HELCOM
The Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission (Helsinki Commission - HELCOM) is an intergovernmental organization governing the Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area (Helsinki Convention). A regional sea convention and a platform for environmental policy making at the regional level, HELCOM works for the protection of the marine environment of the Baltic Sea. HELCOM consists of ten members - the nine Baltic Sea countries Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia and Sweden, plus the European Union.
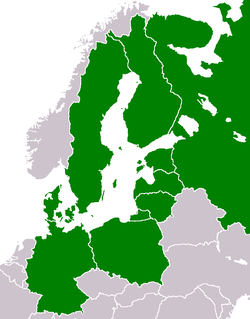 Contracting parties of HELCOM | |
| Formation | 1974 |
|---|---|
| Type | IGO |
| Legal status | Treaty-based |
| Purpose | Protection of the Baltic Sea environment |
| Location | |
Official language | English |
Chairperson | Saara Bäck |
Executive Secretary | Rüdiger Strempel |
Main organ | Ministerial Meeting |
| Website | www |
The Helsinki Convention was signed in 1974 by the Baltic Sea coastal countries to address the increasing environmental challenges from industrialisation and other human activities, and that were having a severe impact on the marine environment. The Helsinki Convention includes the protection of the Baltic Sea from all sources of pollution from land, air and sea. It also commits the signatories to take measures to conserve habitats and biological diversity and to ensure the sustainable use of marine resources. The Helsinki Convention was updated in 1992 to take into account the geopolitical changes and emerging environmental challenges in the region. The current version was ratified in 2000.
Contracting parties of HELCOM are:[1]
The HELCOM Secretariat is located in Helsinki, Finland.
See also
- Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe, an independent U.S. government agency created in 1975
- Marine protected area
- OSPAR
References
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-11-11. Retrieved 2009-11-23.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
- HELCOM official website
- 16 April 2012 (HELCOM Information Services) Continuation of Luga Samplings Expected to Be Discussed this Week