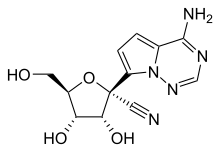
GS-441524
GS-441524 is an antiviral drug which was developed by Gilead Sciences. It is the main metabolite of the antiviral prodrug remdesivir, which the latter is converted into inside the body. GS-441524 is then phosphorylated to the active nucleotide triphosphate form. GS-441524 has also been researched in its own right, as a treatment for feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), a lethal coronavirus disease which affects domestic cats.[1][2]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H13N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 291.26 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Use
Since FIP is usually fatal and there are no approved treatments available, GS-441524 has reportedly been sold on the black market and used by pet owners to treat affected cats, despite not having been officially approved for veterinary use.[3]
GS-441524 is the nucleoside of phosphate pro-drug remdesivir. Studies have shown that even when remdesivir is administered, that GS-441524 is the predominant metabolite circulating in serum due to rapid hydrolysis of the remdesivir prodrugs, followed by dephosphorylation.[4][5][6] Some researchers have suggested its utility as a treatment for COVID-19.[7][8]
References
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. (2018). "The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies". Veterinary Microbiology. 219: 226–233. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.04.026. PMC 7117434. PMID 29778200.
- Pedersen, Niels C; Perron, Michel; Bannasch, Michael; Montgomery, Elizabeth; Murakami, Eisuke; Liepnieks, Molly; Liu, Hongwei (2019). "Efficacy and safety of the nucleoside analog GS-441524 for treatment of cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis". Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 21 (4): 271–281. doi:10.1177/1098612X19825701. PMC 6435921. PMID 30755068.
- Burns K (15 January 2020). "FIP drugs continue to show promise, while being sold on black market". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association News.
- Warren, Travis K.; Jordan, Robert; Lo, Michael K.; Ray, Adrian S.; Mackman, Richard L.; Soloveva, Veronica; Siegel, Dustin; Perron, Michel; Bannister, Roy; Hui, Hon C.; Larson, Nate; Strickley, Robert; Wells, Jay; Stuthman, Kelly S.; Van Tongeren, Sean A.; Garza, Nicole L.; Donnelly, Ginger; Shurtleff, Amy C.; Retterer, Cary J.; Gharaibeh, Dima; Zamani, Rouzbeh; Kenny, Tara; Eaton, Brett P.; Grimes, Elizabeth; Welch, Lisa S.; Gomba, Laura; Wilhelmsen, Catherine L.; Nichols, Donald K.; Nuss, Jonathan E.; Nagle, Elyse R.; Kugelman, Jeffrey R.; Palacios, Gustavo; Doerffler, Edward; Neville, Sean; Carra, Ernest; Clarke, Michael O.; Zhang, Lijun; Lew, Willard; Ross, Bruce; Wang, Queenie; Chun, Kwon; Wolfe, Lydia; Babusis, Darius; Park, Yeojin; Stray, Kirsten M.; Trancheva, Iva; Feng, Joy Y.; Barauskas, Ona; Xu, Yili; Wong, Pamela; Braun, Molly R.; Flint, Mike; McMullan, Laura K.; Chen, Shan-Shan; Fearns, Rachel; Swaminathan, Swami; Mayers, Douglas L.; Spiropoulou, Christina F.; Lee, William A.; Nichol, Stuart T.; Cihlar, Tomas; Bavari, Sina (March 2016). "Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys". Nature. 531 (7594): 381–385. doi:10.1038/nature17180. PMC 5551389. PMID 26934220.
- Sheahan, Timothy P.; Sims, Amy C.; Graham, Rachel L.; Menachery, Vineet D.; Gralinski, Lisa E.; Case, James B.; Leist, Sarah R.; Pyrc, Krzysztof; Feng, Joy Y.; Trantcheva, Iva; Bannister, Roy; Park, Yeojin; Babusis, Darius; Clarke, Michael O.; Mackman, Richard L.; Spahn, Jamie E.; Palmiotti, Christopher A.; Siegel, Dustin; Ray, Adrian S.; Cihlar, Tomas; Jordan, Robert; Denison, Mark R.; Baric, Ralph S. (28 June 2017). "Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses". Science Translational Medicine. 9 (396): eaal3653. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653. PMC 5567817. PMID 28659436.
- Williamson, Brandi N.; Feldmann, Friederike; Schwarz, Benjamin; Meade-White, Kimberly; Porter, Danielle P.; Schulz, Jonathan; Doremalen, Neeltje van; Leighton, Ian; Yinda, Claude Kwe; Pérez-Pérez, Lizzette; Okumura, Atsushi; Lovaglio, Jamie; Hanley, Patrick W.; Saturday, Greg; Bosio, Catharine M.; Anzick, Sarah; Barbian, Kent; Cihlar, Tomas; Martens, Craig; Scott, Dana P.; Munster, Vincent J.; Wit, Emmie de (22 April 2020). "Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2". bioRxiv: 2020.04.15.043166. doi:10.1101/2020.04.15.043166.
- Yan, Victoria C; Muller, Florian L "Gilead should ditch remdesivir and focus on its simpler ancestor". STAT. 14 May 2020.
- Yan, Victoria C and Muller; Florian L. Advantages of the Parent Nucleoside GS-441524 over Remdesivir for Covid-19 Treatment. (2020) ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00316