Dumbbell Nebula
The Dumbbell Nebula (also known as Apple Core Nebula, Messier 27, M 27, or NGC 6853) is a planetary nebula in the constellation Vulpecula, at a distance of about 1227 light-years.[1] This object was the first planetary nebula to be discovered; by Charles Messier in 1764. At its brightness of visual magnitude 7.5 and its diameter of about 8 arcminutes, it is easily visible in binoculars,[5] and a popular observing target in amateur telescopes.
| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
| Planetary nebula | |
 Image of the Dumbbell Nebula (Messier 27, M 27) by the Very Large Telescope | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 19h 59m 36.340s[1] |
| Declination | +22° 43′ 16.09″[1] |
| Distance | 417+49 −65 pc[2][3] 376.3±6.2[1] pc |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 7.5[1] |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 8.0′ × 5.6′[4] |
| Constellation | Vulpecula |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | 1.44+0.21 −0.16[a] ly |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | −0.6+0.4 −0.3[d] |
| Notable features | Central star radius is among the largest known for a white dwarf. |
| Designations | NGC 6853,[1] M 27,[1] Diabolo Nebula,[1] Dumb-Bell Nebula,[1] |
Shape and size
The Dumbbell Nebula appears to be shaped like a prolate spheroid and is viewed from our perspective along the plane of its equator. In 1992, Moreno-Corral et al. computed that its rate of expansion in the plane of the sky was no more than 2.3" per century. From this, an upper limit to the age of 14,600 yr may be determined. In 1970, Bohuski, Smith, and Weedman found an expansion velocity of 31 km/s. Given its semi-minor axis radius of 1.01 ly, this implies that the kinematic age of the nebula is some 9,800 years.[4][6]
Structure
Like many nearby planetary nebulae, the Dumbbell contains knots. Its central region is marked by a pattern of dark and bright cusped knots and their associated dark tails (see picture). The knots vary in appearance from symmetric objects with tails to rather irregular tail-less objects. Similarly to the Helix Nebula and the Eskimo Nebula, the heads of the knots have bright cusps which are local photoionization fronts.[6]
Central star
The central star, a white dwarf progenitor, is estimated to have a radius which is 0.055±0.02 R☉ (0.13 light seconds) which gives it a size larger than most other known white dwarfs.[2] The central star mass was estimated in 1999 by Napiwotzki to be 0.56±0.01 M☉.[2]
Appearance
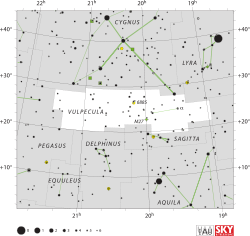 It is located in the faint constellation Vulpecula, between Cyngus and Aquila, within the Summer Triangle. |
 It can be located in the sky a few degrees north of γ Sagittae, near the star 14 Vulpeculae. |
The Dumbbell nebula can be easily seen in binoculars in a dark sky, just above the small constellation of Sagitta.
As seen in amateur telescopes:
 North is diagonal left-up
North is diagonal left-up North is left
North is left
See also
- Messier object
- List of Messier objects
- List of planetary nebulae
- New General Catalogue
Notes
- ^ Radius = distance × sin(angular size / 2) = 1240+180
−140[3] * sin(8′.0 / 2) = 1.44+0.21
−0.16 ly - ^ Semi minor axis = distance × sin(minor axis size / 2) = 1240+180
−140[3] × sin(5′.6 / 2) = 1.01+0.15
−0.11 ly - ^ Kinematic age = semi-minor axis / expansion rate = 1.01+0.15
−0.11[b] ly / 31 km/s = 9.56+1.42
−1.04×1012 km / 31[4] km/s = 3.08+0.46
−0.34×1011 s = 9800+1500
−1100 yr - ^ 7.5 apparent magnitude - 5 × (log10(420+50
−70 pc distance) - 1) = −0.6+0.4
−0.3 absolute magnitude
References
- "M 27". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2007-01-03.
- Benedict, G. Fritz; McArthur, B. E.; Fredrick, L. W.; Harrison, T. E.; et al. (2003). "Astrometry with The Hubble Space Telescope: A Parallax of the Central Star of the Planetary Nebula NGC 6853". Astronomical Journal. 126 (5): 2549–2556. arXiv:astro-ph/0307449. Bibcode:2003AJ....126.2549B. doi:10.1086/378603.
- Harris, Hugh C.; Dahn, Conard C.; Canzian, Blaise; Guetter, Harry H.; et al. (2007). "Trigonometric Parallaxes of Central Stars of Planetary Nebulae". Astronomical Journal. 133 (2): 631–638. arXiv:astro-ph/0611543. Bibcode:2007AJ....133..631H. doi:10.1086/510348.
- O'Dell, C. R.; Balick, B.; Hajian, A. R.; Henney, W. J.; et al. (2002). "Knots in Nearby Planetary Nebulae". Astronomical Journal. 123 (6): 3329–3347. Bibcode:2002AJ....123.3329O. doi:10.1086/340726.
- "M 27". 2016-10-15.
- O'dell, C. R.; Balick, B.; Hajian, A. R.; Henney, W. J.; et al. (2003). "Knots in Planetary Nebulae". Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica, Serie de Conferencias. 15: 29–33. Bibcode:2003RMxAC..15...29O.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dumbbell Nebula. |
- SEDS: Messier Object 27
- The Dumbbell Nebula on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
- M27 on astro-pics.com
- Szymanek, Nik; Merrifield, Michael. "M27 – Dumbbell Nebula". Deep Sky Videos. Brady Haran.
- M27
- Dumbbell Nebula (M27) at Constellation Guide
