Lycopodium
Lycopodium (from Greek lukos, wolf and podion, diminutive of pous, foot) is a genus of clubmosses, also known as ground pines or creeping cedars,[2] in the family Lycopodiaceae. Two very different circumscriptions of the genus are in use. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), Lycopodium is one of nine genera in the subfamily Lycopodioideae, and has from 9 to 15 species.[1][3] In other classifications, the genus is equivalent to the whole of the subfamily, since it includes all the other genera. There are then more than 40 accepted species.[4]
| Lycopodium | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Lycopodium clavatum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Lycophytes |
| Class: | Lycopodiopsida |
| Order: | Lycopodiales |
| Family: | Lycopodiaceae |
| Subfamily: | Lycopodioideae |
| Genus: | Lycopodium L.[1] |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Description
They are flowerless, vascular, terrestrial or epiphytic plants, with widely branched, erect, prostrate or creeping stems, with small, simple, needle-like or scale-like leaves that cover the stem and branches thickly. The leaves contain a single, unbranched vascular strand and are microphylls by definition. The kidney-shaped or reniform spore-cases (sporangia) contain spores of one kind only[5] (isosporous, homosporous) and are borne on the upper surface of the leaf blade of specialized leaves (sporophylls) arranged in a cone-like strobilus at the end of upright stems. The club-shaped appearance of these fertile stems gives the clubmosses their common name.
Lycopods reproduce asexually by spores. The plants have an underground sexual phase that produces gametes, and this alternates in the lifecycle with the spore-producing plant. The prothallium developed from the spore is a subterranean mass of tissue of considerable size and bears both the male and female organs (antheridia and archegoniae).[5] However, they are more commonly distributed vegetatively through above- or below-ground rhizomes.
Taxonomy
The genus Lycopodium was first published by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.[6] He placed it in the Musci (mosses) along with genera such as Sphagnum and included species such as Lycopodium selaginoides,[7] now placed in the genus Selaginella in a different order to Lycopodium. Different sources use substantially different circumscriptions of the genus. Traditionally, Lycopodium was considered to be the only extant genus in the family Lycopodiaceae, so including all the species in the family, although sometimes excluding one placed in the monotypic genus Phylloglossum.[8] Other sources divide Lycopodiaceae species into three broadly defined genera, Lycopodium, Huperzia (including Phylloglossum) and Lycopodiella. In this approach, Lycopodium sensu lato has about 40 species.[9][4] In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), the broadly defined genus is equivalent to the subfamily Lycopodioideae, and Lycopodium is one of 16 genera in the family Lycopodiaceae, with between 9 and 15 species.[1][3]
| Traditional[8] | Christenhusz & Chase (2014)[9] | PPG I[3] |
|---|---|---|
| Lycopodium + Phylloglossum | Lycopodium s.l. | Lycopodium s.s. + 8 other genera making up subfamily Lycopodioideae |
| Two other genera | 7 genera (including Phylloglossum) in two subfamilies |
Species
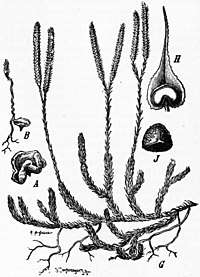
Using the narrow circumscription of Lycopodium, in which it is one of nine genera in the subfamily Lycopodioideae, the Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World recognized the following species as of December 2019:[1]
- Lycopodium clavatum L. – stag's-horn clubmoss; subcosmopolitan
- Lycopodium diaphanum (P.Beauv.) Sw. – Tristan da Cunha
- Lycopodium hygrophilum Alderw. – New Guinea
- Lycopodium japonicum Thunb. – eastern Asia (Japan west and south to India and Sri Lanka)
- Lycopodium lagopus (Laest. ex C.Hartm.) Zinserl. ex Kuzen. – circumpolar arctic and subarctic
- Lycopodium papuanum Nessel – New Guinea
- Lycopodium pullei Alderw. – New Guinea
- Lycopodium venustulum Gaudich. – Hawaii, Western Samoa, the Society Islands
- Lycopodium vestitum Desv. ex Poir. – northwest South America (Andes)
Using the broader circumscription of the genus, Plants of the World Online recognized the following additional Lycopodium species as of December 2019.[4] Using the narrow circumscription of the genus Lycopodium, the Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World divided them among eight other genera:[10]
- Lycopodium alpinum L. = Diphasiastrum alpinum
- Lycopodium annotinum L. = Spinulum annotinum
- Lycopodium assurgens Fée = Austrolycopodium assurgens
- Lycopodium carolinum (Lawalrée) J.P.Roux = Diphasiastrum carolinum
- Lycopodium casuarinoides Spring = Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides
- Lycopodium complanatum L. = Diphasiastrum complanatum
- Lycopodium confertum Willd. = Austrolycopodium confertum
- Lycopodium dendroideum Michx. = Dendrolycopodium dendroideum
- Lycopodium deuterodensum Herter = Pseudolycopodium densum
- Lycopodium digitatum Dill. ex A.Braun = Diphasiastrum digitatum
- Lycopodium erectum Phil. = Austrolycopodium erectum
- Lycopodium fastigiatum R.Br. = Austrolycopodium fastigiatum
- Lycopodium fawcettii F.E.Lloyd & Underw. = Diphasiastrum fawcettii
- Lycopodium gayanum Brongn. = Diphasium gayanum
- Lycopodium habereri House = Diphasiastrum habereri
- Lycopodium hickeyi (Beitel & R.C.Moran) W.H.Wagner, Beitel & R.C.Moran = Dendrolycopodium hickeyi
- Lycopodium juniperoideum Sw. = Dendrolycopodium juniperoideum
- Lycopodium jussiaei Desv. = Diphasium jussiaei
- Lycopodium lawessonianum B.Øllg. = Diphasium lawessonianum
- Lycopodium madeirense J.H.Wilce = Diphasiastrum madeirense
- Lycopodium magellanicum (P.Beauv.) Sw. = Austrolycopodium magellanicum
- Lycopodium multispicatum J.H.Wilce = Diphasiastrum multispicatum
- Lycopodium nikoense Franch. & Sav. = Diphasiastrum nikoense
- Lycopodium obscurum L. = Dendrolycopodium obscurum
- Lycopodium oellgaardi (Stoor, Boudrie, Jérôme, K.Horn & Bennert) B.Bock = Diphasiastrum oellgaardii
- Lycopodium paniculatum Desv. = Austrolycopodium paniculatum
- Lycopodium platyrhizoma J.H.Wilce = Diphasiastrum platyrhizoma
- Lycopodium sabinifolium Willd. = Diphasiastrum sabinifolium
- Lycopodium scariosum G.Forst. = Diphasium scariosum
- Lycopodium sitchense Rupr. = Diphasiastrum sitchense
- Lycopodium spectabile Blume = Pseudodiphasium volubile
- Lycopodium subarcticum V.N.Vassil. = Spinulum annotinum ssp. alpestre
- Lycopodium thyoides Willd. = Diphasiastrum thyoides
- Lycopodium tristachyum Pursh = Diphasiastrum tristachyum
- Lycopodium volubile G.Forst. = Pseudodiphasium volubile
- Lycopodium yueshanense C.M.Kuo = Diphasiastrum yueshanense
- Lycopodium zanclophyllum J.H.Wilce = Diphasiastrum zanclophyllum
- Lycopodium × zeilleri (Rouy) Greuter & Burdet = Diphasiastrum zeilleri
Uses
The spores of Lycopodium species are harvested and are sold as lycopodium powder.
Lycopodium sp. herb has been used in the traditional Austrian medicine internally as tea or externally as compresses for treatment of disorders of the locomotor system, skin, liver and bile, kidneys and urinary tract, infections, rheumatism, and gout,[11] though claims of efficacy are unproven. It has also been used in some United States government chemical warfare test programs such as Operation Dew. Lycopodium powder was also used to determine the molecular size of oleic acid.
References
- Hassler, Michael & Schmitt, Bernd (November 2019). "Lycopodium". Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World. 8.11. Retrieved 2019-12-09.
- The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition, 2008
- PPG I (2016). "A community-derived classification for extant lycophytes and ferns". Journal of Systematics and Evolution. 54 (6): 563–603. doi:10.1111/jse.12229.
- "Lycopodium L.". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 2019-12-09.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 17 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 153.
- "Lycopodium L". The International Plant Names Index. Retrieved 2019-12-21.
- Linnaeus, C. (1753). "Lycopodium". Species Plantarum. vol. II. pp. 1100ff. Retrieved 2019-12-21.
- Sporne, K.R. (1966). The Morphology of Pteridophytes (2nd ed.). London: Hutchinson. chap. 4. OCLC 253704767.
- Christenhusz, Maarten J.M. & Chase, Mark W. (2014). "Trends and concepts in fern classification". Annals of Botany. 113 (9): 571–594. doi:10.1093/aob/mct299. PMC 3936591. PMID 24532607.
- Hassler, Michael & Schmitt, Bernd (November 2019). Checklist of Ferns and Lycophytes of the World. 8.11. Retrieved 2019-12-09.
- Vogl, S; Picker, P; Mihaly-Bison, J; Fakhrudin, N; Atanasov, A. G.; Heiss, E. H.; Wawrosch, C; Reznicek, G; Dirsch, V. M.; Saukel, J; Kopp, B (2013). "Ethnopharmacological in vitro studies on Austria's folk medicine--an unexplored lore in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of 71 Austrian traditional herbal drugs". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 149 (3): 750–71. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.007. PMC 3791396. PMID 23770053.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lycopodium. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Lycopodium |
- Species list (takes a broad view of the genus, including the species here separated in the genus Diphasiastrum)
- Burning Lycopodium Powder: Simulating a Grain Elevator Explosion by Kevin A. Boudreaux