Hoste Island
Hoste Island (Spanish: Isla Hoste) is one of the southernmost islands in Chile, lying south, across the Beagle Channel, from Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego and west of Navarino Island, from which it is separated by the Murray Channel. Hoste Island has the southernmost trees on earth, Nothofagus antarctica. In Magellania, Jules Verne described an imaginary republic on the island.[2]
| Native name: Isla Hoste | |
|---|---|
 A view across the Beagle Channel to Isla Hoste from Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego | |
 Hoste Island Hoste Island at the end of Tierra del Fuego | |
| Geography | |
| Coordinates | 55°15′S 69°0′W |
| Archipelago | Tierra del Fuego |
| Area | 4,117 km2 (1,590 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 1,402 m (4,600 ft) |
| Highest point | Hoste High Point[1] |
| Administration | |
| Region | Magallanes Region |
| Province | Antártica Chilena Province |
| Commune | Cabo de Hornos |
| Demographics | |
| Population | virtually uninhabited |
| Additional information | |
| NGA UFI -884382 | |
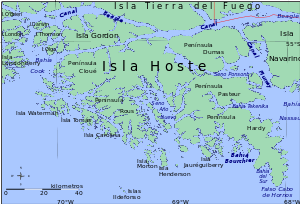
Geography
With an area of 4,117 square kilometers (1,590 sq mi), Hoste is the second largest island of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, after Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. The western area of the island forms part of the Alberto de Agostini National Park, and has the most southerly trees in the world, the "antarctic beech" Nothofagus antarctica. The most southern point of the island is the False Cape Horn, on the Hardy Peninsula. It has 5 peninsulas: Hardy, Cloué, Rous, Pasteur and Dumas.
Peninsula Hardy (sometimes called "Pen Hardy") is located at one of the most southerly extremes of South America. It is the southern landform which extends into the Drake Passage to make the Bahia Nassau. False Cape Horn (Spanish: Falso Cabo de Hornos) is located at the southern tip of this peninsula.
History
French Scientific Mission to Cape Horn aboard the Frigate Romanche
The island was explored by the French scientific expedition La Romanche in 1881–1882. It is named after William Hoste, one of Lord Nelson's protégés.
Tekenika
As of 1894 the Stirling House, a prefab house built on behalf of the South American Mission Society, was reinstalled in Tekenika Bay, on the southeast coast of Hoste Island in order to avoid the abuses and crimes caused by the recent arrival of miners and diseases in Ushuaia. (Eventually the house was declared a National Monument and was moved to the lands of the Martin Gusinde Anthropological Museum in Puerto Williams).[3]
There had already been unsuccessful attempts at cattle farming by the Chilean government, after which the island was abandoned. Well into the 20th century, a few Yaghan families lived on the island. These indigenous peoples vanished after contact with adventurers and fishermen. Since then, the island has remained virtually uninhabited. The 1992 census reported a population of six living in three houses in the Hoste census enumeration district , however some if not all this population could be located on one or more of the smaller islands nearby which also belonged to the same district.
Operation Soberania
In 1978, the island served as a station for Chilean warships during Operation Soberania.
See also
- Isla Navarino
- List of islands of Chile
References
- South America Island High Points above 1000 meters
- Verne, J. (1909). Magellania (translated into English by Benjamin Ivry). Welcome Rain Publishers, 2002.
- The Stirling House and the History of the anglican missions in Tierra del Fuego