Churchill Falls
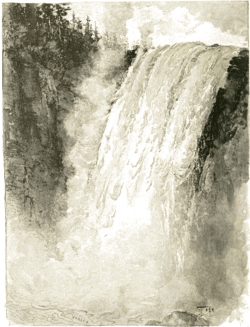
Churchill Falls is a 75 m (245 ft) high waterfall on the Churchill River in Labrador, Canada. Formerly counted among the most impressive natural features of Canada, the diversion of the river for the Churchill Falls Generating Station has cut off almost all of the falls' former flow, leaving a small stream winding through its old bed and trickling down the rocks.
| Churchill Falls | |
|---|---|
| Grand Falls | |
 | |
| Location | Labrador |
| Coordinates | 53°35′39.44″N 64°18′28.05″W[1] |
| Type | Segmented Block |
| Total height | 245 ft (75 m) |
| Watercourse | Churchill River |


Names
John McLean called the cascades the Grand Falls,[2] as the Churchill River at that time was usually still known as the Grand River as a calque of its indigenous name. The Innu had a separate name for the falls, Patshishetshuanau ("Place where the Current Makes Clouds").[3] Captain William Martin's 1821 renaming of the river after Labrador's colonial governor Charles Hamilton gradually became more common but the falls continued to be known as the "Grand Falls" or less often as the McLean Falls.[4][5] On 1 February 1965, the provincial premier Joey Smallwood renamed the river and the falls after the former British prime minister Winston Churchill ahead of approving its large hydroelectric project.
History
The falls were a significant landmark for local indigenous peoples. The Innu believed that to look on these awe-inspiring falls meant death[3] and maintained a strong taboo against visiting into the early 20th century.[6]
In 1839, a team under Scoto-Canadian trader John McLean—seeking a riverine route between Fort Chimo in northwest Labrador and Fort Smith on Lake Melville in southeast Labrador for the Hudson's Bay Company—were the first Europeans to reach the area. He was mostly annoyed that the falls meant abandoning a direct route along the Churchill and retracing his path back north, but still overwhelmed by the falls' majesty.[6]
In 1894, Albert Peter Low of Canada's Geological Survey reached the falls.[7]
Plans were made as early as 1915 to divert the river above the falls for power generation, but they were abandoned as unfeasible at the time. Following the development of the iron ore mines in western Labrador and the construction of the Quebec North Shore and Labrador Railway in 1954, the project became workable and surveys and planning began. The Churchill Falls Generating Station started construction in 1967 and, in 1970, almost all of the Churchill's water was diverted into a reservoir upstream of the falls. Only a small stream remains; even when the reservoir hits its maximum water levels, usually a once-a-decade event, the controlled release over the falls amounts to only about 10% of the falls' former flow.[8]
Legacy
The nearby company town of Churchill Falls is named for the falls.
References
Citations
- "GeoNames Query - Churchill Falls: Query Record Details". Natural Resources Canada. Government of Canada. 2008-11-09. Archived from the original on 2011-06-08. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
- Butts, Ed (1 July 2015), "Guelph Man Key in Saving Rupert's Land for Canada", Guelph Mercury, Guelph: Torstar.
- James Marsh (2010). "Churchill Falls". The Canadian Encyclopedia. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
- Low (1896), p. 142–3.
- Carter, Dave, "Hidden Treasures: Explorer Made Home in Guelph", Guelph Mercury, Guelph: Torstar.
- Bryant, Henry Grier (1892), A Journey to the Grand Falls of Labrador, Philadelphia: Geographical Society of Philadelphia.
- Low (1896), p. 6.
- "Water will be released over Churchill Falls for 4th time in about 30 years". CBC. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
Bibliography
- Low, Albert Peter (1896), Report on Explorations in the Labrador Peninsula along the East Main, Koksoak, Hamilton, Manicuagan, and Portions of Other Rivers in 1892-93-94-95, Geological Survey of Canada, Ottawa: S.E. Dawson.
External links
