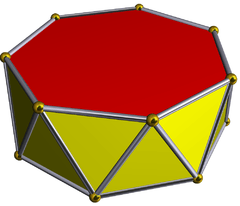
Heptagonal antiprism
In geometry, the heptagonal antiprism is the fifth in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps.
| Uniform heptagonal antiprism | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Prismatic uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 16, E = 28 V = 14 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 14{3}+2{7} |
| Schläfli symbol | s{2,14} sr{2,7} |
| Wythoff symbol | | 2 2 7 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | D7d, [2+,14], (2*7), order 28 |
| Rotation group | D7, [7,2]+, (722), order 14 |
| References | U77(e) |
| Dual | Heptagonal trapezohedron |
| Properties | convex |
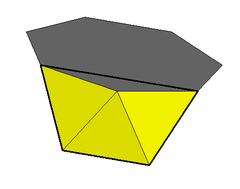 Vertex figure 3.3.3.7 | |
Antiprisms are similar to prisms except the bases are twisted relative to each other, and that the side faces are triangles, rather than quadrilaterals.
In the case of a regular 7-sided base, one usually considers the case where its copy is twisted by an angle 180°/n. Extra regularity is obtained by the line connecting the base centers being perpendicular to the base planes, making it a right antiprism. As faces, it has the two n-gonal bases and, connecting those bases, 2n isosceles triangles.
If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.
See also
| Family of uniform antiprisms n.3.3.3 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyhedron | ||||||||||||
| Tiling | ||||||||||||
| Config. | V2.3.3.3 | 3.3.3.3 | 4.3.3.3 | 5.3.3.3 | 6.3.3.3 | 7.3.3.3 | 8.3.3.3 | 9.3.3.3 | 10.3.3.3 | 11.3.3.3 | 12.3.3.3 | ...∞.3.3.3 |
External links
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra www.georgehart.com: The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- VRML model
- Conway Notation for Polyhedra Try: "A7"
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.