List of cities in Malaysia
This is a list of cities of Malaysia. In Malaysia, there are populated areas which are granted city status (bandar raya) by law. However, there are also highly urbanised and populated areas which does not have city status, but are sometimes colloquially also referred to as cities. City status is granted to a place within a local government area. Other populated areas which do not have city status are legally categorised as municipalities or towns.
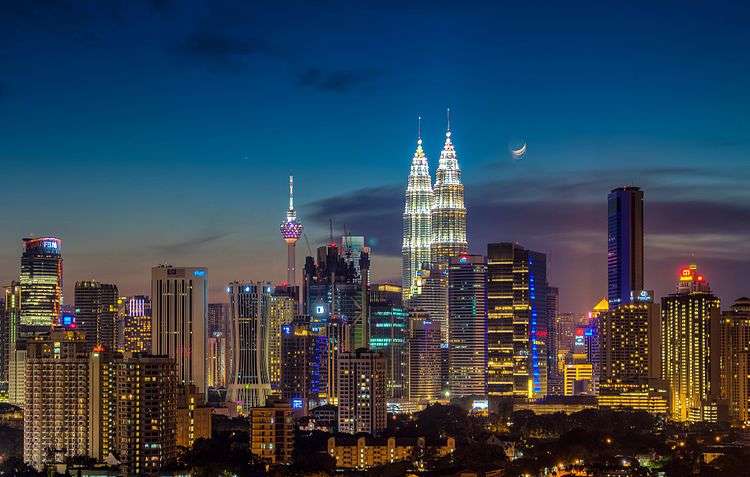



Cities of Malaysia
The following is a list of places in Malaysia in order by the date they were granted city status.
- Former city within Malaysia
| Name | State | Local government | Chartered | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore | Singapore City Council | 22 September 1951 | expelled from the Malaysian Federation on 9 August 1965 |
Penang
George Town became a city on 1 January 1957 by a royal charter granted by Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II, becoming the first town in the Federation of Malaya to become a city (Singapore became a city in 1951). The royal charter stated that :
"... the said Municipality of George Town shall on the First Day of January in the year of Our Lord One thousand nine hundred and fifty seven and forever thereafter be a city and shall be called and styled the CITY OF GEORGE TOWN instead of the Municipality of George Town and shall thenceforth have all such rank, liberties, privileges and immunities as are incident to a City."
However, local government elections were abolished by the federal government in 1965, and the functions of the City Council were transferred to the Chief Minister of Penang in 1966. A Municipal Council for the whole of Penang Island, the Penang Island Municipal Council, was set up between 1974 and 1976.
Although the city status of George Town was never officially revoked, George Town's existence as a corporate entity was in doubt, let alone as a city. This is similar to the position of the former city of Rochester in England, the site of England's second-oldest cathedral, which had been a city from 1211 until 1998, when it was merged with a neighbouring borough. As the new council was not granted city status, and the city through oversight failed to appoint charter trustees to inherit the city charter, the city ceased to exist.
This view was disagreed with by most local residents, who held that as George Town's city status has never been revoked, it remains a city to this day. According to lawyer, Datuk Anwar Fazal, George Town "legally has been and is still a city because the City of George Town Ordinance 1957 had not been repealed".[3] As city status is a matter of law, the actual legal position will depend on an analysis of the City Council of Penang (Transfer of Functions) Order 1966 and the Local Government Act 1976.
On 1 January 2015, the Malaysian federal government upgraded the Penang Island Municipal Council into the present-day Penang Island City Council, thereby expanding the city limit of George Town to encompass the entirety of Penang Island, as well as a handful of surrounding islets.[1][2]
Subsequent cities
The royal charters for Kuala Lumpur, Kuching, Kota Kinabalu, Shah Alam, Malacca City, Alor Setar and Miri were from the Malaysian head of state, the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, while Ipoh, Johor Bahru and Iskandar Puteri were granted by their respective state sultans.[4] Malacca City was declared a "historical city" prior to being granted city status in 2003.
Kuala Lumpur, the largest city, is the federal capital and a federal territory, but as of 2003, most government executive bodies are moving to the new administrative capital and federal territory of Putrajaya.
Criteria
Among the latest (2008) basic criteria for granting City status on a local government is that it has a minimum population of 500,000 and an annual income of not less than RM 100 million.[5]
Locations of cities
Population
Kuala Lumpur is by far the largest urban area as well as the largest metropolitan area in Malaysia. George Town, the capital city of Penang, is the second largest city in Malaysia and the heart of Malaysia's second largest conurbation. To the south, the twin cities of Johor Bahru and Iskandar Puteri form the core of the third largest metropolitan area in the country. Other metropolitan areas with a population of more than 500,000 include Ipoh, Kuching and Kota Kinabalu.
The following table shows the largest cities by population in Malaysia.
Gallery
- Cities of Malaysia
 1. Kuala Lumpur
1. Kuala Lumpur
 3. George Town
3. George Town 4. Ipoh
4. Ipoh.jpg)
 6. Shah Alam
6. Shah Alam- 7. Seremban
 8. Johor Bahru
8. Johor Bahru- 9. Melaka
 10. Kota Kinabalu
10. Kota Kinabalu 11. Alor Setar
11. Alor Setar.jpg) 12. Kuala Terengganu
12. Kuala Terengganu 13. Kuching
13. Kuching- 14. Miri
See also
References
- Cavina Lim (25 March 2015). "Penang's First Mayor A Woman". The Star. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- "George Town meliputi 'pulau', jelas Datuk Bandar" (PDF). Buletin Mutiara. 1 May 2015.
- "Seberang Prai achieves city status". The Star Online. 16 September 2019. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- "Sultan of Johor launches Mersing Harbour Centre". NST Online. 2017-09-10. Retrieved 2017-11-21.
- "Criteria Status for Local Authority". Local Government Department. 30 June 2011. Archived from the original on 15 July 2015. Retrieved 24 April 2012.
External links
- Map at Archive.today (archived 2013-01-05)
- Population of cities in Malaysia from World Gazetteer at Archive.today (archived 2012-12-09)