Lillian, Alabama
Lillian is an unincorporated community in eastern Baldwin County, Alabama, United States. Lillian is located on U.S. Route 98 on the western shore of Perdido Bay, 9.5 miles (15.3 km) east of Elberta.
Lillian, Alabama | |
|---|---|
county_park_at_lillian_alabama_(8638118965).jpg) County park at Lillian, Alabama | |
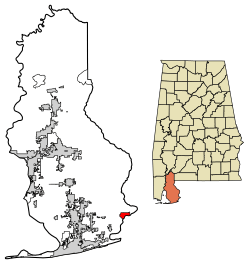 Location of Lillian in Baldwin County, Alabama. | |
 Lillian, Alabama Location within the state of Alabama  Lillian, Alabama Lillian, Alabama (the United States) | |
| Coordinates: 30°24′47″N 87°26′13″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alabama |
| County | Baldwin |
| Government | |
| • Type | Baldwin Cty. Lillian is unincorporated |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3.53 sq mi (9.14 km2) |
| • Land | 1.91 sq mi (4.94 km2) |
| • Water | 1.62 sq mi (4.20 km2) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 117 |
| • Estimate (2016)[2] | N/A |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (CST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| FIPS code | 01-42928 |
History
The community was named for Lillian Kee, the daughter of William Thomas Kee, postmaster.[3] In 1630, the King of Spain gave land grants to the Suarez family that included the current site of Lillian.[4] The Baldwin Colonization Company purchased the area around Lillian in 1923 to promote the area as a resort location. Lillian was once home to a school and hotel.[5] The hotel was originally located in Elberta then dismantled and moved to Lillian.[6]
The Lillian post office was established in 1884.[7]
The Perdido Bay Bridge, which spans Perdido Bay from Lillian to Florida, was first constructed in 1916. The bridge replaced a ferry that operated between Alabama and Florida.[5] The original bridge was operated by the Perdido Bay Bridge and Ferry Company, but ownership was transferred to the states of Alabama and Florida when a second bridge was completed in 1930.[8] The bridge was originally operated as a toll bridge, but tolls were discontinued in 1943.[9] The current bridge was completed in 1980.[5]
The Old Spanish Cemetery in Lillian includes burials from as early as the 16th century.[10][11]
The Lillian Swamp is managed as a nature preserve as part of the Forever Wild Land Trust.[12] The swamp is also listed as an Alabama Gulf Ecological Management Site due to its importance as an estuarine habitat and stopover for migratory birds.[13]
References
- "2016 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved Jul 17, 2017.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- Foscue, Virginia (1989). Place Names in Alabama. Tuscaloosa: The University of Alabama Press. p. 84. ISBN 0-8173-0410-X.
- O. Lawrence Burnette (2007). Historic Baldwin County: A Bicentennial History. HPN Books. p. 6. ISBN 978-1-893619-80-7.
- "Historic markers placed at boat launch, church in Lillian". Gulf Coast News Today. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- Harriet Brill Outlaw; Penny H. Taylor (2013). Foley. Arcadia Publishing. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-7385-9869-7.
- Helbock, Richard W. (2007) United States Post Offices, Volume VIII - The Southeast, p. 124, Scappoose, Oregon: La Posta Publications
- United States. Department of State (1929). United States Statutes at Large: 1927-1929. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 1510.
- "Lillian Bridge Toll End". Fort Lauderdale News. 10 December 1943. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- AL-59 Relocation, Foley to I-10, Baldwin County: Environmental Impact Statement. 1975. p. 67.
- Morton, Patricia Hoskins. "Baldwin County". Encyclopedia of Alabama. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- "Lillian Swamp Complex". Alabama Forever Wild. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- "Lillian Swamp" (PDF). Mobile Bay National Estuary Program. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
