "Evolutionary Transitions Among Dinosaurs: Examples from the Jurassic of China". Evolution: Education and Outreach. 2 (2): 243–244. doi:10.1007/s12052-009-0137-0.
- British Geological Survey. 2011. Stratigraphic framework for the Middle Jurassic strata of Great Britain and the adjoining continental shelf: research report RR/11/06. British Geological Survey, Keyworth, Nottingham.
- Benson RBJ, Campione NE, Carrano MT, Mannion PD, Sullivan C, Upchurch P, and Evans DC. 2014. Rates of dinosaur body mass evolution indicate 170 million years of sustained ecological innovation on the avian stem lineage. PLoS Biology 12, no. 5: e1001853.
- Close, Roger A.; Friedman, Matt; Lloyd, Graeme T.; Benson, Roger B.J. (2015). "Evidence for a mid-Jurassic adaptive radiation in mammals". Current Biology. 25 (16): 2137–2142. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.06.047. PMID 26190074.
- Kielan-Jaworowska, Z., Cifelli, R.L., and Luo, Z.-X. 2004. Mammals from the age of dinosaurs: origins evolution and structure. 630 pp. Columbia University Press, New York.
- Panciroli, E. 2017. The First Mammals Palaeontology Online.
- Kemp, T 2005. The Origin and Evolution of Mammals. Oxford University Press.