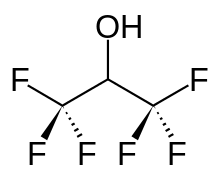
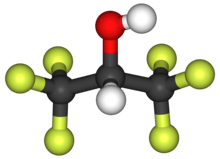
Hexafluoro-2-propanol
Hexafluoroisopropanol, commonly abbreviated HFIP, is the organic compound with the formula (CF3)2CHOH. This fluoroalcohol finds use as solvent and synthetic intermediate. It appears as a colorless, volatile liquid that is characterized by a strong, pungent odor. As a solvent hexafluoro-2-propanol is polar and exhibits strong hydrogen bonding properties enabling it to dissolve substances that serve as hydrogen-bond acceptors, such as amides and ethers. Hexafluoro-2-propanol is transparent to UV light with high density, low viscosity and low refractive index.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexafluoro-propan-2-ol | |
| Other names
Hexafluoroisopropanol, Hexafluoroisopropyl alcohol, HFIP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.873 |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H2F6O | |
| Molar mass | 168.038 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.596 g/mL |
| Melting point | −3.3 °C (26.1 °F; 269.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 58.2 °C (136.8 °F; 331.3 K) |
| Miscible | |
| Vapor pressure | 16 kPa at 20 °C |
| Viscosity | 1.65 cP at 20 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive (C) |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R20/22, R34, R41 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26, S36/37/39, S45 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | > 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related Organofluorides; alcohols |
Hexafluoroacetone; Isopropyl alcohol, 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and uses
Hexafluoro-propan-2-ol is prepared from hexafluoropropylene through hexafluoroacetone, which is then hydrogenated.[1]
- (CF3)2CO + H2 → (CF3)2CHOH
Hexafluoro-propan-2-ol is a speciality solvent for some polar polymers and organic synthesis.[2][3] It is especially effective for solubilizing a wide range of polymers, including those that are not soluble in the most common organic solvents, such as: polyamides, polyacrylonitriles, polyacetals, polyesters (e.g. polyglycolide), and polyketones. It has also found use in biochemistry to solubilize peptides and to monomerize β-sheet protein aggregates. Because of its acidity (pKa = 9.3), it can be used as acid in volatile buffers for ion pair HPLC - mass spectrometry of nucleic acids.[4]
Medicine
It is both the precursor and the chief metabolite of the inhalation anesthetic sevoflurane.
Safety
Hexafluoro-2-propanol is a volatile, corrosive liquid that can cause severe burns and respiratory problems.[5]
References
Notes
- Günter Siegemund, Werner Schwertfeger, Andrew Feiring, Bruce Smart, Fred Behr, Herward Vogel, Blaine McKusick “Fluorine Compounds, Organic” in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 2007. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_349
- Bégué, J.-P.; Bonnet-Delpon, D.; Crousse, B. (2004). "Fluorinated Alcohols: A New Medium for Selective and Clean Reaction". Synlett (1): 18–29. doi:10.1055/s-2003-44973.
- Shuklov, Ivan A.; Dubrovina, Natalia V.; Börner, Armin (2007). "Fluorinated Alcohols as Solvents, Cosolvents and Additives in Homogeneous Catalysis". Synthesis: 2925–2943. doi:10.1055/s-2007-983902.
- Apffel, A.; Chakel, J.A.; Fischer, S.; Lichtenwalter, K.; Hancock, W.S. (1997). "Analysis of oligonucleotides by HPLC-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry". Anal. Chem. 69: 1320–1325. doi:10.1021/ac960916h.
- "HFIP MSDS". Fisher Scientific. Retrieved 2014-08-18.
Sources
- Radlick, Phillip C (1982-02-02). "Methods of synthesizing hexafluoroisopropanol from impure mixtures and synthesis of a fluoromethyl ether therefrom". United States Patent 4,314,087. Retrieved 2006-10-18.
- Cheminal, Bernard; H. Mathais; M. Thomarat (1987-03-03). "Process for the synthesis of 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol and 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropanol". United States Patent 4,647,706. Retrieved 2006-10-18.
- "Hexafluoroisopropanol datasheet". DuPont. Archived from the original on 2006-10-08. Retrieved 2006-10-18.
