Diflomotecan
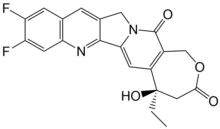
Diflomotecan (also known as BN80905) is a chemotherapeutic agent that is a topoisomerase inhibitor (Top1). It varies from other camptothecin based Top1 inhibitors like topotecan in having a 7-membered E-ring. The oxepan-2-one ring in the homocamptothecin analogues is more stable in plasma compared to the 6-membered lactone in camptothecin.[1] Diflomotecan was the first homocamptothecin to enter clinical trials[2] and is currently in phase I for treating patients with sensitive small cell lung cancer (SCLC).[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Diflomotecan |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H16F2N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 398.366 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Bailly C (2003). "Homocamptothecins: potent topoisomerase I inhibitors and promising anticancer drugs". Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 45: 91–108. doi:10.1016/s1040-8428(02)00090-2.
- Kroep JR, Gelderblom H (2009). "Diflomotecan, a promising homocamptothecin for cancer therapy". Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18: 69–75. doi:10.1517/13543780802571674.
- "Diflomotecan (BN80915) Administered Once Every 3 Weeks in Treating Patients With Sensitive Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov". clinicaltrials.gov.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.