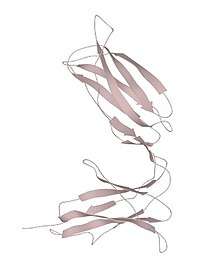
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL3
KIR2DL3, Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL3 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed by the natural killer cells and the subsets of the T-cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic, which means that they have many different alleles. The KIR genes are also extremely homologous, which means that they are similar in position, structure and evolutionary origin, but not necessarily in function.
Natural killer (NK) cells are an important component of innate antiviral immune response. Have the ability to lyse target cells without prior sensitization antigen and regulate the immune responses by secreting chemokine adaptive and cytokines. Activation of NK cells is determined by integration of inhibitory signals and activating issued by several families of different receptors, including immunoglobulin-like killer cell receptors (KIR) that predominantly recognize antigens of class I human leukocyte antigen ( HLA).[2]
Structure and location
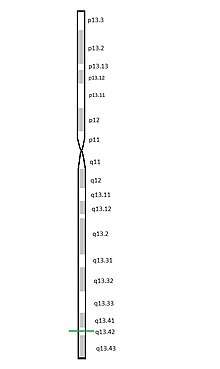
The genes responsible for coding of KIR proteins are found along the 19th chromosome section 19q 13.4 within the 1Mb Leukocyte Receptor Complex(LRC). The subsets of the KIR proteins are classified by their number of extracellular IG domains and by whether they have a long (L) or short(S) cytoplasmic domain-tail. The number coming at the end of the name of protein classifies it as a branch of the subset it belongs to.[3][4][5]
Function
KIR proteins with long tailed cytoplasmic domains transduce the inhibitory signals upon the ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), whereas the KIR proteins of short-tailed cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM and instead associate with Tyrosine kinase binding protein (TYRO) to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules. The KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulating of the immune responses. The HLA molecules are human leukocyte antigens and are the gene complexes to encode Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) proteins in human beings. Plays a great role in regulating the immune response. HLA are polymorphic, thus the MHCs of humans differ from an individual to another. KIR2DL3 is a protein complex of two extracellular domains and a long tailed endo-cellular cytoplasmatic tail, which assign it in charge of sending inhbitory signals throughout the cell.[6]
Pathology
The protein KIR2DL3 transduces inhibitory signals upon the ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif(ITIM) to its long inner cytoplasmic tail. The tyrosine kinase based transductions are enzymatic transferences of a phosphate group from an ATP molecule to a protein in the cell. Thus functioning as an ' on ' and ' off ' switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine Kinases are a sub-class of the protein-kinase. Phosphorylation of proteins is a necessary step in transduction of signals withina cell in order to regulate the cellular activity. Protein Kinases might get stuck in ' off ' position and inhibit the cell reproduction for good, or on the contrary might get stuck in ' on 'position, thus rendering the cell to reproduce unregulatedly, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer.[7][8][9]
Other Killer-cell IG-like receptors
References
- "KIR2DL3 - Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL3 precursor - Homo sapiens (Human) - KIR2DL3 gene & protein". www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 2018-11-18.
- Hölzemer, Angelique; Thobakgale, Christina F.; Jimenez Cruz, Camilo A.; Garcia-Beltran, Wilfredo F.; Carlson, Jonathan M.; van Teijlingen, Nienke H.; Mann, Jaclyn K.; Jaggernath, Manjeetha; Kang, Seung-gu (2015-11-17). "Selection of an HLA-C*03:04-Restricted HIV-1 p24 Gag Sequence Variant Is Associated with Viral Escape from KIR2DL3+ Natural Killer Cells: Data from an Observational Cohort in South Africa". PLoS Medicine. 12 (11): e1001900, discussion e1001900. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001900. ISSN 1549-1277. PMC 4648589. PMID 26575988.
- Hölzemer, Angelique; Thobakgale, Christina F.; Jimenez Cruz, Camilo A.; Garcia-Beltran, Wilfredo F.; Carlson, Jonathan M.; van Teijlingen, Nienke H.; Mann, Jaclyn K.; Jaggernath, Manjeetha; Kang, Seung-gu (2015-11-17). "Selection of an HLA-C*03:04-Restricted HIV-1 p24 Gag Sequence Variant Is Associated with Viral Escape from KIR2DL3+ Natural Killer Cells: Data from an Observational Cohort in South Africa". PLOS Medicine. 12 (11): e1001900. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001900. ISSN 1549-1676. PMC 4648589. PMID 26575988.
- Frazier, William R.; Steiner, Noriko; Hou, Lihua; Dakshanamurthy, Sivanesan; Hurley, Carolyn Katovich (2013-06-15). "Allelic Variation in KIR2DL3 Generates a KIR2DL2-like Receptor with Increased Binding to Its HLA-C Ligand". Journal of Immunology. 190 (12): 6198–6208. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1300464. ISSN 0022-1767. PMC 3679298. PMID 23686481.
- Lunemann, Sebastian; Martrus, Gloria; Hölzemer, Angelique; Chapel, Anais; Ziegler, Maja; Körner, Christian; Beltran, Wilfredo Garcia; Carrington, Mary; Wedemeyer, Heiner (August 2016). "Sequence variations in HCV core-derived epitopes alter binding of KIR2DL3 to HLA-C*03:04 and modulate NK cell function". Journal of Hepatology. 65 (2): 252–258. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2016.03.016. ISSN 0168-8278. PMC 4955726. PMID 27057987.
- Sim, Malcolm J. W.; Stowell, Janet; Sergeant, Ruhena; Altmann, Daniel M.; Long, Eric O.; Boyton, Rosemary J. (January 2016). "KIR2DL3 and KIR2DL1 show similar impact on licensing of human NK cells". European Journal of Immunology. 46 (1): 185–191. doi:10.1002/eji.201545757. ISSN 0014-2980. PMC 4737201. PMID 26467237.
- Gendzekhadze, Ketevan; Norman, Paul J.; Abi-Rached, Laurent; Graef, Thorsten; Moesta, Achim K.; Layrisse, Zulay; Parham, Peter (2009-11-03). "Co-evolution of KIR2DL3 with HLA-C in a human population retaining minimal essential diversity of KIR and HLA class I ligands". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 106 (44): 18692–18697. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10618692G. doi:10.1073/pnas.0906051106. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 2774017. PMID 19837691.
- Roberts, Chrissy h.; Molina, Sandra; Makalo, Pateh; Joof, Hassan; Harding-Esch, Emma M.; Burr, Sarah E.; Mabey, David C. W.; Bailey, Robin L.; Burton, Matthew J. (2014-03-20). "Conjunctival Scarring in Trachoma Is Associated with the HLA-C Ligand of KIR and Is Exacerbated by Heterozygosity at KIR2DL2/KIR2DL3". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 8 (3): e2744. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002744. ISSN 1935-2727. PMC 3961204. PMID 24651768.
- Isitman, Gamze; Tremblay-McLean, Alexandra; Lisovsky, Irene; Bruneau, Julie; Lebouché, Bertrand; Routy, Jean-Pierre; Bernard, Nicole F. (2016-10-12). "NK Cells Expressing the Inhibitory Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors (iKIR) KIR2DL1, KIR2DL3 and KIR3DL1 Are Less Likely to Be CD16+ than Their iKIR Negative Counterparts". PLoS ONE. 11 (10): e0164517. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1164517I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0164517. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5061331. PMID 27732638.
- Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "KIR2DL3 Gene - GeneCards | KI2L3 Protein | KI2L3 Antibody". www.genecards.org. Retrieved 2018-11-18.